filmov
tv
Photosynthesis - Light Dependent Reactions

Показать описание
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that can later be released to fuel the organisms' activities (energy transformation). This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis.
In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis is largely responsible for producing and maintaining the oxygen content of the Earth's atmosphere, and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.
In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, long-term energy storage in the form of sugars is produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle; some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle, to achieve the same end. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP).Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.
Photosynthesis occurs in two stages. In the first stage, light-dependent reactions or light reactions capture the energy of light and use it to make the energy-storage molecules ATP and NADPH. During the second stage, the light-independent reactions use these products to capture and reduce carbon dioxide.
Site of Photosynthesis is in Chloroplasts.
Light Reactions in Thylakoid Membrane
Calvin Cycle in Stroma
In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis is largely responsible for producing and maintaining the oxygen content of the Earth's atmosphere, and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.
In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, long-term energy storage in the form of sugars is produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle; some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle, to achieve the same end. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP).Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.
Photosynthesis occurs in two stages. In the first stage, light-dependent reactions or light reactions capture the energy of light and use it to make the energy-storage molecules ATP and NADPH. During the second stage, the light-independent reactions use these products to capture and reduce carbon dioxide.
Site of Photosynthesis is in Chloroplasts.
Light Reactions in Thylakoid Membrane
Calvin Cycle in Stroma
Комментарии
 0:03:55
0:03:55
 0:17:46
0:17:46
 0:07:59
0:07:59
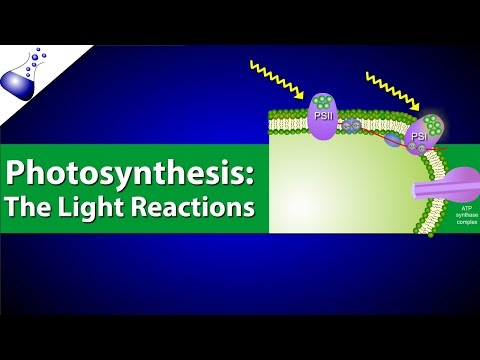 0:04:18
0:04:18
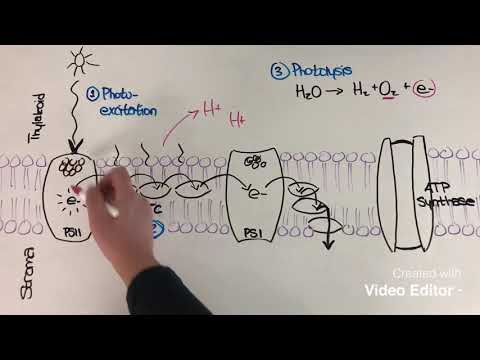 0:07:21
0:07:21
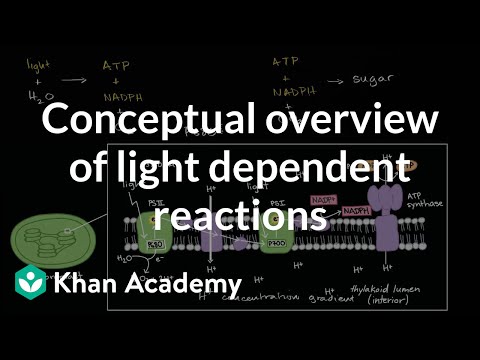 0:09:04
0:09:04
 0:06:43
0:06:43
 0:08:21
0:08:21
 4:46:28
4:46:28
 0:06:19
0:06:19
 0:03:24
0:03:24
 0:13:15
0:13:15
 0:09:10
0:09:10
 0:07:27
0:07:27
 0:20:16
0:20:16
 0:06:07
0:06:07
 0:08:27
0:08:27
 0:09:58
0:09:58
 0:11:22
0:11:22
 0:17:13
0:17:13
 0:13:32
0:13:32
 0:12:27
0:12:27
 0:13:15
0:13:15
 0:02:59
0:02:59