filmov
tv
Write a numerical expression to represent a verbal description of a calculation

Показать описание
Write a numerical expression to represent a verbal description of a calculation
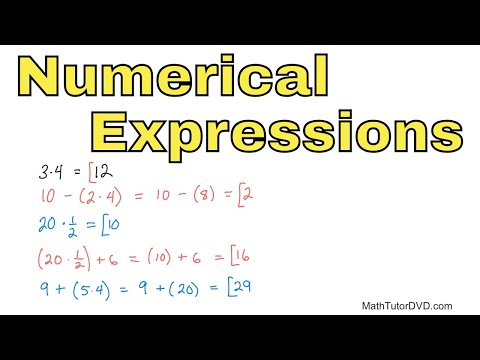
In this lesson, you will learn how to translate a verbal description of a calculation by writing it as a numerical expression.
ADDITIONAL MATERIALS
STANDARDS
VA.CE.4.4.d create and solve single-step and multistep practical problems involving addition, subtraction, and multiplication, and single-step practical problems involving division with whole numbers.
VA.CE.5.5.b create and solve single-step and multistep practical problems involving addition, subtraction, and multiplication of decimals, and create and solve single-step practical problems involving division of decimals.
VA.CE.3.3.b create and solve single-step and multistep practical problems involving sums or differences of two whole numbers, each 9,999 or less.
VA.CE.5.4 The student will create and solve single-step and multistep practical problems involving addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of whole numbers.
CCSS.5.OA.A.2 Write simple expressions that record calculations with numbers, and interpret numerical expressions without evaluating them. For example, express the calculation “add 8 and 7, then multiply by 2” as 2 × (8 + 7). Recognize that 3 × (18932 + 921) is three times as large as 18932 + 921, without having to calculate the indicated sum or product.
FL.MAFS.5.OA.1.2 Write simple expressions that record calculations with numbers, and interpret numerical expressions without evaluating them. For example, express the calculation “add 8 and 7, then multiply by 2” as 2 × (8 + 7). Recognize that 3 × (18932 + 921) is three times as large as 18932 + 921, without having to calculate the indicated sum or product.
IN.5.AT.8 Define and use up to two variables to write linear expressions that arise from real-world problems, and evaluate them for given values.
TEKS.3.5.C describe a multiplication expression as a comparison such as 3 x 24 represents 3 times as much as 24;
TEKS.3.5.A represent one- and two-step problems involving addition and subtraction of whole numbers to 1,000 using pictorial models, number lines, and equations;
In this lesson, you will learn how to translate a verbal description of a calculation by writing it as a numerical expression.
ADDITIONAL MATERIALS
STANDARDS
VA.CE.4.4.d create and solve single-step and multistep practical problems involving addition, subtraction, and multiplication, and single-step practical problems involving division with whole numbers.
VA.CE.5.5.b create and solve single-step and multistep practical problems involving addition, subtraction, and multiplication of decimals, and create and solve single-step practical problems involving division of decimals.
VA.CE.3.3.b create and solve single-step and multistep practical problems involving sums or differences of two whole numbers, each 9,999 or less.
VA.CE.5.4 The student will create and solve single-step and multistep practical problems involving addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of whole numbers.
CCSS.5.OA.A.2 Write simple expressions that record calculations with numbers, and interpret numerical expressions without evaluating them. For example, express the calculation “add 8 and 7, then multiply by 2” as 2 × (8 + 7). Recognize that 3 × (18932 + 921) is three times as large as 18932 + 921, without having to calculate the indicated sum or product.
FL.MAFS.5.OA.1.2 Write simple expressions that record calculations with numbers, and interpret numerical expressions without evaluating them. For example, express the calculation “add 8 and 7, then multiply by 2” as 2 × (8 + 7). Recognize that 3 × (18932 + 921) is three times as large as 18932 + 921, without having to calculate the indicated sum or product.
IN.5.AT.8 Define and use up to two variables to write linear expressions that arise from real-world problems, and evaluate them for given values.
TEKS.3.5.C describe a multiplication expression as a comparison such as 3 x 24 represents 3 times as much as 24;
TEKS.3.5.A represent one- and two-step problems involving addition and subtraction of whole numbers to 1,000 using pictorial models, number lines, and equations;
 0:05:12
0:05:12
 0:08:35
0:08:35
 0:05:44
0:05:44
 0:02:58
0:02:58
 0:01:03
0:01:03
 0:01:13
0:01:13
 0:06:36
0:06:36
 0:01:49
0:01:49
 0:00:58
0:00:58
 0:02:04
0:02:04
 0:03:44
0:03:44
 0:03:29
0:03:29
 0:11:32
0:11:32
 0:02:43
0:02:43
 0:05:43
0:05:43
 0:01:22
0:01:22
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:05:06
0:05:06
 0:10:25
0:10:25
 0:05:03
0:05:03
 0:03:00
0:03:00
 0:14:57
0:14:57
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:05:26
0:05:26