filmov
tv
6. Prove that |z1+z2|^2+|z1-z2|^2=2(|z1|^2+|z2|^2) for complex numbers z1 and z2

Показать описание
Mathematics foundation
6. Prove that |z1+z2|^2+|z1-z2|^2=2(|z1|^2+|z2|^2) for complex numbers z1 and z2
Complex playlist of chapter 1 mathematical methods
6. Prove that |z1+z2|^2+|z1-z2|^2=2(|z1|^2+|z2|^2) for complex numbers z1 and z2
Complex playlist of chapter 1 mathematical methods
6. Prove that |z1+z2|^2+|z1-z2|^2=2(|z1|^2+|z2|^2) for complex numbers z1 and z2
Prove |z1+z2|^2+|z1-z2|^2=2(|z1|^2+|z2|^2) for any Complex no | Properties of Complex Numbers
Prove that |z_1+z_2 |^2= |z_1 |^2+|z_2 |^2+2Re(z_1 z_2^* ) Complex Numbers Modulus Properties
Prove that |Z1+Z2|≤ |Z1|+|Z2| and |Z1+Z2|≥ ||Z1|-|Z2|| for Complex Numbers
2. Find the greatest and least values of |Z1+Z2| or Prove that |z1+z2|≤|z1|+|z2| | AdnanAlig
Properties of Conjugate Complex Numbers | Complex no | Conjugate Complex Numbers | Trignometry
How to prove : |Z1-Z2|^2 + |Z1+Z2|^2 = 2(|Z1|^2 + |Z2|^2)
|z1z2| = |z1||z2|
Prove |z1+z2+z3|^2+|-z1+z2+z3|^2+|z1-z2+z3|^2+|z1+z2-z3|^2=4[|z1|^2+|z2|^2+|z3|^2].
If z_1 and z_2 be any two complex numbers such that |z_1+z_2 |=|z_1 |+|z_2 |, then arg〖 z〗_1-arg
5.Find the greatest and least values of |Z1+Z2| or Prove that ||z1|-|z2||≤|z1+z2|≤|z1|+|z2|
Lecture no.6 prove that zˉz=x^2+y^2, Z1+Z2=z+ˉz
How to prove that (z1+z2)/(z1-z2) is purely imaginary when |z1|=|z2| using geometrical means
conjugate(z1 z2) = conjugate(z1) conjugate(z2)
Prove that the modulus of sum and difference of two complex numbers is always, less than or equal...
Q11- If Z1, Z2, Z3 represent the vertices of an equilateral triangle, Z1^2+Z2^2+Z3^2=Z1Z2+Z2Z3+Z3Z1
Solving Equations With Complex Numbers
If 2z1/3z2 is a purely imaginary number, then find the value of | ( z1 - z2 )/( z1 + z2 ) 11th Maths
2. For any two complex numbers z1 and z2, prove the Re(z1.z2)= Re z1 Rez2- Im z1 Imz2
Z1=2 +2i, z2= -3-2i then mod (z1+z2) (GTU SUMMER 2017 advance mathematics ) Q1(3)
Complex Analysis | Unit 2 | Lecture 13 | Example of Cauchy's Integral Formula
VSAQ Video 4 || If z1=(2,-1) , z2=(6,3) find z1-z2
If z_1, z_2 and z_3 are the vertices of an isosceles triangle right angled at the vertices z_2 , ...
`arg(z_1/z_2)=arg(z_1)-arg(z_2)`
Комментарии
 0:11:05
0:11:05
 0:04:04
0:04:04
 0:11:43
0:11:43
 0:11:00
0:11:00
 0:05:12
0:05:12
 0:13:51
0:13:51
 0:05:42
0:05:42
 0:04:25
0:04:25
![Prove |z1+z2+z3|^2+|-z1+z2+z3|^2+|z1-z2+z3|^2+|z1+z2-z3|^2=4[|z1|^2+|z2|^2+|z3|^2].](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/ActGGodJFwI/hqdefault.jpg) 0:09:51
0:09:51
 0:01:10
0:01:10
 0:23:14
0:23:14
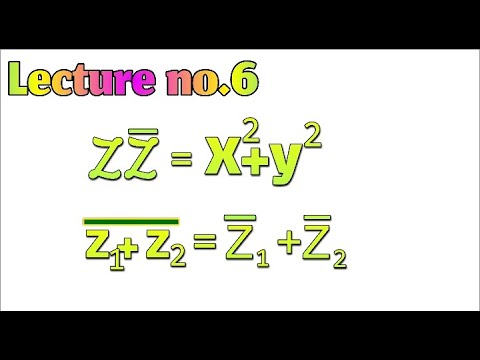 0:02:25
0:02:25
 0:11:32
0:11:32
 0:04:17
0:04:17
 0:18:32
0:18:32
 0:07:44
0:07:44
 0:02:07
0:02:07
 0:03:23
0:03:23
 0:02:18
0:02:18
 0:00:51
0:00:51
 0:09:05
0:09:05
 0:02:07
0:02:07
 0:09:37
0:09:37
 0:04:34
0:04:34