filmov
tv
Semiconductor: P-Type and N-Type, Intrinsic and Extrinsic.
Показать описание
In this video, Semiconductors and Its Types have been explained with examples
Semiconductor materials like Silicon and Germanium are widely used in almost all electronic devices, Their controlled conduction capability makes them ideal to be used in making electronic devices like diodes, transistors, integrated circuits and etc.
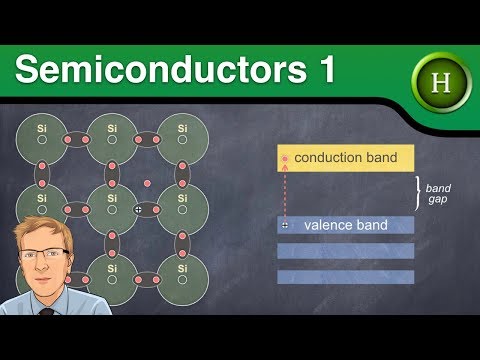
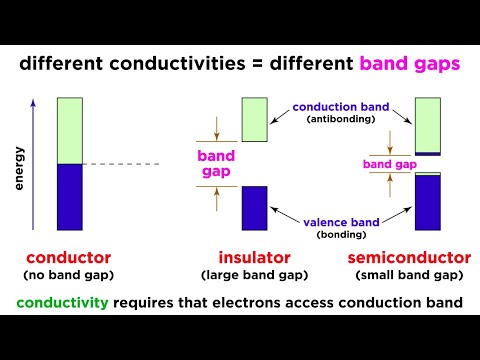
In terms of conductivity, the conductivity of the semiconductor materials is in between the conductor and insulator.
The electrons in the outermost orbit of an atom determine the electrical property of an element
Conductors have less than 4 valance electrons,
Semiconductors have 4 Valance electrons,
Insulators have 8 Valance electrons.
There are two types of charges which contribute to the flow of current in semiconductors
1) Electrons
2) Holes
By adding the external impurities, the conductivity of a semiconductor can be changed. the concentration of electrons and holes can be controlled.
The semiconductors can be classified into two categories
1) Intrinsic Semiconductor
2) Extrinsic Semiconductor
Intrinsic semiconductor: No external impurities are added. the concentration of holes and electrons is equal at the given temperature.
Extrinsic semiconductor: Exernal impurities are added and depending on the type of external impurity, the extrinsic semiconductor can be classified as
1) P-type semiconductor
2) N-type semiconductor
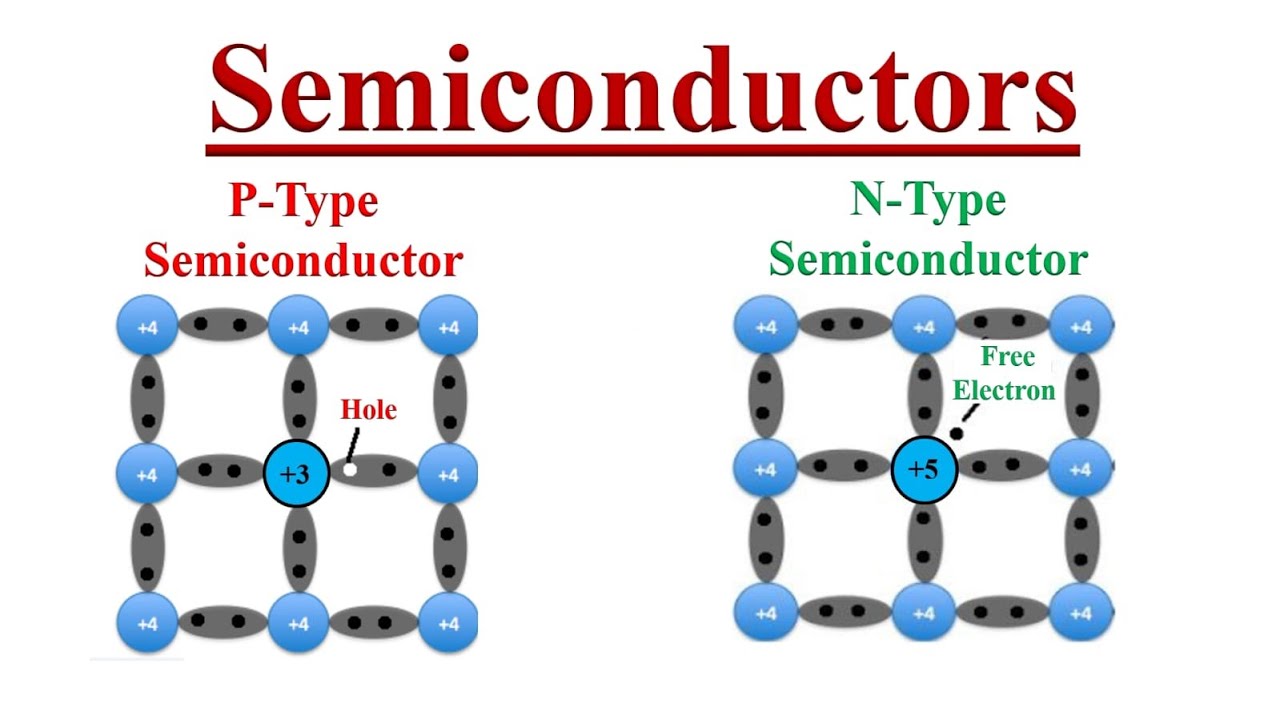
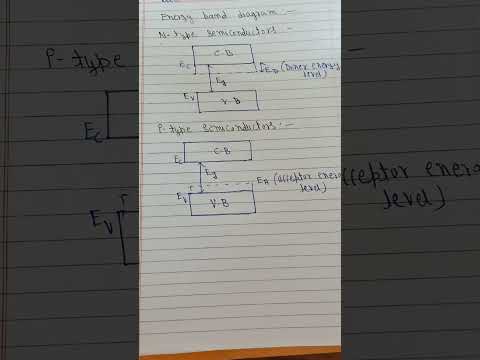
P-type semiconductor:
Trivalent impurities like Boron, Aluminum, and Gallium are added to pure semiconductor to generate excessive holes. So Holes are majority carriers and Electrons are minority carriers.
N-type semiconductor:
Pentavalent atoms like arsenic, antimony and phosphorous are added to pure semiconductor to generated excessive electrons. So Electrons are majority carriers and Holes are minority carreiers.
This video will be helpful to all the students of science and engineering in understanding the basics of the semiconductor.
#Semiconductor
#ptype Semiconductor
#ntype Semiconductor
#types of Semiconductors
#intrinsic Semiconductor
#extrinsic Semiconductor
Timestamps for various topics covered in this video are as follows:
0:39 Conductors, Semiconductors, and Insulators,
2:09 Why electrical conductivity is diifferent in materials,
4:29 Behavior of semiconductors (Holes and Electrons),
7:43 Types of Semiconductors (Intrinsic and Extrinsic),
8:38 P-type and N-type semiconductors.
The links of related videos of Basic electronics
Conductors, Insulators, and Semiconductors
What is Resistor
Ohm's Law
How does a capacitor work?
Inductors Explained
Please SUBSCRIBE my youtube channel
Music Credit:
"Keep Learning and Keep Growing".
Semiconductor materials like Silicon and Germanium are widely used in almost all electronic devices, Their controlled conduction capability makes them ideal to be used in making electronic devices like diodes, transistors, integrated circuits and etc.
In terms of conductivity, the conductivity of the semiconductor materials is in between the conductor and insulator.
The electrons in the outermost orbit of an atom determine the electrical property of an element
Conductors have less than 4 valance electrons,
Semiconductors have 4 Valance electrons,
Insulators have 8 Valance electrons.
There are two types of charges which contribute to the flow of current in semiconductors
1) Electrons
2) Holes
By adding the external impurities, the conductivity of a semiconductor can be changed. the concentration of electrons and holes can be controlled.
The semiconductors can be classified into two categories
1) Intrinsic Semiconductor
2) Extrinsic Semiconductor
Intrinsic semiconductor: No external impurities are added. the concentration of holes and electrons is equal at the given temperature.
Extrinsic semiconductor: Exernal impurities are added and depending on the type of external impurity, the extrinsic semiconductor can be classified as
1) P-type semiconductor
2) N-type semiconductor
P-type semiconductor:
Trivalent impurities like Boron, Aluminum, and Gallium are added to pure semiconductor to generate excessive holes. So Holes are majority carriers and Electrons are minority carriers.
N-type semiconductor:
Pentavalent atoms like arsenic, antimony and phosphorous are added to pure semiconductor to generated excessive electrons. So Electrons are majority carriers and Holes are minority carreiers.
This video will be helpful to all the students of science and engineering in understanding the basics of the semiconductor.
#Semiconductor
#ptype Semiconductor
#ntype Semiconductor
#types of Semiconductors
#intrinsic Semiconductor
#extrinsic Semiconductor
Timestamps for various topics covered in this video are as follows:
0:39 Conductors, Semiconductors, and Insulators,
2:09 Why electrical conductivity is diifferent in materials,
4:29 Behavior of semiconductors (Holes and Electrons),
7:43 Types of Semiconductors (Intrinsic and Extrinsic),
8:38 P-type and N-type semiconductors.
The links of related videos of Basic electronics
Conductors, Insulators, and Semiconductors
What is Resistor
Ohm's Law
How does a capacitor work?
Inductors Explained
Please SUBSCRIBE my youtube channel
Music Credit:
"Keep Learning and Keep Growing".
Комментарии
 0:05:12
0:05:12
 0:10:50
0:10:50
 0:13:13
0:13:13
 0:12:44
0:12:44
 0:08:23
0:08:23
 0:04:31
0:04:31
 0:03:43
0:03:43
 0:00:05
0:00:05
 0:00:53
0:00:53
 0:00:11
0:00:11
 0:08:39
0:08:39
 0:06:32
0:06:32
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:09:15
0:09:15
 0:04:53
0:04:53
 0:11:04
0:11:04
 0:01:29
0:01:29
 0:08:59
0:08:59
 0:00:23
0:00:23
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:13:56
0:13:56
 0:00:22
0:00:22
 0:00:14
0:00:14
 0:00:13
0:00:13