filmov
tv
Java RMI implementation | Java | RMI

Показать описание
RMI (Remote Method Invocation)
Remote Method Invocation (RMI)
Understanding stub and skeleton
stub
skeleton
Requirements for the distributed applications
Steps to write the RMI program
RMI Example
The RMI (Remote Method Invocation) is an API that provides a mechanism to create distributed application in java. The RMI allows an object to invoke methods on an object running in another JVM.
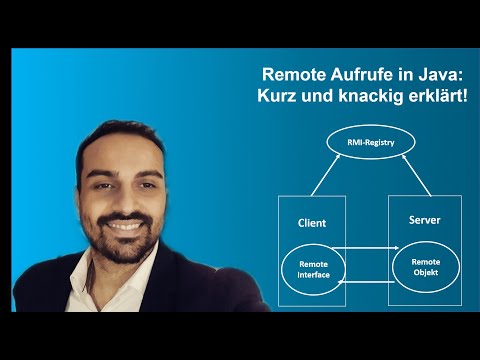
The RMI provides remote communication between the applications using two objects stub and skeleton.
Understanding stub and skeleton
RMI uses stub and skeleton object for communication with the remote object.
A remote object is an object whose method can be invoked from another JVM. Let's understand the stub and skeleton objects:
stub
The stub is an object, acts as a gateway for the client side. All the outgoing requests are routed through it. It resides at the client side and represents the remote object. When the caller invokes method on the stub object, it does the following tasks:
It initiates a connection with remote Virtual Machine (JVM),
It writes and transmits (marshals) the parameters to the remote Virtual Machine (JVM),
It waits for the result
It reads (unmarshals) the return value or exception, and
It finally, returns the value to the caller.
skeleton
The skeleton is an object, acts as a gateway for the server side object. All the incoming requests are routed through it. When the skeleton receives the incoming request, it does the following tasks:
It reads the parameter for the remote method
It invokes the method on the actual remote object, and
It writes and transmits (marshals) the result to the caller.
In the Java 2 SDK, an stub protocol was introduced that eliminates the need for skeletons. stub and skeleton in RMI
Understanding requirements for the distributed applications
If any application performs these tasks, it can be distributed application.
.
The application need to locate the remote method
It need to provide the communication with the remote objects, and
The application need to load the class definitions for the objects.
The RMI application have all these features, so it is called the distributed application.
Java RMI Example
The is given the 6 steps to write the RMI program.
Create the remote interface
Provide the implementation of the remote interface
Compile the implementation class and create the stub and skeleton objects using the rmic tool
Start the registry service by rmiregistry tool
Create and start the remote application
Create and start the client application
RMI Example
In this example, we have followed all the 6 steps to create and run the rmi application. The client application need only two files, remote interface and client application. In the rmi application, both client and server interacts with the remote interface. The client application invokes methods on the proxy object, RMI sends the request to the remote JVM. The return value is sent back to the proxy object and then to the client application.
Комментарии
 0:25:53
0:25:53
 0:12:06
0:12:06
 0:13:19
0:13:19
 0:07:05
0:07:05
 0:14:46
0:14:46
 1:27:03
1:27:03
 0:05:54
0:05:54
 0:13:59
0:13:59
 0:04:31
0:04:31
 0:02:06
0:02:06
 0:05:15
0:05:15
 1:10:57
1:10:57
 0:05:46
0:05:46
 0:16:05
0:16:05
 0:49:00
0:49:00
 0:21:00
0:21:00
 0:08:45
0:08:45
 0:03:26
0:03:26
 0:04:10
0:04:10
 0:03:02
0:03:02
 0:03:09
0:03:09
 0:08:11
0:08:11
 0:01:15
0:01:15
 0:12:16
0:12:16