filmov
tv
Immunology: NK cells, macrophags, and dendritic cells

Показать описание
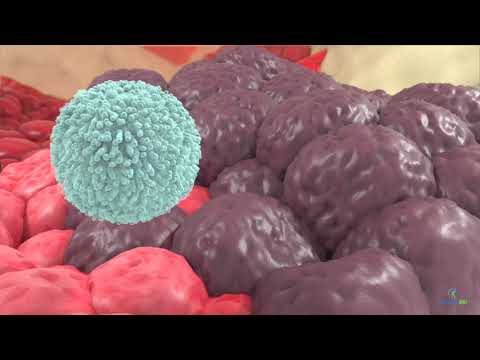
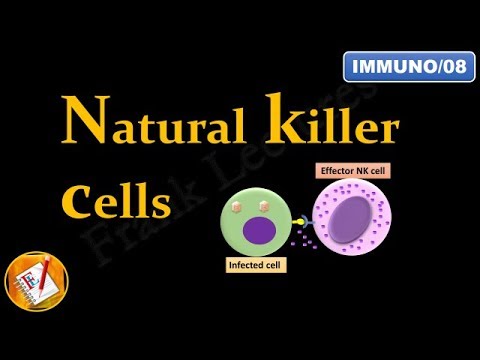
Natural killer cells or NK cells are a type of cytotoxic lymphocyte critical to the innate immune system. The role NK cells play is analogous to that of cytotoxic T cells in the vertebrate adaptive immune response. NK cells provide rapid responses to viral-infected cells, acting at around 3 days after infection, and respond to tumor formation. Typically, immune cells detect major histocompatibility complex (MHC) presented on infected cell surfaces, triggering cytokine release, causing lysis or apoptosis. NK cells are unique, however, as they have the ability to recognize stressed cells in the absence of antibodies and MHC, allowing for a much faster immune reaction. They were named "natural killers" because of the initial notion that they do not require activation to kill cells that are missing "self" markers of MHC class 1.[1] This role is especially important because harmful cells that are missing MHC 1 markers cannot be detected and destroyed by other immune cells, such as T lymphocyte cells.
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as accessory cells) of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. They act as messengers between the innate and the adaptive immune systems.
1976 copyright act enables fair use for nonprofit educational purposes, and is extended under the DMCA
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as accessory cells) of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. They act as messengers between the innate and the adaptive immune systems.
1976 copyright act enables fair use for nonprofit educational purposes, and is extended under the DMCA
Комментарии
 0:06:33
0:06:33
 0:05:03
0:05:03
 0:04:10
0:04:10
 0:01:02
0:01:02
 0:08:53
0:08:53
 0:13:06
0:13:06
 0:02:42
0:02:42
 0:00:14
0:00:14
 0:21:26
0:21:26
 0:12:03
0:12:03
 0:13:59
0:13:59
 0:22:38
0:22:38
 0:10:01
0:10:01
 0:04:30
0:04:30
 0:02:03
0:02:03
 0:16:31
0:16:31
 0:11:57
0:11:57
 0:15:24
0:15:24
 0:00:57
0:00:57
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:03:03
0:03:03
 0:09:01
0:09:01
 0:00:11
0:00:11
 0:00:15
0:00:15