filmov
tv
Physics Problems - 2-D Motion -Position Velocity Acceleration- Calculus-Based Problem Example 3

Показать описание
The position of a dragonfly that is flying parallel to the ground is given as a function of time by r ⃗ =[2.90 m + (0.0900 m/s^2)t^2] i ̂ – (0.0150 m/s^3)t^3 j ̂.
a.) At what value of t does the velocity vector of the dragonfly make an angle of 30.0° clockwise from the +x-axis?
b.) At the time calculated in part (a), what are the magnitude and direction of the dragonfly’s acceleration vector?
The best way to learn how to solve a Physics problem is to understand examples. NO AUDIO.
All problems are solved following the same basic problem-solving techniques: Break down the problem to identify given and unknown variables. Draw a model if needed. Identify relevant equations and concepts. Solve for the unknown variables. Evaluate equations with given variables.
Follow along as I break down the question and then use standard equations to solve the problem. FF, Pause, or Rewind as needed.
There are often multiple ways to get to the same answer, so don’t be concerned if your path is different, as long as the final answer is the same.
#physics #twodimensionalmotion #velocity #acceleration #position #calculus #integration
a.) At what value of t does the velocity vector of the dragonfly make an angle of 30.0° clockwise from the +x-axis?
b.) At the time calculated in part (a), what are the magnitude and direction of the dragonfly’s acceleration vector?
The best way to learn how to solve a Physics problem is to understand examples. NO AUDIO.
All problems are solved following the same basic problem-solving techniques: Break down the problem to identify given and unknown variables. Draw a model if needed. Identify relevant equations and concepts. Solve for the unknown variables. Evaluate equations with given variables.
Follow along as I break down the question and then use standard equations to solve the problem. FF, Pause, or Rewind as needed.
There are often multiple ways to get to the same answer, so don’t be concerned if your path is different, as long as the final answer is the same.
#physics #twodimensionalmotion #velocity #acceleration #position #calculus #integration
 0:12:30
0:12:30
 0:07:06
0:07:06
 0:28:19
0:28:19
 0:10:06
0:10:06
 0:12:27
0:12:27
 0:22:08
0:22:08
 0:08:44
0:08:44
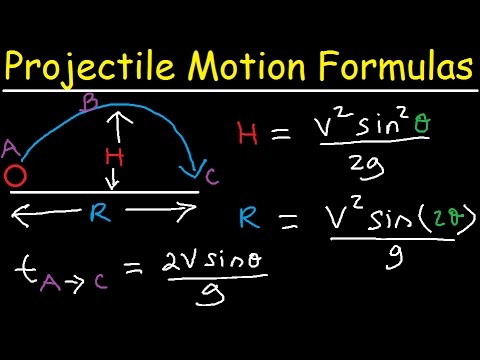 0:28:11
0:28:11
 0:35:32
0:35:32
 0:06:38
0:06:38
 0:07:07
0:07:07
 0:10:25
0:10:25
 0:16:50
0:16:50
 0:12:47
0:12:47
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:11:53
0:11:53
 0:12:38
0:12:38
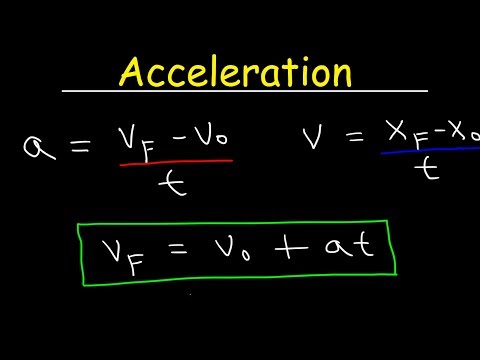 0:18:58
0:18:58
 0:25:19
0:25:19
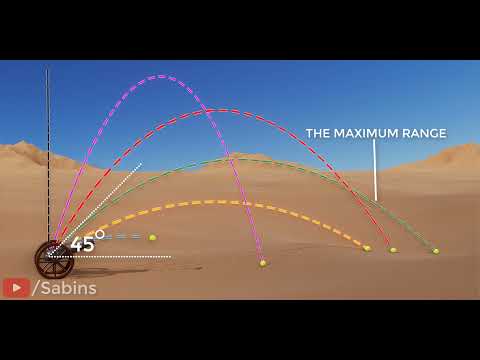 0:05:09
0:05:09
 0:08:02
0:08:02
 1:06:49
1:06:49
 1:20:26
1:20:26
 0:07:42
0:07:42