filmov
tv
What Is Char Data Type | Char Type Data Type | C Programming Tutorial | Frustrated Londa

Показать описание
Data Types in C
Each variable in C has an associated data type. Each data type requires different amounts of memory and has some specific operations which can be performed over it. Let us briefly describe them one by one:
Following are the examples of some very common data types used in C:
char: The most basic data type in C. It stores a single character and requires a single byte of memory in almost all compilers.
int: As the name suggests, an int variable is used to store an integer.
float: It is used to store decimal numbers (numbers with floating point value) with single precision.
double: It is used to store decimal numbers (numbers with floating point value) with double precision.
Different data types also have different ranges upto which they can store numbers. These ranges may vary from compiler to compiler. Below is list of ranges along with the memory requirement and format specifiers on 32 bit gcc compiler.
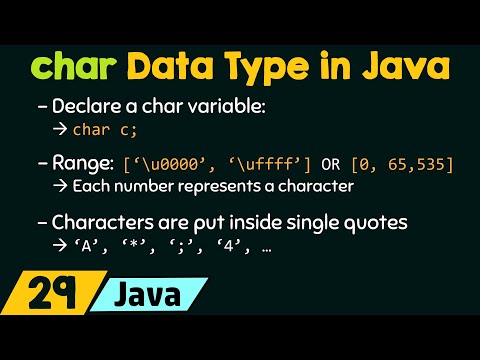
C uses char type to store characters and letters. However, the char type is integer type because underneath C stores integer numbers instead of characters.In C, char values are stored in 1 byte in memory,and value range from -128 to 127 or 0 to 255.
In order to represent characters, the computer has to map each integer with a corresponding character using a numerical code. The most common numerical code is ASCII, which stands for American Standard Code for Information Interchange.
Use the Char data type when you need to hold only a single character and do not need the overhead of String. In some cases you can use Char(), an array of Char elements, to hold multiple characters.
The default value of Char is the character with a code point of 0.
Each variable in C has an associated data type. Each data type requires different amounts of memory and has some specific operations which can be performed over it. Let us briefly describe them one by one:
Following are the examples of some very common data types used in C:
char: The most basic data type in C. It stores a single character and requires a single byte of memory in almost all compilers.
int: As the name suggests, an int variable is used to store an integer.
float: It is used to store decimal numbers (numbers with floating point value) with single precision.
double: It is used to store decimal numbers (numbers with floating point value) with double precision.
Different data types also have different ranges upto which they can store numbers. These ranges may vary from compiler to compiler. Below is list of ranges along with the memory requirement and format specifiers on 32 bit gcc compiler.
C uses char type to store characters and letters. However, the char type is integer type because underneath C stores integer numbers instead of characters.In C, char values are stored in 1 byte in memory,and value range from -128 to 127 or 0 to 255.
In order to represent characters, the computer has to map each integer with a corresponding character using a numerical code. The most common numerical code is ASCII, which stands for American Standard Code for Information Interchange.
Use the Char data type when you need to hold only a single character and do not need the overhead of String. In some cases you can use Char(), an array of Char elements, to hold multiple characters.
The default value of Char is the character with a code point of 0.
 0:06:55
0:06:55
 0:03:41
0:03:41
 0:00:13
0:00:13
 0:08:42
0:08:42
 0:07:29
0:07:29
 0:06:43
0:06:43
 0:18:58
0:18:58
 0:12:38
0:12:38
 0:27:30
0:27:30
 0:12:25
0:12:25
 0:11:53
0:11:53
 0:03:53
0:03:53
 0:08:23
0:08:23
 0:11:08
0:11:08
 0:06:50
0:06:50
 0:04:15
0:04:15
 0:01:33
0:01:33
 0:02:43
0:02:43
 0:11:43
0:11:43
 0:04:47
0:04:47
 0:03:34
0:03:34
 0:00:21
0:00:21
 0:00:11
0:00:11
 0:20:13
0:20:13