filmov
tv
Orthogonality of functions and vectors: key to Fourier analysis!

Показать описание
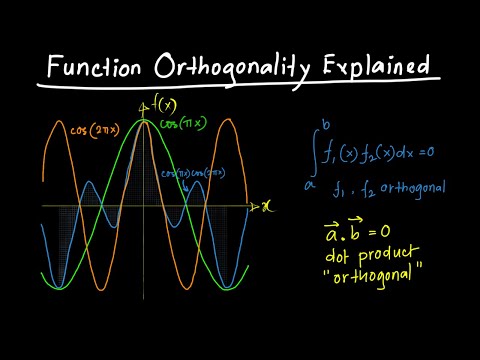
Discrete case: element by element multiplication of 2 vectors, and summing the result, gives zero for vectors which are orthogonal to each other
Continuous case: multiplying 2 continuous functions, then integratiing, gives zero for functions which are orthogonal to each other
Continuous case: multiplying 2 continuous functions, then integratiing, gives zero for functions which are orthogonal to each other
Orthogonality and Orthonormality
Function Orthogonality Explained
11.1: Orthogonal Functions
Introduction to orthonormal bases | Linear Algebra | Khan Academy
Orthogonality of functions and vectors: key to Fourier analysis!
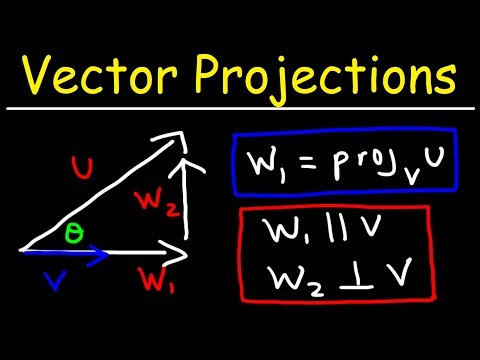
Calculus 3 - Vector Projections & Orthogonal Components
What Are Orthogonal Polynomials? Inner Products on the Space of Functions
Orthogonal & orthonormal Vectors
What are the Orthogonal and Orthonormal Vectors ?
Orthogonality
Advanced Linear Algebra, Lecture 5.2: Orthogonality
Orthogonal bases are easy to work with!
Orthogonal and Orthonormal Sets of Vectors
The beautiful geometric view of FOURIER SERIES // The Linear Algebra Perspective
Abstract vector spaces | Chapter 16, Essence of linear algebra
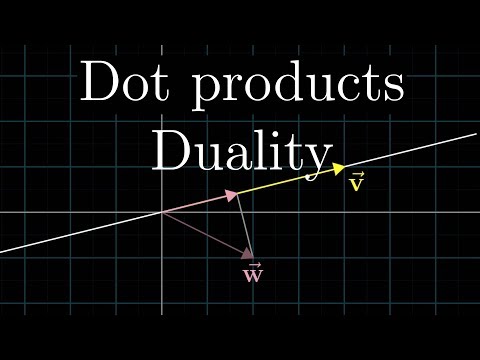
Dot products and duality | Chapter 9, Essence of linear algebra
Linear Algebra 6.1.2 Orthogonal Vectors
Orthogonal Basis Functions in the Fourier Transform
The Gram-Schmidt Process
Orthogonality and Orthonormality of Wavefunctions | Physical Significance | Quantum Mechanics
Inner Product and Orthogonal Functions , Quick Example
Vector Projections | Vector Calculus #17
ORTHOGONAL Vectors | Orthonormal Basis - Concept & Properties of Inner Product | Liner Algebra
What are Orthogonal and Orthonormal functions?
Комментарии
 0:11:48
0:11:48
 0:11:13
0:11:13
 0:30:00
0:30:00
 0:11:16
0:11:16
 0:20:10
0:20:10
 0:12:14
0:12:14
 0:10:52
0:10:52
 0:05:34
0:05:34
 0:04:45
0:04:45
 0:12:11
0:12:11
 0:48:14
0:48:14
 0:04:50
0:04:50
 0:06:52
0:06:52
 0:16:03
0:16:03
 0:16:46
0:16:46
 0:14:12
0:14:12
 0:07:17
0:07:17
 0:08:54
0:08:54
 0:10:07
0:10:07
 0:02:50
0:02:50
 0:03:29
0:03:29
 0:05:17
0:05:17
 0:10:44
0:10:44
 0:02:26
0:02:26