filmov
tv
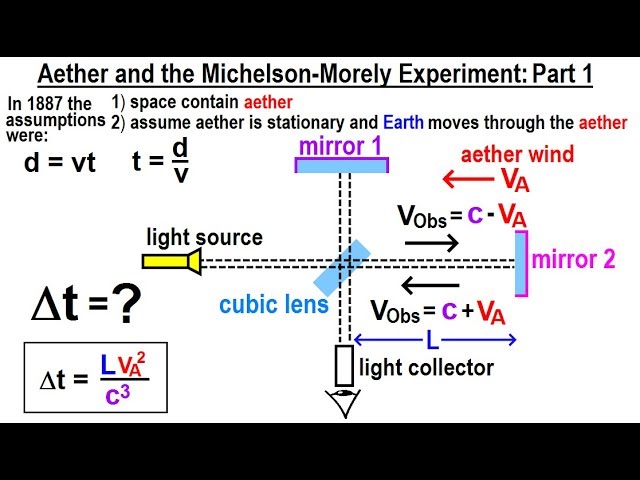
Astronomy - Ch. 31: What is Space Made of? (4 of 15) Aether and the Michelson-Morley Exp.: Part 1
Показать описание
To donate:
We will learn the aether and the Michelson-Marley experiment and its calculation of trying to show space is made of aether. Part 1
Next video in this series can be seen at:
Astronomy - Ch. 31: What is Space Made of? (4 of 15) Aether and the Michelson-Morley Exp.: Part 1
Astronomy - Ch. 31: What is Space Made of? (3 of 15) Aether and the Michelson-Morley Exp.: Concepts
Astronomy - Ch. 31: What is Space Made of? (6 of 15) Einstein Quotes & Other Thoughts
Astronomy - Ch. 31: What is Space Made of? (7 of 15) Analogy of Waves on a String
Astronomy - Ch. 31: What is Space Made of? (5 of 15) Aether and the Michelson-Morley Exp.: Part 2
Astronomy - Ch. 31: What is Space Made of? (1 of 15) Is Space Made of Aether?
Astronomy - Ch. 31: What is space made of? (2 of 15) How Space, Gravity, and Light Behave in Aether?
Astronomy - Ch. 31: What is Space Made of? (8 of 15) Pound-Rebka Experiment (Havard Tower)
Astronomy - Ch. 31: What is Space Made of? (9 of 15) Hubble's Law & it's Implication f...
Astronomy - Ch. 9.1: Earth's Atmosphere (31 of 61) The Daily Warming Cycle: Part 3
Astronomy - Ch. 13: Jupiter (31 of 37) Galilean Moon: Io Interior
Astronomy - Ch. 13: Jupiter (30 of 37) Galilean Moon: Io Plasma Torus
Astronomy - Ch. 17: The Nature of Stars (31 of 37) Determining Stellar Radii
Astronomy - Ch. 7: The Solar Sys - Comparative Planetology (31 of 33) Comets 2
Why Planets Are Spheres - Not Cubes or Donuts 🪐🧊 🍩 #astronomy #planets #outerspace #gravity...
Lesson 31 - Lecture 1 - Conclusion - OpenStax Astronomy 2023
ch 31
What will happen if JWT is pointed towards earth#astronomy #universe #space #facts #earth #Cosmos
Astronomy - Ch. 21: Life & Death of a High Mass Star (12 of 12) Light Curve of a Type 2 Supernov...
Neil deGrasse Tyson on multiverse #astrophysics #astronomy #multiverse
Saturn 🪐 live through a telescope Tiktok rajs_astrophotography #shorts #astronomy #astrophotography...
Life-Sustaining Exoplanets | Astronomy
Capturing the black hole ton618 #astronomy #astrophoto #nebula #space #spacescience
Astronomy Chapter 5
Комментарии
 0:07:59
0:07:59
 0:03:29
0:03:29
 0:07:55
0:07:55
 0:08:04
0:08:04
 0:10:05
0:10:05
 0:08:07
0:08:07
 0:07:45
0:07:45
 0:07:17
0:07:17
 0:05:45
0:05:45
 0:04:03
0:04:03
 0:05:35
0:05:35
 0:07:10
0:07:10
 0:04:43
0:04:43
 0:04:48
0:04:48
 0:00:17
0:00:17
 0:03:05
0:03:05
 0:06:31
0:06:31
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:05:41
0:05:41
 0:00:31
0:00:31
 0:00:31
0:00:31
 0:00:33
0:00:33
 0:00:25
0:00:25
 0:13:30
0:13:30