filmov
tv
AQA A Level Biology: DNA and RNA

Показать описание
A-Level Biology especially for AQA can be tough but fortunately we’ve made this tutorial to help you score the A* you need for questions on DNA and RNA. ✅
📒The three main aims of this tutorial are to cover: 📒
1. Structure and Function of DNA & RNA
2. Structure and Function of Ribosomes
3. Structure of Nucleotides and Nitrogenous Bases
Function of DNA and RNA (1:53)
DNA is responsible for storing genetic information. RNA is responsible for passing genetic information from DNA to ribosomes.
Structure and Function of Ribosomes (2:38)
Ribosomes “read” information carried by mRNA to make proteins. Ribosomes are made up of ribosomal RNA. Ribosomes are also made up of proteins.
Structure of Nucleotides (3:46)
DNA and RNA are polymers made up of nucleotides. Every nucleotide is made up of 3 components.
Nitrogenous Bases (4:10)
Nitrogenous bases are organic, nitrogen containing chemical groups.
Polynucleotide Structure (6:10)
Nucleotides are bonded to each other through condensation reactions. Phosphodiester bonds form between nucleotides. Phosphodiester bonds create a chain of nucleotides called a polynucleotide chain. Phosphodiester bonds can be broken through hydrolysis reactions.
Structure of DNA (7:18)
DNA is made up of two complementary polynucleotide chains. Hydrogen bonds hold the polynucleotide chains together. There are no other base pairing combinations in DNA. A DNA double helix is formed.
Structure of RNA (8:19)
Like DNA, RNA is also made up of a polynucleotide chain.
It is made up of RNA specific nucleotides and like DNA, RNA nucleotides form a single polynucleotide chain held together by phosphodiester bonds.
Why does DNA replicate?
Cell division occurs continuously. DNA replication occurs before the cell divides. DNA replication mean that parents can pass their DNA to their offspring.
The Process of DNA Replication
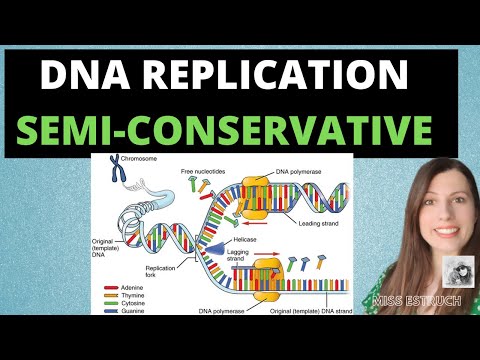
1) Double Helix Unwinding, the first step of DNA replication is unwinding of the DNA double helix. Hydrogen bonds are broken during unwinding. An enzyme called DNA helicase is involved. It is important to understand that the entire DNA does not unwind simultaneously. The unwound region of the DNA is called a “replication fork”.
2) Semi-Conservative Replication DNA replication is semiconservative. The unwound strands of DNA are referred to as the parental strands.
3) DNA Polymerase. Condensation reactions occur to complete DNA replication. DNA polymerase is the key enzyme.
Mechanism of DNA Polymerase
DNA has two ends, a single strand of DNA has two different ends. In a DNA double helix, the two strands are antiparallel. DNA polymerase catalyses addition of free nucleotides. DNA polymerase starts at the 3’ end. DNA polymerase reads the nucleotide sequence. DNA ligase catalyses condensation reactions.
Meselson and Stahl’s Experiment (10:24)
A group of bacteria were cultured in light nitrogen. Another group of bacteria were cultured in heavy nitrogen. Light and heavy nitrogen bacteria DNA settles at different levels. Heavy nitrogen bacteria were added to the light culture. DNA settled at a mid point. DNA replication is therefore semi-conservative. Further tests were done.
To catch our latest videos, subscribe and leave a comment below on a video you’d like us to record!
👇 Subscribe to Study Mind with ONE CLICK👇
👇Revise with free past papers BY TOPIC for AQA A-Level Biology👇
👇Get personalised 1-1 Tutoring at £30ph for GUARANTEED improvement👇
Tags: #AQABiology #ALevelBiology #StudyMind #DNA #RNA
📒The three main aims of this tutorial are to cover: 📒
1. Structure and Function of DNA & RNA
2. Structure and Function of Ribosomes
3. Structure of Nucleotides and Nitrogenous Bases
Function of DNA and RNA (1:53)
DNA is responsible for storing genetic information. RNA is responsible for passing genetic information from DNA to ribosomes.
Structure and Function of Ribosomes (2:38)
Ribosomes “read” information carried by mRNA to make proteins. Ribosomes are made up of ribosomal RNA. Ribosomes are also made up of proteins.
Structure of Nucleotides (3:46)
DNA and RNA are polymers made up of nucleotides. Every nucleotide is made up of 3 components.
Nitrogenous Bases (4:10)
Nitrogenous bases are organic, nitrogen containing chemical groups.
Polynucleotide Structure (6:10)
Nucleotides are bonded to each other through condensation reactions. Phosphodiester bonds form between nucleotides. Phosphodiester bonds create a chain of nucleotides called a polynucleotide chain. Phosphodiester bonds can be broken through hydrolysis reactions.
Structure of DNA (7:18)
DNA is made up of two complementary polynucleotide chains. Hydrogen bonds hold the polynucleotide chains together. There are no other base pairing combinations in DNA. A DNA double helix is formed.
Structure of RNA (8:19)
Like DNA, RNA is also made up of a polynucleotide chain.
It is made up of RNA specific nucleotides and like DNA, RNA nucleotides form a single polynucleotide chain held together by phosphodiester bonds.
Why does DNA replicate?
Cell division occurs continuously. DNA replication occurs before the cell divides. DNA replication mean that parents can pass their DNA to their offspring.
The Process of DNA Replication
1) Double Helix Unwinding, the first step of DNA replication is unwinding of the DNA double helix. Hydrogen bonds are broken during unwinding. An enzyme called DNA helicase is involved. It is important to understand that the entire DNA does not unwind simultaneously. The unwound region of the DNA is called a “replication fork”.
2) Semi-Conservative Replication DNA replication is semiconservative. The unwound strands of DNA are referred to as the parental strands.
3) DNA Polymerase. Condensation reactions occur to complete DNA replication. DNA polymerase is the key enzyme.
Mechanism of DNA Polymerase
DNA has two ends, a single strand of DNA has two different ends. In a DNA double helix, the two strands are antiparallel. DNA polymerase catalyses addition of free nucleotides. DNA polymerase starts at the 3’ end. DNA polymerase reads the nucleotide sequence. DNA ligase catalyses condensation reactions.
Meselson and Stahl’s Experiment (10:24)
A group of bacteria were cultured in light nitrogen. Another group of bacteria were cultured in heavy nitrogen. Light and heavy nitrogen bacteria DNA settles at different levels. Heavy nitrogen bacteria were added to the light culture. DNA settled at a mid point. DNA replication is therefore semi-conservative. Further tests were done.
To catch our latest videos, subscribe and leave a comment below on a video you’d like us to record!
👇 Subscribe to Study Mind with ONE CLICK👇
👇Revise with free past papers BY TOPIC for AQA A-Level Biology👇
👇Get personalised 1-1 Tutoring at £30ph for GUARANTEED improvement👇
Tags: #AQABiology #ALevelBiology #StudyMind #DNA #RNA
Комментарии
 0:07:50
0:07:50
 0:18:23
0:18:23
 0:39:43
0:39:43
 0:32:59
0:32:59
 0:15:53
0:15:53
 0:10:33
0:10:33
 0:14:32
0:14:32
 0:13:43
0:13:43
 0:07:13
0:07:13
 0:07:48
0:07:48
 0:18:58
0:18:58
 0:07:38
0:07:38
 0:13:14
0:13:14
 0:29:42
0:29:42
 0:08:33
0:08:33
 0:05:26
0:05:26
 0:17:52
0:17:52
 0:06:33
0:06:33
 0:08:19
0:08:19
 0:08:58
0:08:58
 0:10:27
0:10:27
 0:09:11
0:09:11
 0:11:51
0:11:51
 0:06:30
0:06:30