filmov
tv
Module 7: DNS Poisoning
Показать описание
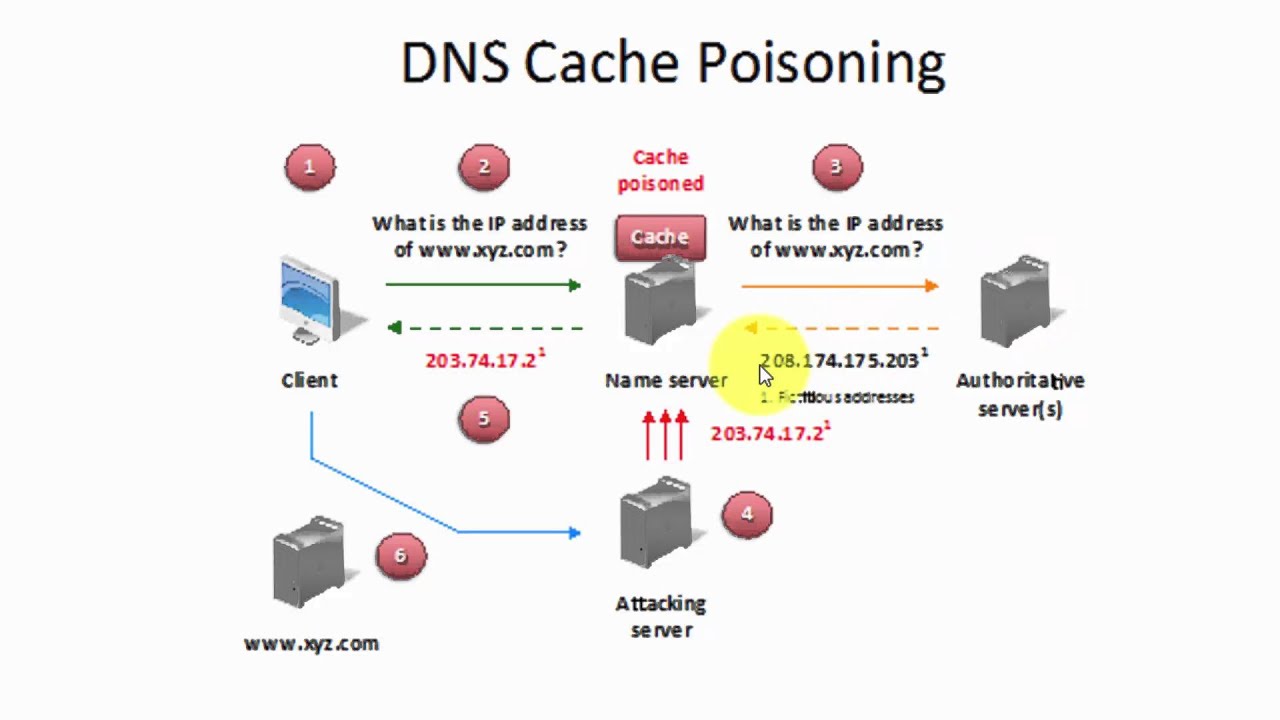
DNS poisoning takes advantage of DNS server’s table of IP addresses and host names by replacing the IP address of a host with another IP address that resolves to an attacker’s system. For example, an attacker can masquerade his or her own web server by poisoning the DNS server into thinking that the host name of the legitimate web server resolves to the IP address of the attackers web server.
References:
Samuelle, T., & Meyers, M. (2009). Network Security. In CompTIA security certification (2nd ed., p. 88). New York: McGraw-Hill.
References:
Samuelle, T., & Meyers, M. (2009). Network Security. In CompTIA security certification (2nd ed., p. 88). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Module 7: DNS Poisoning
How Hackers Use DNS Spoofing to Phish Passwords (WiFi Pineapple Demo)
7.5 - DNS Poisoning
ARP and DNS Spoofing
57# Kali Linux - DNS Spoofing vs DNS Poisoning
Perform DNS poisoning in switch lab9
DNS spoofing vs DNS poisoning
DNS Spoofing Attacks
The complete guidance of DNS Spoofing and DNS Poisoning !
DNS Poisoning Attack Tutorial
DNS Spoofing
101 Labs - Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) - DNS Poisoning
DNS Security - Cache Poisoning
DNS Poisoning
DNS Poisoning Attack
Example of a common DNS cache poisoning attack
Ping 2021: Aula 0x1C - DNS Cache Poisoning
Learn DNS Cache Poisoning
DNS Poisoning and Domain Hijacking - CompTIA Security+ SY0-501 - 1.2
Ataque de Envenamento de DNS
When you first time install Kali linux for hacking 😄😄 #hacker #shorts
What is DNS Poisoning?
DNS Poisoning Attack Practical
Defenses Against DNS Cache Poisoning
Комментарии
 0:02:44
0:02:44
 0:09:15
0:09:15
 0:06:54
0:06:54
 0:02:15
0:02:15
 0:08:20
0:08:20
 0:03:52
0:03:52
 0:08:20
0:08:20
 0:15:40
0:15:40
 0:14:53
0:14:53
 0:03:26
0:03:26
 0:00:56
0:00:56
 0:03:08
0:03:08
 0:08:52
0:08:52
 0:13:45
0:13:45
 0:05:21
0:05:21
 0:01:08
0:01:08
 0:05:31
0:05:31
 0:02:53
0:02:53
 0:04:29
0:04:29
 0:02:01
0:02:01
 0:00:32
0:00:32
 0:07:21
0:07:21
 0:05:07
0:05:07
 0:01:56
0:01:56