filmov
tv
The Critical FPGA Basics: Always blocks, Inferred latches, and why the FPGA needs a clock, anyway?!

Показать описание
Hi, I'm Stacey, and in this video I talk about everything from asynchronous logic, why the FPGA even needs a clock, and inferred latches!
0:00 Intro
0:38 Always blocks
8:27: Why the FPGA needs a clock, and static timing analysis
13:00 Registers and their function
16:00 Synchronus and Asynchronus logic
18:40 Asynchronus loopback paths and inferred latches
23:50 Avoiding inferred latches
27:05 Summary
28:56 Outro
0:00 Intro
0:38 Always blocks
8:27: Why the FPGA needs a clock, and static timing analysis
13:00 Registers and their function
16:00 Synchronus and Asynchronus logic
18:40 Asynchronus loopback paths and inferred latches
23:50 Avoiding inferred latches
27:05 Summary
28:56 Outro
The Critical FPGA Basics: Always blocks, Inferred latches, and why the FPGA needs a clock, anyway?!
The 'Do Anything' Chip: FPGA
HDMI FPGA | FGPA4fun code updated to Vivado 2020.1
FPGA Timing Optimization: Timer Example OLD
How to fix Timing Errors in your FPGA design during Place and Route, meeting clock constraints
AXI Stream basics for beginners! A Stream FIFO example in Verilog.
FPGA vs. Microcontroller: How to choose the right one for your project
Understanding Timing Analysis in FPGAs
4. LUTs and FPGA Architecture - Introduction to FPGA Design for Embedded Systems
Trading at light speed: designing low latency systems in C++ - David Gross - Meeting C++ 2022
#17 How to Plan an FPGA Project for Smoother Coding | Beginners Walk Through
uP Vs uC Vs ASIC Vs FPGA Vs Embedded Systems
What is a Flip-Flop? How are they used in FPGAs?
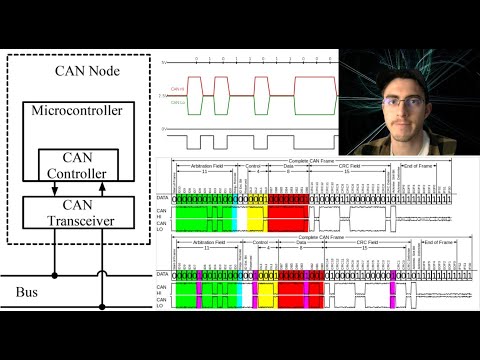
CAN Protocol Explained | Controller Area Network
FPGA Timing & Analysis - FPGA Series Part 4
FPGA Architecture- Basic
5. Altera CPLDs and Small FPGAs - Introduction to FPGA Design for Embedded Systems
FPGA Timing Optimization: Background and Challenges
Got FPGA Timing Problems?
7. Programming the FPGA - Introduction to FPGA Design for Embedded Systems
FPGA Design: Architecture and Implementation - Speed (Timing) Optimization - Part 1
FPGA Timing Optimization (Optimization Strategies) OLD
[Tutorial] Productive Parallel Programming for FPGA with High Level Synthesis
Practical RF Hardware and PCB Design Tips - Phil's Lab #19
Комментарии
 0:29:23
0:29:23
 0:15:28
0:15:28
 0:15:13
0:15:13
 0:14:24
0:14:24
 0:14:00
0:14:00
 0:12:11
0:12:11
 0:14:24
0:14:24
 0:29:41
0:29:41
 0:08:46
0:08:46
 0:59:45
0:59:45
 0:27:44
0:27:44
 0:27:26
0:27:26
 0:24:13
0:24:13
 0:12:09
0:12:09
 0:09:33
0:09:33
 0:25:37
0:25:37
 0:08:20
0:08:20
 0:22:53
0:22:53
 0:43:51
0:43:51
 0:10:09
0:10:09
 0:13:27
0:13:27
 0:40:58
0:40:58
![[Tutorial] Productive Parallel](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/2UvUP2hxMyI/hqdefault.jpg) 3:21:54
3:21:54
 0:18:46
0:18:46