filmov
tv
Introduction to nucleic acid and nucleotide | types of nucleotides |

Показать описание
The two types of nucleic acids, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), enable living organisms to reproduce their complex components from one generation to the next. Unique among molecules, DNA provides
directions for its own replication. DNA also directs RNA synthesis and, through RNA, controls protein synthesis; this entire process is called gene expression.
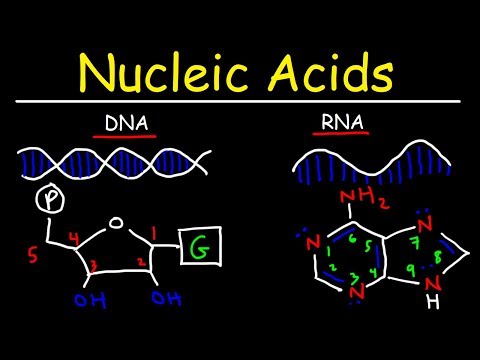
Nucleic acids are macromolecules that exist as polymers called polynucleotides. As indicated by the name, each polynucleotide consists of monomers called nucleotides. A nucleotide, in general, is composed of three
parts: a five-carbon sugar (a pentose), a nitrogen-containing (nitrogenous) base, and one or more phosphate groups. In a polynucleotide, each monomer has only one phosphate group. The portion of a nucleotide without
any phosphate groups is called a nucleoside.
There are two families of nitrogenous bases: pyrimidines and purines. A
pyrimidine has one six-membered ring of carbon and nitrogen atoms. The members of the pyrimidine family are cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U). Purines are larger, with a six-membered ring fused to a five-membered ring.
The purines are adenine (A) and guanine (G). In DNA the sugar is deoxyribose; in RNA it is ribose. The only difference between these two sugars is that deoxyribose lacks an oxygen atom on the second carbon in the ring; hence the name deoxyribose.
#NucleotidComposition
directions for its own replication. DNA also directs RNA synthesis and, through RNA, controls protein synthesis; this entire process is called gene expression.
Nucleic acids are macromolecules that exist as polymers called polynucleotides. As indicated by the name, each polynucleotide consists of monomers called nucleotides. A nucleotide, in general, is composed of three
parts: a five-carbon sugar (a pentose), a nitrogen-containing (nitrogenous) base, and one or more phosphate groups. In a polynucleotide, each monomer has only one phosphate group. The portion of a nucleotide without
any phosphate groups is called a nucleoside.
There are two families of nitrogenous bases: pyrimidines and purines. A
pyrimidine has one six-membered ring of carbon and nitrogen atoms. The members of the pyrimidine family are cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U). Purines are larger, with a six-membered ring fused to a five-membered ring.
The purines are adenine (A) and guanine (G). In DNA the sugar is deoxyribose; in RNA it is ribose. The only difference between these two sugars is that deoxyribose lacks an oxygen atom on the second carbon in the ring; hence the name deoxyribose.
#NucleotidComposition
Комментарии
 0:11:16
0:11:16
 0:06:31
0:06:31
 0:20:32
0:20:32
 0:05:55
0:05:55
 0:02:32
0:02:32
 0:09:58
0:09:58
 0:33:25
0:33:25
 0:07:05
0:07:05
 0:18:50
0:18:50
 0:08:07
0:08:07
 0:08:01
0:08:01
 0:46:23
0:46:23
 0:03:19
0:03:19
 0:12:26
0:12:26
 0:02:04
0:02:04
 0:12:59
0:12:59
 0:12:15
0:12:15
 0:04:34
0:04:34
 0:08:00
0:08:00
 0:05:29
0:05:29
 0:03:06
0:03:06
 0:07:29
0:07:29
 0:28:29
0:28:29
 0:04:34
0:04:34