filmov
tv
Understanding the Poynting Vector – The Key to Electromagnetic Energy Transfer

Показать описание
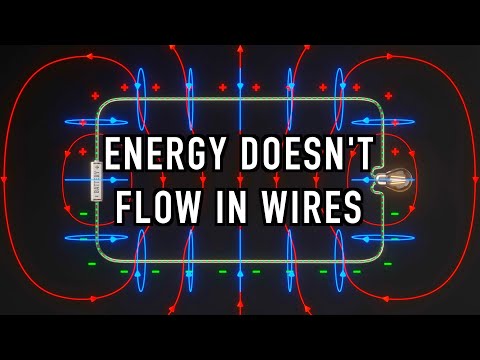
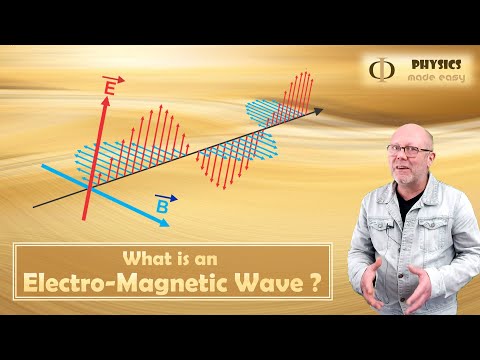
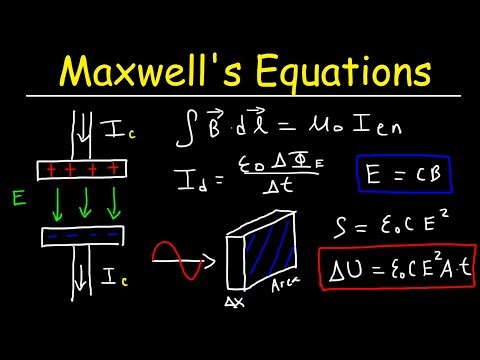
The Poynting vector, introduced by physicist John Henry Poynting in the late 19th century, represents the rate of energy transfer per unit area in an electromagnetic (EM) field. Mathematically, it's the cross-product of the electric field (E) and magnetic field (H) vectors. It describes the flow of energy in EM waves like light, radio waves, and microwaves, with the direction of the Poynting vector indicating energy flow and its magnitude representing energy flux. Its units are W/m² (watts per square meter). The Poynting vector plays a key role in explaining how energy propagates through space, particularly in applications like antennas, wireless communication, and solar energy. It also forms the basis of the Poynting theorem, an expression of energy conservation in electromagnetism, which relates the energy transfer to changes in electromagnetic fields. The concept is vital for understanding power distribution in various EM systems.
#PoyntingVector
#Electromagnetism
#EnergyTransfer
#ElectromagneticWaves
#Physics
#Electrodynamics
#JohnHenryPoynting
#EnergyFlux
#PoyntingTheorem
#EMWaves
#Science
#PhysicsEducation
#WavePropagation
#SolarEnergy
#RadioWaves
#Microwaves
#EnergyFlow
#ScientificDiscovery
#PhysicsConcepts
#PoyntingVector
#Electromagnetism
#EnergyTransfer
#ElectromagneticWaves
#Physics
#Electrodynamics
#JohnHenryPoynting
#EnergyFlux
#PoyntingTheorem
#EMWaves
#Science
#PhysicsEducation
#WavePropagation
#SolarEnergy
#RadioWaves
#Microwaves
#EnergyFlow
#ScientificDiscovery
#PhysicsConcepts
 0:14:24
0:14:24
 0:14:48
0:14:48
 0:12:31
0:12:31
 0:03:16
0:03:16
 0:24:31
0:24:31
 0:08:20
0:08:20
 0:00:33
0:00:33
 0:03:41
0:03:41
 0:16:37
0:16:37
 0:07:50
0:07:50
 0:00:55
0:00:55
 0:09:13
0:09:13
 0:04:49
0:04:49
 0:05:31
0:05:31
 0:07:40
0:07:40
 0:15:42
0:15:42
 0:05:45
0:05:45
 0:00:12
0:00:12
 0:11:58
0:11:58
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:00:57
0:00:57
 0:41:39
0:41:39
 0:05:03
0:05:03
 0:00:15
0:00:15