filmov
tv
nslookup DNS Request Timed Out FIX [Tutorial]

Показать описание
nslookup DNS Request Timed Out FIX [Tutorial].
A server connection timeout means that a server is taking too long to reply to a data request made from another device. Timeouts are not a reply message: they show up when there isn't a reply and a server request is not fulfilled in a predetermined length of time. A server connection timeout error does little to tell you what went wrong or why the error happened: it just identifies that the error occurred. Timeout errors can happen for a number of reasons. The server, the requesting device, the network hardware and even an Internet connection can be at fault.
The purpose of a server timeout is to prevent a device from endlessly waiting for a sever to respond. Server timeouts can occur when using a Web browser to view a site, connecting to an online service with a game or running a program update, among other situations. A task that has timed out or undergone a timeout is considered incomplete or failed. Essentially, the device that made the initial request for data from another device "gives up" on waiting for that information to be sent when a timeout occurs. According to Microsoft, Internet Explorer defaults the timeout duration at 60 minutes. The timeout duration varies depending on which program makes the data request from the server and can range from a few seconds to a few hours.
Issues addressed in this tutorial:
dns request timed out server unknown
dns request timed out timeout was 2 seconds then resolves,
dns request timed out windows 10
dns request timed out timeout was 2 seconds timeout 2 secs sendrequest failed
dns request timed out timeout was 2 seconds nslookup
dns request timed out 2 seconds nslookup
dns request timed out domain controller
dns request timed out nslookup
dns request timed out timeout was 2 seconds
This tutorial will apply for computers, laptops, desktops, and tablets running the Windows 10, Windows 8/8.1, Windows 7 operating systems. Works for all major computer manufactures (Dell, HP, Acer, Asus, Toshiba, Lenovo, Samsung).
A server connection timeout means that a server is taking too long to reply to a data request made from another device. Timeouts are not a reply message: they show up when there isn't a reply and a server request is not fulfilled in a predetermined length of time. A server connection timeout error does little to tell you what went wrong or why the error happened: it just identifies that the error occurred. Timeout errors can happen for a number of reasons. The server, the requesting device, the network hardware and even an Internet connection can be at fault.
The purpose of a server timeout is to prevent a device from endlessly waiting for a sever to respond. Server timeouts can occur when using a Web browser to view a site, connecting to an online service with a game or running a program update, among other situations. A task that has timed out or undergone a timeout is considered incomplete or failed. Essentially, the device that made the initial request for data from another device "gives up" on waiting for that information to be sent when a timeout occurs. According to Microsoft, Internet Explorer defaults the timeout duration at 60 minutes. The timeout duration varies depending on which program makes the data request from the server and can range from a few seconds to a few hours.
Issues addressed in this tutorial:
dns request timed out server unknown
dns request timed out timeout was 2 seconds then resolves,
dns request timed out windows 10
dns request timed out timeout was 2 seconds timeout 2 secs sendrequest failed
dns request timed out timeout was 2 seconds nslookup
dns request timed out 2 seconds nslookup
dns request timed out domain controller
dns request timed out nslookup
dns request timed out timeout was 2 seconds
This tutorial will apply for computers, laptops, desktops, and tablets running the Windows 10, Windows 8/8.1, Windows 7 operating systems. Works for all major computer manufactures (Dell, HP, Acer, Asus, Toshiba, Lenovo, Samsung).
Комментарии
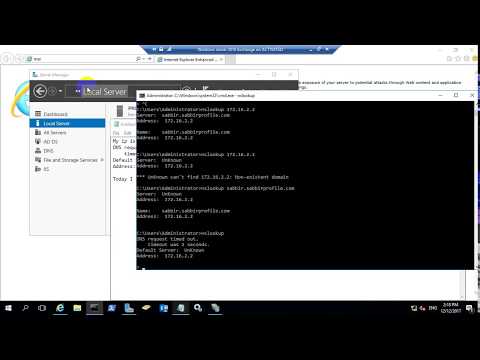 0:02:10
0:02:10
 0:02:15
0:02:15
 0:02:51
0:02:51
 0:03:01
0:03:01
 0:00:48
0:00:48
 0:03:51
0:03:51
 0:01:11
0:01:11
 0:04:06
0:04:06
 0:01:54
0:01:54
 0:02:00
0:02:00
 0:01:02
0:01:02
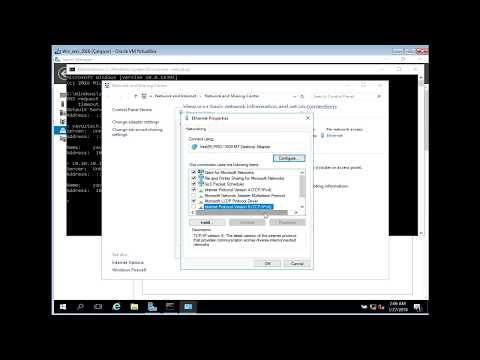 0:01:03
0:01:03
 0:07:52
0:07:52
 0:03:59
0:03:59
 0:04:15
0:04:15
 0:05:11
0:05:11
 0:05:06
0:05:06
 0:08:55
0:08:55
 0:12:11
0:12:11
 0:02:55
0:02:55
 0:10:05
0:10:05
 0:02:47
0:02:47
 0:03:22
0:03:22
 0:14:34
0:14:34