filmov
tv
Example 1.3 || Magnetic Circuit with Air Gap || Rotor & Stator of DC Motor (Error:check description)

Показать описание
"Correction:", 03:29 , Error in converting air-gap lenth lg = 0.05cm into meter. It should be = 0.0005m (not 0.005m as written)
"Correction: 03:29 Error in converting air-gap lenth lg = 0.05cm into meter. It should be = 0.0005m (not 0.005m as written)"
EM1.4(5)(E) (Chapman) Example 1.3
In this video we solve problem 1.3 from book Electric Machinery Fundamentals by Stephen J. Chapman
ERROR: I have made mistake in converting lengths from cm to m (instead of dividing by 100, I have divided by 10).
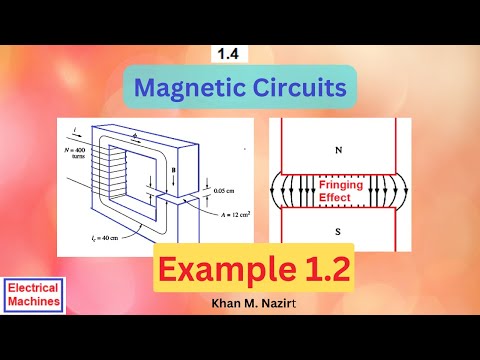
Figure 1-9a shows a simplified rotor and stator for a dc motor. The mean path length of the stator is 50 cm, and its cross-sectional area is 12 cm2. The mean path length of the rotor is 5 em, and its cross-sectional area also may be assumed to be 12 cm2. Each air gap between the rotor and the stator is 0.05 cm wide, and the cross-sectional area of each air gap (including fringing) is 14 cm2. The iron of the core has a relative permeability of 2000, and there are 200 turns of wire on the core. If the current in the
wire is adjusted to be 1A, what will the resulting flux density in the air gaps be?
In this video, delve into the magnetic circuit with an air gap, understand the components of the rotor and stator in a DC motor, and explore the analysis of Example 1.3 (Ch) in the context of EM 1.4(5)(E). Gain insights into the efficiency and operation of DC motors through magnetic circuit analysis. Watch now to enhance your understanding of this essential topic!
Hashtags:
#MagneticCircuit #AirGap #Rotor #Stator #DCMotor #Example1.3 #Ch #EM1.4(5)(E) #Analysis #Engineering
SEO Tags:
Magnetic Circuit with Air Gap, Rotor and Stator, DC Motor Components, Example 1.3, Ch, EM 1.4(5)(E), Magnetic Circuit Analysis, DC Motor Efficiency, Engineering, Rotor Stator Analysis, DC Motor Operation, EM Concepts
"Correction: 03:29 Error in converting air-gap lenth lg = 0.05cm into meter. It should be = 0.0005m (not 0.005m as written)"
EM1.4(5)(E) (Chapman) Example 1.3
In this video we solve problem 1.3 from book Electric Machinery Fundamentals by Stephen J. Chapman
ERROR: I have made mistake in converting lengths from cm to m (instead of dividing by 100, I have divided by 10).
Figure 1-9a shows a simplified rotor and stator for a dc motor. The mean path length of the stator is 50 cm, and its cross-sectional area is 12 cm2. The mean path length of the rotor is 5 em, and its cross-sectional area also may be assumed to be 12 cm2. Each air gap between the rotor and the stator is 0.05 cm wide, and the cross-sectional area of each air gap (including fringing) is 14 cm2. The iron of the core has a relative permeability of 2000, and there are 200 turns of wire on the core. If the current in the
wire is adjusted to be 1A, what will the resulting flux density in the air gaps be?
In this video, delve into the magnetic circuit with an air gap, understand the components of the rotor and stator in a DC motor, and explore the analysis of Example 1.3 (Ch) in the context of EM 1.4(5)(E). Gain insights into the efficiency and operation of DC motors through magnetic circuit analysis. Watch now to enhance your understanding of this essential topic!
Hashtags:
#MagneticCircuit #AirGap #Rotor #Stator #DCMotor #Example1.3 #Ch #EM1.4(5)(E) #Analysis #Engineering
SEO Tags:
Magnetic Circuit with Air Gap, Rotor and Stator, DC Motor Components, Example 1.3, Ch, EM 1.4(5)(E), Magnetic Circuit Analysis, DC Motor Efficiency, Engineering, Rotor Stator Analysis, DC Motor Operation, EM Concepts
Комментарии
 0:09:41
0:09:41
 0:18:24
0:18:24
 0:09:33
0:09:33
 0:23:51
0:23:51
 0:05:46
0:05:46
 0:11:26
0:11:26
 0:09:23
0:09:23
 0:52:46
0:52:46
 0:12:23
0:12:23
 0:14:34
0:14:34
 0:10:24
0:10:24
 0:10:03
0:10:03
 0:14:40
0:14:40
 0:03:42
0:03:42
 0:11:13
0:11:13
 0:14:43
0:14:43
 0:08:30
0:08:30
 0:02:09
0:02:09
 0:08:56
0:08:56
 0:47:34
0:47:34
 0:16:47
0:16:47
 0:14:28
0:14:28
 0:09:41
0:09:41
 1:11:23
1:11:23