filmov
tv
Introduction to cells - plant and animal cells

Показать описание
This video talks about cells the smallest structural and functional unit of an organism.
Image References:
Script:
A cell by definition is: “the smallest structural and functional unit of an organism, which is typically microscopic and consists of cytoplasm and a nucleus enclosed in a membrane.” You can think of cells as tiny pieces of lego, that come together to make an organism.
There are many different types of organisms, and they can be classed into 2 categories:
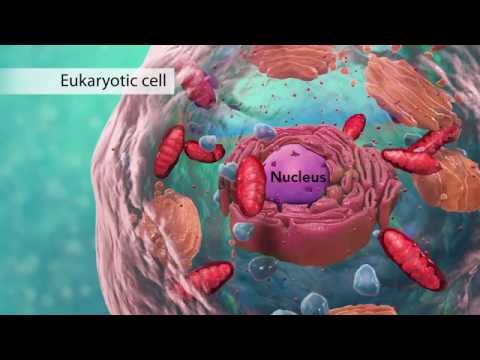
EUKARYOTIC (a plant or animal cell with a nucleus)
PROKARYOTIC (a bacterial cell without a nucleus)
In this video, we are going to explore the structure eukaryotic cells.
Now, we will look at the basic cell structure of an animal (including you and me).
The outer edge of the cell is a CELL MEMBRANE, a selective barrier that controls which substances enter or leave the cell.
The NUCLEUS [at the centre of the cell] contains the organism’s genetic material (DNA) that determines the cell’s activities(for example to make certain proteins).
The jelly like substance surrounding the nucleus is called the CYTOPLASM, in which vital chemical reactions take place which allow the cell to survive.
One such chemical reaction is RESPIRATION [the production of energy], that occurs at specific sites in the CYTOPLASM labelled as the MITOCHONDRIA.
Now let’s see what happens when a cell needs to respire. As mentioned before, the process of respiration releases energy which allows people like us to move. You can think of the mitochondria as a tiny factory. It takes in glucose and oxygen and releases carbon dioxide, water and energy.
Now, we will take a look at the basic cell structure of a plant.
The cell is similar to an animal cell with a different shape and a few key additions. In addition to the nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondria and cell membrane, it also has a: cell wall, vacuole and chloroplasts.
The CELL WALL surrounding the cell membrane is a rigid structure made of cellulose and helps to support the cell. The cell wall is an important addition for plants, as they do not have a skeleton to make sure they stand upright, so they need some sort of rigid structure to ensure correct growth.
The VACUOLE has a similar function to some extent, as it is a large structure in the middle of the cell full of CELL SAP [a solution of sugar and salts] that supports the cell and keeps it rigid.
The CHLOROPLASTS floating in the CYTOPLASM contain little green pigments called CHLOROPHYLL, where photosynthesis occurs. Every green part of a plant contains the pigment chlorophyll. Some plants have variegated leaves, which are only half green. You can tell that the green parts contain chloroplasts and the other parts don’t.
Now let’s see what happens when a plant cell needs to PHOTOSYNTHESISE. The process of photosynthesis is used to produce “food” for the plant, in the form of glucose.
You can think of the CHLOROPHYLL as another tiny factory, which takes in carbon dioxide and water and releases glucose and oxygen in the presence of sunlight.
Now that brings us to the end of this video. If you found the video interesting and informative, we would greatly appreciate a like, comment or subscription as it only takes a few seconds of your time and helps us out immensely.
Image References:
Script:
A cell by definition is: “the smallest structural and functional unit of an organism, which is typically microscopic and consists of cytoplasm and a nucleus enclosed in a membrane.” You can think of cells as tiny pieces of lego, that come together to make an organism.
There are many different types of organisms, and they can be classed into 2 categories:
EUKARYOTIC (a plant or animal cell with a nucleus)
PROKARYOTIC (a bacterial cell without a nucleus)
In this video, we are going to explore the structure eukaryotic cells.
Now, we will look at the basic cell structure of an animal (including you and me).
The outer edge of the cell is a CELL MEMBRANE, a selective barrier that controls which substances enter or leave the cell.
The NUCLEUS [at the centre of the cell] contains the organism’s genetic material (DNA) that determines the cell’s activities(for example to make certain proteins).
The jelly like substance surrounding the nucleus is called the CYTOPLASM, in which vital chemical reactions take place which allow the cell to survive.
One such chemical reaction is RESPIRATION [the production of energy], that occurs at specific sites in the CYTOPLASM labelled as the MITOCHONDRIA.
Now let’s see what happens when a cell needs to respire. As mentioned before, the process of respiration releases energy which allows people like us to move. You can think of the mitochondria as a tiny factory. It takes in glucose and oxygen and releases carbon dioxide, water and energy.
Now, we will take a look at the basic cell structure of a plant.
The cell is similar to an animal cell with a different shape and a few key additions. In addition to the nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondria and cell membrane, it also has a: cell wall, vacuole and chloroplasts.
The CELL WALL surrounding the cell membrane is a rigid structure made of cellulose and helps to support the cell. The cell wall is an important addition for plants, as they do not have a skeleton to make sure they stand upright, so they need some sort of rigid structure to ensure correct growth.
The VACUOLE has a similar function to some extent, as it is a large structure in the middle of the cell full of CELL SAP [a solution of sugar and salts] that supports the cell and keeps it rigid.
The CHLOROPLASTS floating in the CYTOPLASM contain little green pigments called CHLOROPHYLL, where photosynthesis occurs. Every green part of a plant contains the pigment chlorophyll. Some plants have variegated leaves, which are only half green. You can tell that the green parts contain chloroplasts and the other parts don’t.
Now let’s see what happens when a plant cell needs to PHOTOSYNTHESISE. The process of photosynthesis is used to produce “food” for the plant, in the form of glucose.
You can think of the CHLOROPHYLL as another tiny factory, which takes in carbon dioxide and water and releases glucose and oxygen in the presence of sunlight.
Now that brings us to the end of this video. If you found the video interesting and informative, we would greatly appreciate a like, comment or subscription as it only takes a few seconds of your time and helps us out immensely.
Комментарии
 0:07:22
0:07:22
 0:09:27
0:09:27
 0:02:14
0:02:14
 0:06:06
0:06:06
 0:14:17
0:14:17
 0:03:16
0:03:16
 0:05:38
0:05:38
 0:04:29
0:04:29
 2:16:22
2:16:22
 0:11:56
0:11:56
 0:05:58
0:05:58
 0:15:08
0:15:08
 0:08:59
0:08:59
 0:04:36
0:04:36
 0:06:49
0:06:49
 0:02:06
0:02:06
 0:13:52
0:13:52
 0:04:14
0:04:14
 0:21:04
0:21:04
 0:04:11
0:04:11
 0:09:20
0:09:20
 0:05:31
0:05:31
 0:04:48
0:04:48
 0:03:13
0:03:13