filmov
tv
Intro to Infinite Series | Real Analysis

Показать описание
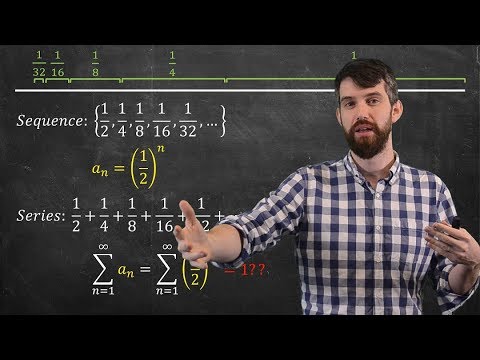
We introduce the definition of infinite series, the definition of a convergent series and the limit of a series, as well as divergent series. We'll discuss partial sums, terms of an infinite series, and look at various examples including geometric series, the harmonic series, and p-series. We'll also discuss Zeno's Paradox about an arrow headed for a target, which seemingly cannot get there! #RealAnalysis
Table of Contents
0:00 Into
1:57 Zeno's Paradox
7:42 Definitions
14:12 Examples
★DONATE★
Thanks to Robert Rennie, Barbara Sharrock, and Rolf Waefler for their generous support on Patreon!
Follow Wrath of Math on...
Table of Contents
0:00 Into
1:57 Zeno's Paradox
7:42 Definitions
14:12 Examples
★DONATE★
Thanks to Robert Rennie, Barbara Sharrock, and Rolf Waefler for their generous support on Patreon!
Follow Wrath of Math on...
Convergence and Divergence - Introduction to Series
Introduction to Infinite Series
Intro to Infinite Series | Real Analysis
Infinite Series - Numberphile
Intro to Series: What is 1/2+1/4+1/8+1/16+...?
Intro to Summation Notation and Infinite Series, Ex 1
Calculus 2 - Geometric Series, P-Series, Ratio Test, Root Test, Alternating Series, Integral Test
Convergence and Divergence: The Return of Sequences and Series
Animate the Definition of Derivative
Arithmetic Sequences and Arithmetic Series - Basic Introduction
A visual infinite sum like you’ve never seen!
Every Student Should See This
Infinite sum of powers of sixths!
Calculus 2 Lecture 9.1: Convergence and Divergence of Sequences
11.2 (part 2) Intro to Infinite Series (Geometric, Test for Divergence, Harmonic, Telescoping)
Calculus II - 9.2.1 Infinite Series
Calculus 2: Infinite Sequences and Series (1 of 86) Overview
Finding The Sum of an Infinite Geometric Series
Infinite Series
Visual Harmonic Series Divergence from Bernoulli!
Calculus 2 Lecture 9.2: Series, Geometric Series, Harmonic Series, and Divergence Test
How to solve ODEs with infinite series | Intro & Easiest Example: y'=y
calculus 2 power series, a detailed introduction (form, radius & interval of convergence)
Sequence & Series | Convergence & Divergence | Introduction | Maths
Комментарии
 0:16:18
0:16:18
 0:08:16
0:08:16
 0:19:40
0:19:40
 0:09:31
0:09:31
 0:05:38
0:05:38
 0:01:38
0:01:38
 0:43:52
0:43:52
 0:09:40
0:09:40
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:44:04
0:44:04
 0:00:57
0:00:57
 0:00:58
0:00:58
 0:00:55
0:00:55
 2:27:29
2:27:29
 0:53:38
0:53:38
 0:08:45
0:08:45
 0:01:21
0:01:21
 0:19:50
0:19:50
 0:14:57
0:14:57
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 2:01:40
2:01:40
 0:11:01
0:11:01
 0:29:00
0:29:00
 0:21:22
0:21:22