filmov
tv
Tuberculosis for USMLE Step 1 and USMLE Step 2

Показать описание
Handwritten video lecture on Tuberculosis for USMLE Step 1 and USMLE Step 2. Reviewing Pathogenesis, Signs and Symptoms, Investigations, and Treatment.
BACTERIOLOGY
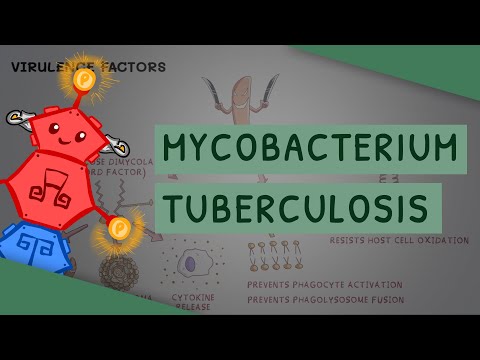
Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis with its main virulence factor is due to its mycolic acid coat that increases immune resistance but the bacteria grows much slower. Ziehl-Neelson staining aka Acid Fast stain can stain tuberculosis, but also stains nocardia, legionella, isospora, and cryptosporidium. Tuberculosis (TB) bacteria is also aerobic.
PATHOGENESIS
EXPOSURE – Tuberculosis (TB) bacteria must first go into the lower respiratory tract. Generally prefers upper part of the middle and lower lobe leading to primary tuberculosis infection.
MACROPHAGE – undergoes phagocytosis by macrophage and the tuberculosis will be inside of phagosome. Normally the lysosome needs to fuse to form phagolysosome. This can be inhibited by tuberculosis bacteria so over time the mycobacterium grows within the phagosome until rupture. Eventually the macrophage will rupture which will then be taken up by macrophages again.
GRANULOMA – Granuloma formed when the number of macrophages with mycobacterium increases. With Cell Mediated Immunity (CMI) activation by T cells release lymphokines that activate macrophages which kills the Tuberculosis (TB) and creates casseous necrosis in the central area. Many of the tuberculosis (TB) bacteria are not killed and remain dormant.
SYMPTOMS
Range from asymptomatic to fever, pleuritic and chest pain. Erythema nodosum, phlyctenuclar conjunctivitis may also be seen. Early there is non-purulent cough that may become plurulent with blood. May also have pleuritic chest pain with dyspnea and respiratory distress.
GHON FOCUS – ghon focus is an actual lesion that is found in the peripheral part of the lung. After some time may travel to hilar lymph node forming the ghon complex.
DORMANT – There is granuloma formation which has live tuberculosis (TB) bacteria. This may reactivate and is known as reactivation TB, Post primary TB, or Secondary TB. Reactivation occurs when the patient later becomes immunocompromised. Location is in upper/posterior lobe because of increased oxygen found.
PROGRESS – Tuberculosis (TB) grows and creates cavity that enlarges. Goes to airways and patient is infectious. If goes to pleura may cause pleural effusion. Hilar lymphadenopathy that may press on trachea. May go to blood vessels and create disseminated tuberculosis.
COURSE – galloping consumption is when it becomes very severe. Consumption is when it takes a chronic course and finally spontaneous remission.
DIAGNOSIS
CHEST X-RAY – May see cavitation, Ghon complex, and calcified nodule
Acid Fast Bacilli (AFB) Microscopy – Done with sputum sample or bronchioalveolar lavage (BAL). Gastric can give high false positive with Ziehl Neelsen Stain
CULTURE – With Lowenstein Jensen, but takes 4-8 weeks to grow.
MOLECULAR TESTS- Include nucleic acid amplification, PCR, MTB and RIF.
TUBERCULIN SKIN TEST (PPD) – May detect latent stage, however, many false negatives and false positive.
TREATMENT
INITIAL PHASE (2 MONTHS) – attempting the kill as much bacteria as possible
CONTINUATION PHASE (2-6 MONTHS) – kille persistent and resistant bacteria.
Isoniazid and Rifampicin is used for 6 months. Pyrazinamide and Ethambutol is used only in first 2 months of treatment.
Must monitor sputum with culture and by 3 months must be culture negative. If persistent than may be bacterial resistance or there is decreased comlaince. Also monitor Drug Toxicity which is unique for each drug. Monitor liver function test, uric acid levels, B6 levels, and optic neuritis.
Direct Observation Treatment (DOT) – helped with compliance with nurse observing patient take the drug.
If there is resistance can add fluoroquinolone, streptomycin, amikacin, kanamycin, capromycin. If resistant to isoniazid and rifampicin then increase treatment to 9 months. Do this also if there is cavitary lesion. Multdrug resistant Tuberculosis (TB) (MDR) you should add Fluoroquinolone and other second line drug. XDR is if there is resistance to first and second line drug.
BACTERIOLOGY
Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis with its main virulence factor is due to its mycolic acid coat that increases immune resistance but the bacteria grows much slower. Ziehl-Neelson staining aka Acid Fast stain can stain tuberculosis, but also stains nocardia, legionella, isospora, and cryptosporidium. Tuberculosis (TB) bacteria is also aerobic.
PATHOGENESIS
EXPOSURE – Tuberculosis (TB) bacteria must first go into the lower respiratory tract. Generally prefers upper part of the middle and lower lobe leading to primary tuberculosis infection.
MACROPHAGE – undergoes phagocytosis by macrophage and the tuberculosis will be inside of phagosome. Normally the lysosome needs to fuse to form phagolysosome. This can be inhibited by tuberculosis bacteria so over time the mycobacterium grows within the phagosome until rupture. Eventually the macrophage will rupture which will then be taken up by macrophages again.
GRANULOMA – Granuloma formed when the number of macrophages with mycobacterium increases. With Cell Mediated Immunity (CMI) activation by T cells release lymphokines that activate macrophages which kills the Tuberculosis (TB) and creates casseous necrosis in the central area. Many of the tuberculosis (TB) bacteria are not killed and remain dormant.
SYMPTOMS
Range from asymptomatic to fever, pleuritic and chest pain. Erythema nodosum, phlyctenuclar conjunctivitis may also be seen. Early there is non-purulent cough that may become plurulent with blood. May also have pleuritic chest pain with dyspnea and respiratory distress.
GHON FOCUS – ghon focus is an actual lesion that is found in the peripheral part of the lung. After some time may travel to hilar lymph node forming the ghon complex.
DORMANT – There is granuloma formation which has live tuberculosis (TB) bacteria. This may reactivate and is known as reactivation TB, Post primary TB, or Secondary TB. Reactivation occurs when the patient later becomes immunocompromised. Location is in upper/posterior lobe because of increased oxygen found.
PROGRESS – Tuberculosis (TB) grows and creates cavity that enlarges. Goes to airways and patient is infectious. If goes to pleura may cause pleural effusion. Hilar lymphadenopathy that may press on trachea. May go to blood vessels and create disseminated tuberculosis.
COURSE – galloping consumption is when it becomes very severe. Consumption is when it takes a chronic course and finally spontaneous remission.
DIAGNOSIS
CHEST X-RAY – May see cavitation, Ghon complex, and calcified nodule
Acid Fast Bacilli (AFB) Microscopy – Done with sputum sample or bronchioalveolar lavage (BAL). Gastric can give high false positive with Ziehl Neelsen Stain
CULTURE – With Lowenstein Jensen, but takes 4-8 weeks to grow.
MOLECULAR TESTS- Include nucleic acid amplification, PCR, MTB and RIF.
TUBERCULIN SKIN TEST (PPD) – May detect latent stage, however, many false negatives and false positive.
TREATMENT
INITIAL PHASE (2 MONTHS) – attempting the kill as much bacteria as possible
CONTINUATION PHASE (2-6 MONTHS) – kille persistent and resistant bacteria.
Isoniazid and Rifampicin is used for 6 months. Pyrazinamide and Ethambutol is used only in first 2 months of treatment.
Must monitor sputum with culture and by 3 months must be culture negative. If persistent than may be bacterial resistance or there is decreased comlaince. Also monitor Drug Toxicity which is unique for each drug. Monitor liver function test, uric acid levels, B6 levels, and optic neuritis.
Direct Observation Treatment (DOT) – helped with compliance with nurse observing patient take the drug.
If there is resistance can add fluoroquinolone, streptomycin, amikacin, kanamycin, capromycin. If resistant to isoniazid and rifampicin then increase treatment to 9 months. Do this also if there is cavitary lesion. Multdrug resistant Tuberculosis (TB) (MDR) you should add Fluoroquinolone and other second line drug. XDR is if there is resistance to first and second line drug.
Комментарии
 0:18:37
0:18:37
 0:27:35
0:27:35
 0:11:32
0:11:32
 0:10:33
0:10:33
 0:11:20
0:11:20
 1:09:29
1:09:29
 0:02:17
0:02:17
 0:15:00
0:15:00
 0:07:36
0:07:36
 0:15:23
0:15:23
 0:14:20
0:14:20
 0:18:17
0:18:17
 0:10:21
0:10:21
 0:12:19
0:12:19
 0:10:51
0:10:51
 0:11:14
0:11:14
 0:30:34
0:30:34
 0:13:51
0:13:51
 0:04:56
0:04:56
 0:00:14
0:00:14
 0:25:03
0:25:03
 0:31:10
0:31:10
 0:10:16
0:10:16
 0:05:23
0:05:23