filmov
tv
Ionic Solids

Показать описание
023 - Ionic Solids
In this video Paul Andersen explains how ionic solids form a lattice between cations and anions. According the Coulomb's Law the lattice energy increases as the ions carry a larger charge and are smaller. Some of the properties of ionic solids are high melting point, low vapor pressure, brittleness and the inability to conduct electricity. Ionic compounds can be readily dissolved by polar molecules like water.
Music Attribution
Title: String Theory
Artist: Herman Jolly
All of the images are licensed under creative commons and public domain licensing:
In this video Paul Andersen explains how ionic solids form a lattice between cations and anions. According the Coulomb's Law the lattice energy increases as the ions carry a larger charge and are smaller. Some of the properties of ionic solids are high melting point, low vapor pressure, brittleness and the inability to conduct electricity. Ionic compounds can be readily dissolved by polar molecules like water.
Music Attribution
Title: String Theory
Artist: Herman Jolly
All of the images are licensed under creative commons and public domain licensing:
Ionic Solids
Ionic solids | Intermolecular forces and properties | AP Chemistry | Khan Academy
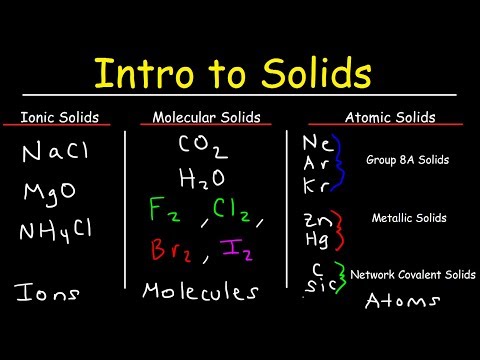
Ionic Solids, Molecular Solids, Metallic Solids, Network Covalent Solids, & Atomic Solids
Lattice Structures in Ionic Solids
Ionic solid | types of solid | ch#4 | 11th class Chemistry
Ionic Compounds & Their Properties | Properties of Matter | Chemistry | FuseSchool
The Structures of Ionic Solids
Types of Crystalline solids | Ionic Solids | complete lecture by Dur chemist
Ionic Solids 1st Year, Chapter-04, Lecture-85
Ionic Solids
Lattice Energy of Ionic Compounds, Basic Introduction, Charge vs Ionic Radius
11.3 Structures of Solids | General Chemistry
Ionic Solids - Chemistry
GCSE Chemistry - What is an Ionic Compound? Ionic Compounds Explained #15
Structure of Ionic Solids
Representing ionic solids using particulate models | AP Chemistry | Khan Academy
2.3 - Structure of Ionic Solids
What are ionic solids??
Lecture 9 Structures of Ionic Solids
7 - Class 12 - Chemistry - Solid State - Structure of Ionic Compounds
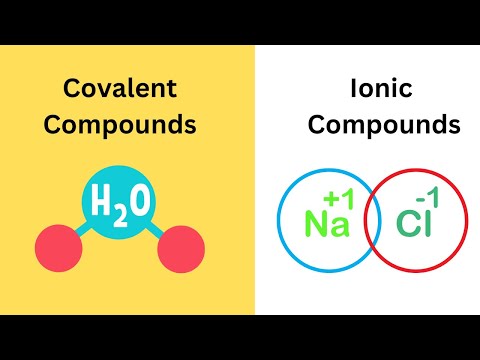
Covalent Compounds VS Ionic Compounds
Properties of Ionic Substances | Properties of Matter | Chemistry | FuseSchool
Introduction to packing in ionic solids
Ionic solids
Комментарии
 0:05:05
0:05:05
 0:07:35
0:07:35
 0:20:19
0:20:19
 0:10:54
0:10:54
 0:23:11
0:23:11
 0:03:36
0:03:36
 0:16:57
0:16:57
 0:19:05
0:19:05
 0:05:09
0:05:09
 0:12:45
0:12:45
 0:13:30
0:13:30
 0:30:27
0:30:27
 0:01:43
0:01:43
 0:06:08
0:06:08
 0:06:17
0:06:17
 0:05:43
0:05:43
 0:02:20
0:02:20
 0:00:56
0:00:56
 0:17:55
0:17:55
 0:05:05
0:05:05
 0:02:55
0:02:55
 0:04:06
0:04:06
 0:12:37
0:12:37
 0:00:35
0:00:35