filmov
tv
What Is Benzene | Organic Chemistry | Chemistry | FuseSchool

Показать описание
What Is Benzene | Organic Chemistry | Chemistry | FuseSchool
Learn the basics about the properties and chemistry of benzene, as a part of organic chemistry.
Benzene is an organic molecule.
Benzene is a colourless liquid at room temperature. Its boiling point is 80 degrees C. It’s found naturally in crude oil and in fact smells a little like petrol or gasoline
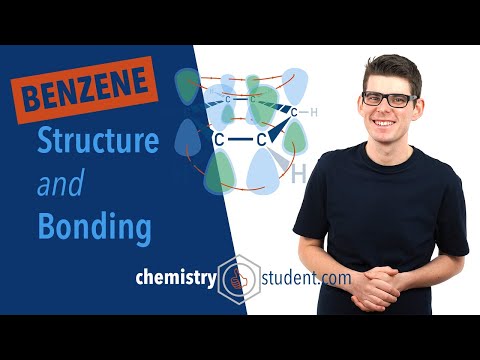
On an atomic level, benzene is made up of 6 carbon atoms covalently bonded in a ring. Each carbon is also covalently bonded to one hydrogen.
Carbon usually forms 4 single covalent bonds and these carbons at the moment only have 3. The molecule now does something very special. The one unpaired electron from each carbon becomes CONJUGATED into the ring. This means they have free movement around all 6 carbons and this gives benzene the property of AROMATICITY.
Aromaticity refers to conjugation in ring-shaped molecules.
Benzene on its own is not a very useful molecule. In fact it can be dangerous, as it’s carcinogenic, that is known to cause cancer in sufficient doses.
Some of the most important and useful drugs are made this way by joining benzene rings to other organic molecules.. For example, here’s Aspirin, one of the most famous painkillers in the world. Here is the more complicated Sitagliptin, which treats diabetes.
It’s almost impossible to do an ADDITION reaction on benzene. Addition destroys the aromaticity of the ring, a process which needs a LOT of energy. So you’ll almost never see this happen.
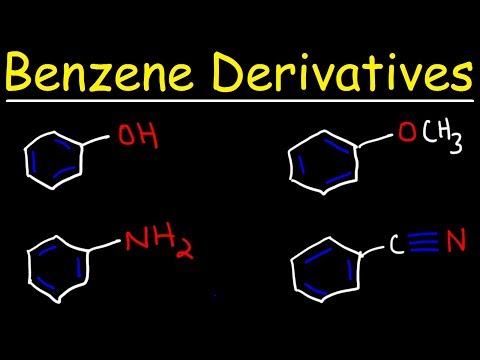
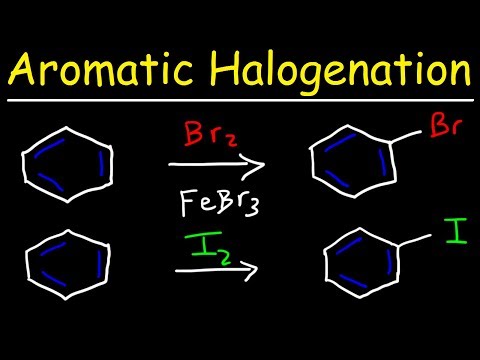
What does often happen is substitution reactions, where one of the protons is kicked out of the compound by another species, which takes its place and the molecule keeps its aromaticity. This can happen more than once and the benzene is said to be mono, di or tri-substituted. In this way, many interesting molecules can be created.
SUBSCRIBE to the FuseSchool YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid.
Learn the basics about the properties and chemistry of benzene, as a part of organic chemistry.
Benzene is an organic molecule.
Benzene is a colourless liquid at room temperature. Its boiling point is 80 degrees C. It’s found naturally in crude oil and in fact smells a little like petrol or gasoline
On an atomic level, benzene is made up of 6 carbon atoms covalently bonded in a ring. Each carbon is also covalently bonded to one hydrogen.
Carbon usually forms 4 single covalent bonds and these carbons at the moment only have 3. The molecule now does something very special. The one unpaired electron from each carbon becomes CONJUGATED into the ring. This means they have free movement around all 6 carbons and this gives benzene the property of AROMATICITY.
Aromaticity refers to conjugation in ring-shaped molecules.
Benzene on its own is not a very useful molecule. In fact it can be dangerous, as it’s carcinogenic, that is known to cause cancer in sufficient doses.
Some of the most important and useful drugs are made this way by joining benzene rings to other organic molecules.. For example, here’s Aspirin, one of the most famous painkillers in the world. Here is the more complicated Sitagliptin, which treats diabetes.
It’s almost impossible to do an ADDITION reaction on benzene. Addition destroys the aromaticity of the ring, a process which needs a LOT of energy. So you’ll almost never see this happen.
What does often happen is substitution reactions, where one of the protons is kicked out of the compound by another species, which takes its place and the molecule keeps its aromaticity. This can happen more than once and the benzene is said to be mono, di or tri-substituted. In this way, many interesting molecules can be created.
SUBSCRIBE to the FuseSchool YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid.
Комментарии
 0:03:50
0:03:50
 0:21:46
0:21:46
 0:03:19
0:03:19
 0:00:07
0:00:07
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:02:38
0:02:38
 0:17:12
0:17:12
 0:09:50
0:09:50
 0:00:11
0:00:11
 0:12:33
0:12:33
 0:10:00
0:10:00
 0:00:44
0:00:44
 0:06:08
0:06:08
 0:00:11
0:00:11
 0:00:58
0:00:58
 0:08:40
0:08:40
 0:00:05
0:00:05
 0:00:31
0:00:31
 0:12:00
0:12:00
 0:10:43
0:10:43
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:00:11
0:00:11
 0:00:52
0:00:52
 0:09:43
0:09:43