filmov
tv
Intro Stats, Lect 9B, Discrete & Continuous Random Variables, Means and Standard Deviations

Показать описание
(0:00) Find a probability by calculating the area under a triangular distribution.
(3:32) With random continuous variables like this, the "strictness" of the inequalities doesn't matter (since lines have no areas). It does matter for discrete random variables.
(4:14) Normal distribution example (hummingbird weights).
(5:40) Use probability notation and convert to z scores within the probability notation.
(7:27) Use a standard Normal table to find the probability.
(9:23) Summary of discrete and continuous random variables.
(11:25) Summary of our main use of random variables: sample statistics are random variables and their sampling distributions are used to find probabilities related to them.
(14:30) Formula for the mean of a discrete random variable (with finitely many values) and a summary of how to use it with a table.
(17:14) Formulas for the variance and standard deviation of a discrete random variable (with finitely many values).
(20:00) Manufacturing costs example (based on # of weeks for developing product specifications and # of weeks for designing the manufacturing process).
(23:23) Relate the mean of the combined variable to the means of its "parts".
(24:23) Use a spreadsheet to find the means of the parts.
 0:02:08
0:02:08
 0:27:52
0:27:52
 0:14:24
0:14:24
 0:05:11
0:05:11
 0:17:59
0:17:59
 0:06:58
0:06:58
 0:00:48
0:00:48
 0:01:30
0:01:30
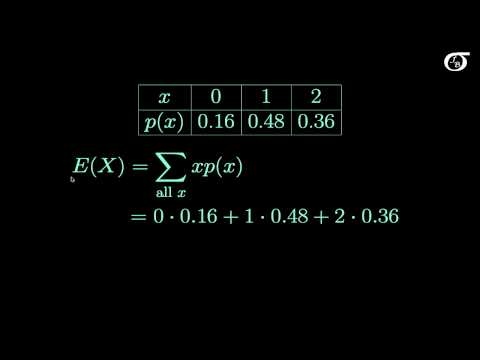 0:07:57
0:07:57
 0:08:11
0:08:11
 0:00:22
0:00:22
 0:05:17
0:05:17
 0:27:48
0:27:48
 0:11:04
0:11:04
 0:00:47
0:00:47
 1:44:19
1:44:19
 0:11:19
0:11:19
 0:27:33
0:27:33
 0:33:25
0:33:25
 0:26:51
0:26:51
 0:34:43
0:34:43
 0:24:13
0:24:13
 0:43:58
0:43:58