filmov
tv
STRATIGRAPHY EXPLAINED

Показать описание
Stratigraphy is a fundamental concept in geology, often likened to reading the Earth's history in the layers of rock. Picture the Earth's crust as a historical record, with each layer of rock acting as a separate chapter or time period in this geological story.
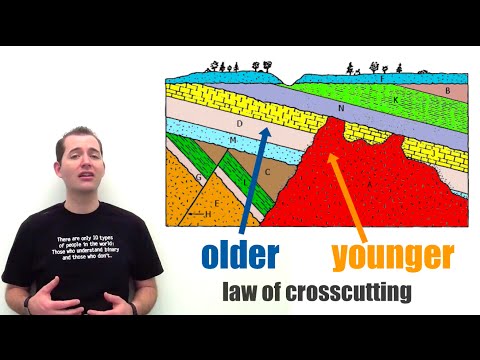
The basic idea behind stratigraphy is that rock layers are not randomly arranged but are organized in a specific order. This order, known as the Law of Superposition, states that in an undisturbed sequence of rocks, the youngest rocks are at the top, while the oldest rocks are at the bottom. This principle helps geologists establish a timeline of events that have shaped the Earth over millions of years.
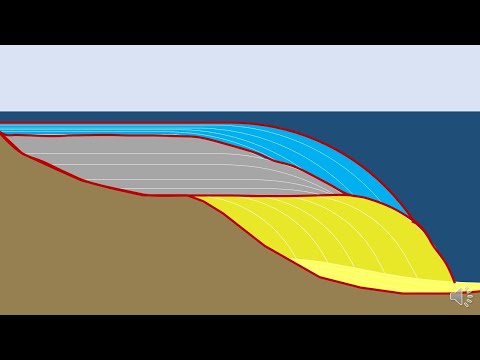
These layers, or strata, can vary in thickness, composition, and type. They are formed through various geological processes, such as sediment deposition, volcanic activity, and tectonic movements. As new layers of sediment or volcanic material accumulate over time, they bury older layers, creating a sort of time capsule within the Earth's crust.
By examining these strata, geologists can unlock valuable information about the past. For instance, they can determine when specific events occurred, such as the extinction of certain species or the emergence of new life forms. They can also decipher environmental changes, like when ancient seas dried up or mountains formed.
Moreover, fossils are often found in certain rock layers. These fossils are like the characters in our geological story. They provide insight into the ancient life forms that once inhabited the Earth, offering clues about the evolution of species and the environmental conditions of the time.
In summary, stratigraphy is a crucial tool for geologists to piece together the Earth's history. By studying the arrangement of rock layers, the fossils they contain, and the changes in environmental conditions, scientists can reconstruct a detailed narrative of our planet's past, like reading a captivating history book composed of rock layers.
#Stratigraphy
#GeologicalHistory
#RockLayers
#EarthScience
#FossilRecord
#GeologicalChronicles
#SedimentaryRocks
#GeologicalDating
#HistoricalGeology
#PaleontologicalClues
#RockStrata
#LawOfSuperposition
#GeologicalPuzzle
#TimeInRocks
#EarthHistory
The basic idea behind stratigraphy is that rock layers are not randomly arranged but are organized in a specific order. This order, known as the Law of Superposition, states that in an undisturbed sequence of rocks, the youngest rocks are at the top, while the oldest rocks are at the bottom. This principle helps geologists establish a timeline of events that have shaped the Earth over millions of years.
These layers, or strata, can vary in thickness, composition, and type. They are formed through various geological processes, such as sediment deposition, volcanic activity, and tectonic movements. As new layers of sediment or volcanic material accumulate over time, they bury older layers, creating a sort of time capsule within the Earth's crust.
By examining these strata, geologists can unlock valuable information about the past. For instance, they can determine when specific events occurred, such as the extinction of certain species or the emergence of new life forms. They can also decipher environmental changes, like when ancient seas dried up or mountains formed.
Moreover, fossils are often found in certain rock layers. These fossils are like the characters in our geological story. They provide insight into the ancient life forms that once inhabited the Earth, offering clues about the evolution of species and the environmental conditions of the time.
In summary, stratigraphy is a crucial tool for geologists to piece together the Earth's history. By studying the arrangement of rock layers, the fossils they contain, and the changes in environmental conditions, scientists can reconstruct a detailed narrative of our planet's past, like reading a captivating history book composed of rock layers.
#Stratigraphy
#GeologicalHistory
#RockLayers
#EarthScience
#FossilRecord
#GeologicalChronicles
#SedimentaryRocks
#GeologicalDating
#HistoricalGeology
#PaleontologicalClues
#RockStrata
#LawOfSuperposition
#GeologicalPuzzle
#TimeInRocks
#EarthHistory
 0:01:43
0:01:43
 0:02:15
0:02:15
 0:00:35
0:00:35
 0:06:21
0:06:21
 0:03:38
0:03:38
 0:12:08
0:12:08
 0:00:52
0:00:52
 0:13:00
0:13:00
 0:02:40
0:02:40
 0:00:47
0:00:47
 0:04:11
0:04:11
 0:00:19
0:00:19
 0:10:56
0:10:56
 0:04:18
0:04:18
 0:01:20
0:01:20
 0:00:36
0:00:36
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:00:39
0:00:39
 0:13:12
0:13:12
 0:16:31
0:16:31
 0:31:41
0:31:41
 0:00:06
0:00:06
 0:16:23
0:16:23
 0:11:14
0:11:14