filmov
tv
Newton's Third Law of Motion: Action and Reaction

Показать описание
Are you tired of Newton's laws of motion yet? Well, lucky you, this is the last one. And it's the most misunderstood as well! People love making inappropriate metaphors with scientific principles, unfortunately. Watch this to make sure you don't do the same!
Check out "Is This Wi-Fi Organic?", my book on disarming pseudoscience!
Check out "Is This Wi-Fi Organic?", my book on disarming pseudoscience!
Newton's 3 Laws, with a bicycle - Joshua Manley
Newton's Third Law of Motion: Action and Reaction
Newton’s Third Law of Motion Demonstrated in Space
Newton's third law of motion | Videos for kids | #amusum #kids #education #science #learn
Action and Reaction: Newton’s Third Law (updated)
Newton's Third Law of Motion - Action and Reaction Forces
Newton's Third Law of Motion | Newton's Laws of Motion | Video for Kids
Best Film on Newton's Third Law. Ever.
'Mastering Problem Solving in Gravitation: Key to Success in JEE & NEET | Class XI CBSE Phy...
Newton's Third Law | Forces & Motion | Physics | FuseSchool
Newton's Third Law of Motion | Forces and Motion | Physics | Infinity Learn
GCSE Physics - Newton’s Third Law #57
Newton's third law - Best Demonstration EVER !! - by Prof. Walter Lewin
Newton's Third Law of Motion | Newton's Law | Video for Kids
Newton's 3rd Law of Motion
Newton's 3rd Law - Why does a swimmer push the water backward? | #aumsum #kids #science
Newton's 3rd Law Explained with Skateboard, Rocket
Balloon Rocket! Newton's Third Law of Motion.
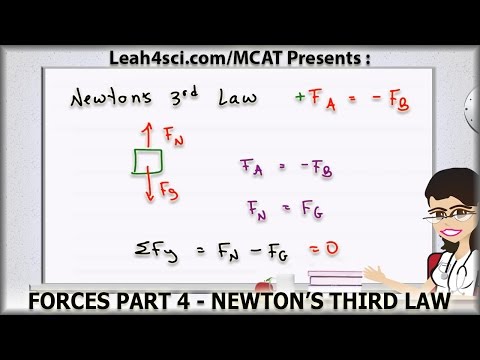
Newtons Third Law of Motion FA= -FB MCAT Physics Forces
How Wings Work and Create Lift - Newton's 3rd Law of Motion
Newton's Third Law of Motion
Science of Golf: Newton's Third Law of Motion
Newton's Third Law
Newton's Third Law of Motion - A Level Physics
Комментарии
 0:03:33
0:03:33
 0:04:55
0:04:55
 0:03:08
0:03:08
 0:04:39
0:04:39
 0:02:15
0:02:15
 0:11:08
0:11:08
 0:04:26
0:04:26
 0:04:38
0:04:38
 1:23:05
1:23:05
 0:04:48
0:04:48
 0:04:09
0:04:09
 0:02:36
0:02:36
 0:00:52
0:00:52
 0:03:02
0:03:02
 0:01:31
0:01:31
 0:01:40
0:01:40
 0:04:04
0:04:04
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:07:40
0:07:40
 0:02:43
0:02:43
 0:02:29
0:02:29
 0:04:19
0:04:19
 0:06:01
0:06:01
 0:04:33
0:04:33