filmov
tv
Parts Of A Long Bone - Structure Of A Long Bone
Показать описание
In this video we discuss the parts of a long bone and some of the functions of each of those bone parts. We cover the diaphysis, the epiphysis, spongy and compact bone, bone marrow, the periosteum and the medullary cavity.
Transcript/notes
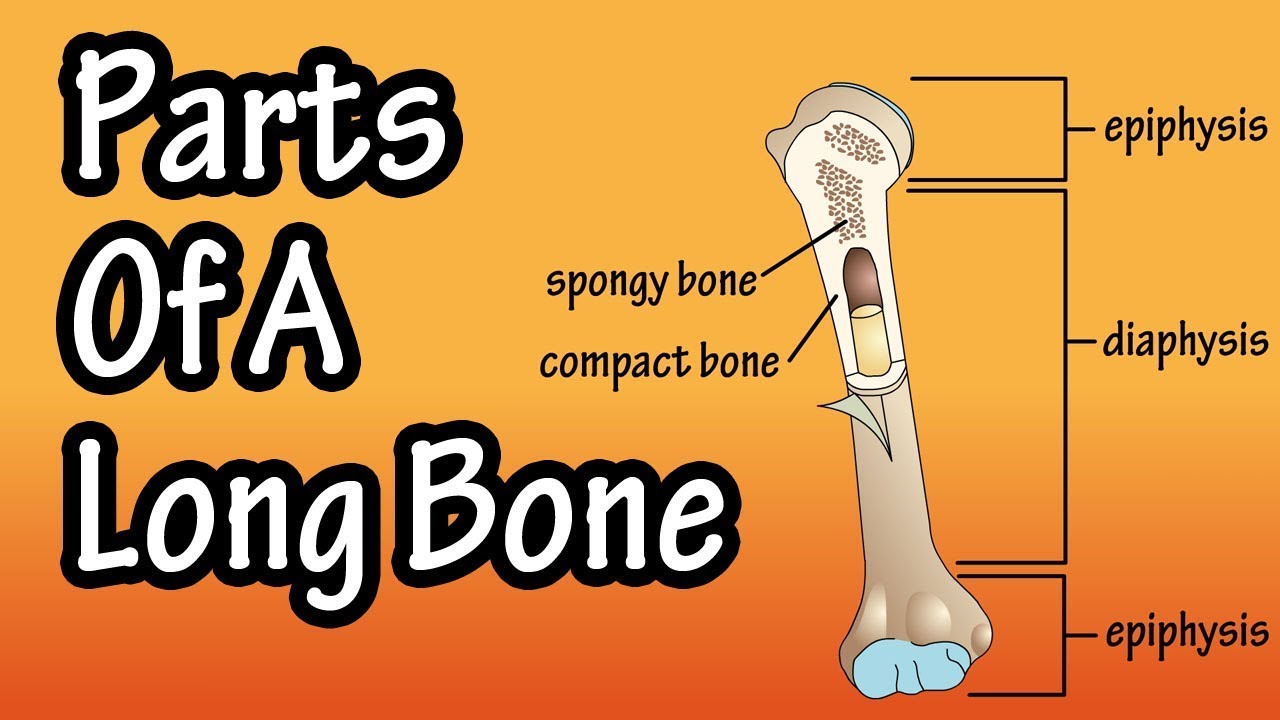
Parts of a long bone.
In this video we are going to go over a very basic overview of the parts of a long bone.
The diaphysis is the shaft of a bone, and its function is to be rigid enough to tolerate strong forces and not bend or break. The diaphysis is comprised of compact bone tissue and spongy bone tissue.
At each end of the diaphysis is a epiphysis, which is composed mainly of spongy bone tissue. The spaces of spongy bone tissue contain red marrow, which produces red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. You can see at the epiphysis the bone widens out, this is so a joint can be formed with another bone. By the widening out of these bone ends, a larger surface area is created, providing for better joint stability.
Where bones come together to form joints is a smooth tissue called articular cartilage. It provide shock absorption, cushioning and minimizes friction as the bones move. Because articular cartilage has a poor blood supply, it does not heal very well once it has been damaged.
There is a thin fibrous membrane called periosteum that covers the entire bone surface except where the articular cartilage is. This membrane allows for attachment of ligaments and muscle tendons, and houses cells that are important in bone formation and repairing bone tissue. The periosteum has many nerve fibers, so it can be very painful when bruised.
Inside the diaphysis is a tubelike area called the medullary cavity, which houses red marrow during childhood, which is replaced by yellow marrow as a person ages.
There is a thin membrane that lines the medullary cavity called the endosteum, which contains cells that are important in bone growth and repair.
Bones are also well supplied with arteries and veins.
Timestamps
0:00 The diaphysis
0:17 The epiphysis
0:41 Articular cartilage
0:56 Periosteum
1:17 Medullary cavity
1:28 The endosteum
Transcript/notes
Parts of a long bone.
In this video we are going to go over a very basic overview of the parts of a long bone.
The diaphysis is the shaft of a bone, and its function is to be rigid enough to tolerate strong forces and not bend or break. The diaphysis is comprised of compact bone tissue and spongy bone tissue.
At each end of the diaphysis is a epiphysis, which is composed mainly of spongy bone tissue. The spaces of spongy bone tissue contain red marrow, which produces red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. You can see at the epiphysis the bone widens out, this is so a joint can be formed with another bone. By the widening out of these bone ends, a larger surface area is created, providing for better joint stability.
Where bones come together to form joints is a smooth tissue called articular cartilage. It provide shock absorption, cushioning and minimizes friction as the bones move. Because articular cartilage has a poor blood supply, it does not heal very well once it has been damaged.
There is a thin fibrous membrane called periosteum that covers the entire bone surface except where the articular cartilage is. This membrane allows for attachment of ligaments and muscle tendons, and houses cells that are important in bone formation and repairing bone tissue. The periosteum has many nerve fibers, so it can be very painful when bruised.
Inside the diaphysis is a tubelike area called the medullary cavity, which houses red marrow during childhood, which is replaced by yellow marrow as a person ages.
There is a thin membrane that lines the medullary cavity called the endosteum, which contains cells that are important in bone growth and repair.
Bones are also well supplied with arteries and veins.
Timestamps
0:00 The diaphysis
0:17 The epiphysis
0:41 Articular cartilage
0:56 Periosteum
1:17 Medullary cavity
1:28 The endosteum
Комментарии
 0:01:52
0:01:52
 0:09:49
0:09:49
 0:03:24
0:03:24
 0:08:09
0:08:09
 0:01:04
0:01:04
 0:10:14
0:10:14
 0:12:11
0:12:11
 0:04:55
0:04:55
 0:02:55
0:02:55
 0:05:36
0:05:36
 0:06:29
0:06:29
 0:07:51
0:07:51
 0:09:05
0:09:05
 0:06:24
0:06:24
 0:04:18
0:04:18
 0:05:18
0:05:18
 0:01:08
0:01:08
 0:11:29
0:11:29
 0:00:46
0:00:46
 0:10:38
0:10:38
 0:00:32
0:00:32
 0:07:55
0:07:55
 0:04:55
0:04:55
 0:07:41
0:07:41