filmov
tv
Ionic Bond and ionic solids or compounds | Chemistry | by Imran Yaseen

Показать описание
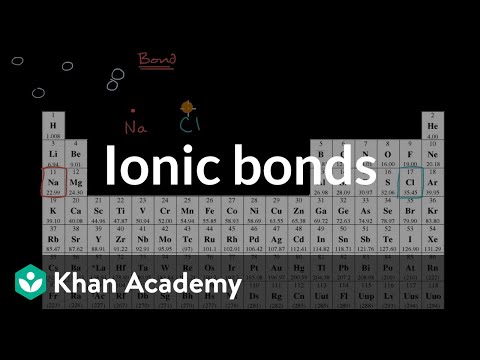
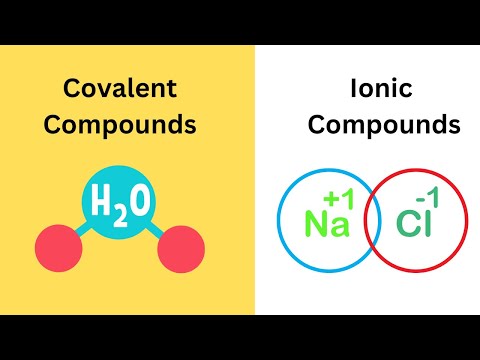
An ionic bond is a type of chemical bond that forms between two atoms when one atom transfers electrons to another atom. This transfer of electrons results in the formation of ions, which are atoms that have gained or lost electrons and therefore carry a net electrical charge.
In an ionic bond, one atom typically donates one or more electrons to another atom, resulting in the formation of positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged ions (anions). The positively charged ion is attracted to the negatively charged ion, leading to the formation of an electrostatic attraction between them, known as an ionic bond.
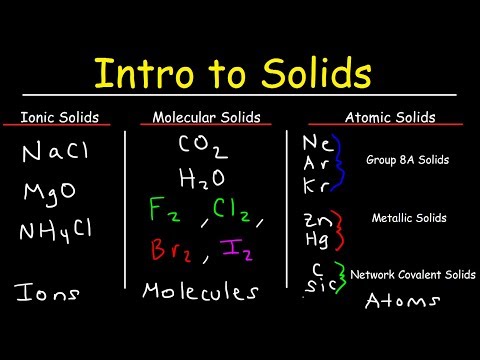
Ionic solids or compounds are substances composed of ions held together by ionic bonds. These compounds typically consist of a lattice structure in which positively charged ions are surrounded by negatively charged ions and vice versa. Ionic solids have high melting and boiling points due to the strong electrostatic forces between ions, which require a significant amount of energy to break.
Ionic compounds exhibit several characteristic properties:
1. **Electrical Conductivity**: In the solid state, ionic compounds do not conduct electricity because the ions are held in fixed positions in the lattice. However, when melted or dissolved in water (forming an aqueous solution), ionic compounds can conduct electricity because the ions are free to move and carry electrical charge.
2. **Solubility**: Many ionic compounds are soluble in water, as water molecules can surround and separate the individual ions, allowing them to dissolve.
3. **Brittleness**: Ionic solids are often brittle because the layers of ions can slide past each other under stress, causing the crystal lattice to break apart.
4. **Crystalline Structure**: Ionic compounds typically form crystals with regular, repeating patterns due to the arrangement of ions in the lattice structure.
Common examples of ionic compounds include sodium chloride (table salt), potassium chloride, calcium carbonate (limestone), and magnesium oxide. Ionic bonding and ionic compounds play a significant role in various aspects of chemistry, including materials science, biochemistry, and environmental chemistry.
Bond is a force that keeps atoms or molecules together. Within the molecule, it is called intramolecular force and between the molecules, it is called intermolecular force. The key terms explained in this lecture are ionic bond, covalent bond, coordinate covalent bond, metallic bond, dipole-dipole forces, and hydrogen bonding.
#tothepoint #easychemistry Chemistry #shorts
In an ionic bond, one atom typically donates one or more electrons to another atom, resulting in the formation of positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged ions (anions). The positively charged ion is attracted to the negatively charged ion, leading to the formation of an electrostatic attraction between them, known as an ionic bond.
Ionic solids or compounds are substances composed of ions held together by ionic bonds. These compounds typically consist of a lattice structure in which positively charged ions are surrounded by negatively charged ions and vice versa. Ionic solids have high melting and boiling points due to the strong electrostatic forces between ions, which require a significant amount of energy to break.
Ionic compounds exhibit several characteristic properties:
1. **Electrical Conductivity**: In the solid state, ionic compounds do not conduct electricity because the ions are held in fixed positions in the lattice. However, when melted or dissolved in water (forming an aqueous solution), ionic compounds can conduct electricity because the ions are free to move and carry electrical charge.
2. **Solubility**: Many ionic compounds are soluble in water, as water molecules can surround and separate the individual ions, allowing them to dissolve.
3. **Brittleness**: Ionic solids are often brittle because the layers of ions can slide past each other under stress, causing the crystal lattice to break apart.
4. **Crystalline Structure**: Ionic compounds typically form crystals with regular, repeating patterns due to the arrangement of ions in the lattice structure.
Common examples of ionic compounds include sodium chloride (table salt), potassium chloride, calcium carbonate (limestone), and magnesium oxide. Ionic bonding and ionic compounds play a significant role in various aspects of chemistry, including materials science, biochemistry, and environmental chemistry.
Bond is a force that keeps atoms or molecules together. Within the molecule, it is called intramolecular force and between the molecules, it is called intermolecular force. The key terms explained in this lecture are ionic bond, covalent bond, coordinate covalent bond, metallic bond, dipole-dipole forces, and hydrogen bonding.
#tothepoint #easychemistry Chemistry #shorts
 0:04:12
0:04:12
 0:02:55
0:02:55
 0:06:08
0:06:08
 0:05:05
0:05:05
 0:13:30
0:13:30
 0:03:36
0:03:36
 0:07:20
0:07:20
 0:04:06
0:04:06
 0:50:45
0:50:45
 0:03:46
0:03:46
 0:05:44
0:05:44
 0:47:35
0:47:35
 0:02:01
0:02:01
 0:04:48
0:04:48
 0:04:10
0:04:10
 0:11:50
0:11:50
 0:20:19
0:20:19
 0:04:30
0:04:30
 0:07:02
0:07:02
 0:02:55
0:02:55
 0:03:23
0:03:23
 0:21:57
0:21:57
 0:06:23
0:06:23
 0:03:03
0:03:03