filmov
tv
First Aid in case of Heart Attack

Показать описание
Promptly attending to an individual experiencing a heart attack at workplace is crucial to preventing additional damage. Dr. Parneesh Arora, Director, Interventional Cardiology, Max Hospital, Patparganj, talks about the mandatory do’s and don’ts before the patient is given medical treatment.
Follow Max Healthcare on social media to get latest updates:
Follow Max Healthcare on social media to get latest updates:
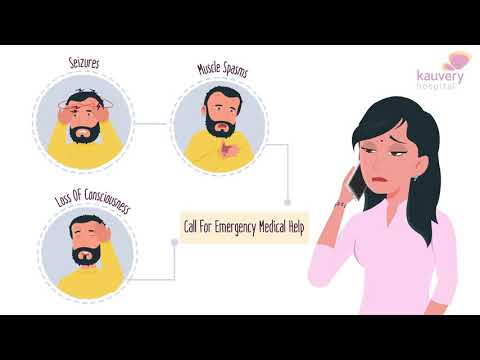
Apollo Hospitals | First Aid in Seizure | What to do in case of seizure ?
How to Treat Cuts and Grazes - First Aid Training - St John Ambulance
#FirstAidSeries | First Aid in case of Electric Shock
#FirstAidSeries | First Aid in case of Nosebleed
How to use first-aid in case of fractures | Medanta
The Recovery Position - First Aid Training - St John Ambulance
How to do the Primary Survey - First Aid Training - St John Ambulance
Learn first aid gestures: React in case of a house fire
Why Your Heart Attack Isn’t Shocking #shorts #heartattack
FIRST AID IN CASE OF UNCONSCIOUSNESS
Children First Aid: Choking Child part 1 | First Aid | British Red Cross
First aid. What to do in case of extremity fracture in a wind turbine
How to use first-aid in case of heart attacks | Medanta
Medical Emergencies in First Aid
Save the boy - first aid advert by St John Ambulance
What To Do If Someone Has A Seizure - First Aid Training - St John Ambulance
#FirstAidSeries | First Aid in case of Choking
What first aid steps must you take in the case of a snake or spider bite? | Apollo Hospitals
Service Training - First Aid
How to Use your First Aid Kit & Contents - First Aid Training - St John Ambulance
Learn first aid gestures: How to react in case of loss of consciousness
#FirstAidSeries | First Aid In case of Electric Shock - Tamil Version
First aid in case of cut wound - How to use sticking plaster DIY
Children First Aid: Choking Baby | First Aid | British Red Cross
Комментарии
 0:03:12
0:03:12
 0:01:29
0:01:29
 0:01:09
0:01:09
 0:00:55
0:00:55
 0:01:07
0:01:07
 0:02:32
0:02:32
 0:04:03
0:04:03
 0:02:16
0:02:16
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:02:52
0:02:52
 0:00:23
0:00:23
 0:02:15
0:02:15
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:38:38
0:38:38
 0:01:02
0:01:02
 0:02:36
0:02:36
 0:01:22
0:01:22
 0:01:11
0:01:11
 0:29:06
0:29:06
 0:02:05
0:02:05
 0:02:14
0:02:14
 0:01:14
0:01:14
 0:02:09
0:02:09
 0:00:37
0:00:37