filmov
tv
Measurement of potential difference class 10 | voltmeter class 10 | how to connect voltmeter

Показать описание
Measurement of potential difference and EMF 10th physics chapter 14 | Voltmeter 10th physics | urdu hindi
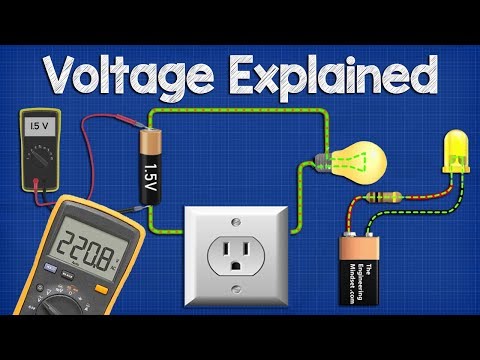
The Measurement of Potential Difference
The potential difference across a circuit component (e.g. light
bulb) can be measured by a voltmeter (Fig. 14.7) connected
directly across the terminals of the component. The positive
terminal of the battery is connected to the positive terminal of
the voltmeter and the negative terminal of the battery is
connected to the negative terminal of the voltmeter.
An ideal voltmeter should have very large value of resistance
so that no current passes through it. Voltmeter is always
connected in parallel with the device across which the
potential difference is to be measured .(Fig. 14.8)
Fig.14.7: A voltmeter
CURRENT ELECTRICITY
Not For Sale – PESRP
Charge
The Measurement of e.m.f
In general, e.m.f refers to the potential difference across the
terminals of the battery when it is not driving current in the
external circuit. So in order to measure e.m.f of the battery
we connect voltmeter directly
SUMMARY
The time rate of flow of electric charge through any cross section is called electric
current.
The current due to flow of positive charge which is equivalent to current due to flow
of negative charge in opposite direction is known as conventional current.
Ampere is the SI unit of current.
e.m.f. is the total amount of energy supplied by the battery or the cell in moving a
one coulomb of positive charge from the -ve to the +ve terminal of the battery.
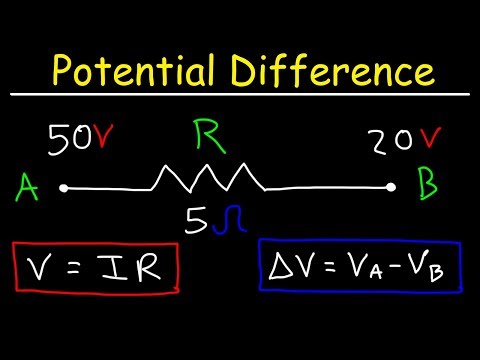
Ohm's law states that the current I passing through a conductor is directly
proportional to the potential difference V applied across its ends provided the
temperature and physical state of the conductor do not change.
Resistance R is a measure of opposition to the flow of current through a conductor.
Its SI unit is ohm. It is denoted by the symbol Ω. When a potential difference of one
volt is applied across the ends of a conductor and one ampere of current passes
through it, then its resistance will be one ohm.
Materials in which electrons can freely move so as to pass electricity are called
conductors while in insulators no free electrons are available for the conduction of
electricity.
The equivalent resistance R of a series combination of ‘n’ resistances is given by e
The equivalent resistance R of a parallel combination of ‘n’ resistances is given by e
Galvanometer is a sensitive instrument which detects current in a circuit. It is always
connected in series with the circuit.
Ammeter is an electrical instrument which measures larger current. It is always
connected in series in a circuit.
Voltmeter is an electrical instrument used to measure potential difference betw
The amount of heat energy generated in a resistance due to flow of electric current
is equal to the product of the square of current, resistance and the time interval ( W
2
= I Rt). This is called Joule's law.
kilowatt-hour is the amount of energy obtained from a source of one kilowatt in one
hour. It is equal to 3.6 mega joule.
The current which does not change its direction of flow is known as direct current or
d.c.
The current which changes its direc
Related searches
1. Measurement of potential difference
2. Measurement of emf
3. Measurement of potential difference in urdu
4. Measurement of emf in urdu
5. Measurement of potential difference sabaq
6. Measurement of emf in hindi
7. Measurement of potential difference haythem
8. Measurement of emf haythem
9. Measurement of potential difference khan
10. Measurement of emf khan
11. Measurement of potential difference academy
12. Measurement of emf academy
13. Measurement of potential difference foundation
14. Measurement of emf foundation
15. Measurement of potential difference ilm
16. Measurement of potential difference 10th physics
17. Measurement of emf 10th physics
18. Measurement of potential difference 10 physics
19. Measurement of emf 10 physics
20. Measurement of potential difference 10th class physics
21. Measurement of emf 10th class physics
22. Voltmeter 10th physics
23. Voltmeter 10th class physics
24. Voltmeter 10 class physics
25. Voltmeter physics class 10
26. Voltmeter sabaq
27. Voltmeter ilm
28. Voltmeter foundation
29. Voltmeter khan
30. Voltmeter haythem
31. Ammeter in urdu
#voltmeter
#10thphysics
#measurementofpotentialdifferenceand
The Measurement of Potential Difference
The potential difference across a circuit component (e.g. light
bulb) can be measured by a voltmeter (Fig. 14.7) connected
directly across the terminals of the component. The positive
terminal of the battery is connected to the positive terminal of
the voltmeter and the negative terminal of the battery is
connected to the negative terminal of the voltmeter.
An ideal voltmeter should have very large value of resistance
so that no current passes through it. Voltmeter is always
connected in parallel with the device across which the
potential difference is to be measured .(Fig. 14.8)
Fig.14.7: A voltmeter
CURRENT ELECTRICITY
Not For Sale – PESRP
Charge
The Measurement of e.m.f
In general, e.m.f refers to the potential difference across the
terminals of the battery when it is not driving current in the
external circuit. So in order to measure e.m.f of the battery
we connect voltmeter directly
SUMMARY
The time rate of flow of electric charge through any cross section is called electric
current.
The current due to flow of positive charge which is equivalent to current due to flow
of negative charge in opposite direction is known as conventional current.
Ampere is the SI unit of current.
e.m.f. is the total amount of energy supplied by the battery or the cell in moving a
one coulomb of positive charge from the -ve to the +ve terminal of the battery.
Ohm's law states that the current I passing through a conductor is directly
proportional to the potential difference V applied across its ends provided the
temperature and physical state of the conductor do not change.
Resistance R is a measure of opposition to the flow of current through a conductor.
Its SI unit is ohm. It is denoted by the symbol Ω. When a potential difference of one
volt is applied across the ends of a conductor and one ampere of current passes
through it, then its resistance will be one ohm.
Materials in which electrons can freely move so as to pass electricity are called
conductors while in insulators no free electrons are available for the conduction of
electricity.
The equivalent resistance R of a series combination of ‘n’ resistances is given by e
The equivalent resistance R of a parallel combination of ‘n’ resistances is given by e
Galvanometer is a sensitive instrument which detects current in a circuit. It is always
connected in series with the circuit.
Ammeter is an electrical instrument which measures larger current. It is always
connected in series in a circuit.
Voltmeter is an electrical instrument used to measure potential difference betw
The amount of heat energy generated in a resistance due to flow of electric current
is equal to the product of the square of current, resistance and the time interval ( W
2
= I Rt). This is called Joule's law.
kilowatt-hour is the amount of energy obtained from a source of one kilowatt in one
hour. It is equal to 3.6 mega joule.
The current which does not change its direction of flow is known as direct current or
d.c.
The current which changes its direc
Related searches
1. Measurement of potential difference
2. Measurement of emf
3. Measurement of potential difference in urdu
4. Measurement of emf in urdu
5. Measurement of potential difference sabaq
6. Measurement of emf in hindi
7. Measurement of potential difference haythem
8. Measurement of emf haythem
9. Measurement of potential difference khan
10. Measurement of emf khan
11. Measurement of potential difference academy
12. Measurement of emf academy
13. Measurement of potential difference foundation
14. Measurement of emf foundation
15. Measurement of potential difference ilm
16. Measurement of potential difference 10th physics
17. Measurement of emf 10th physics
18. Measurement of potential difference 10 physics
19. Measurement of emf 10 physics
20. Measurement of potential difference 10th class physics
21. Measurement of emf 10th class physics
22. Voltmeter 10th physics
23. Voltmeter 10th class physics
24. Voltmeter 10 class physics
25. Voltmeter physics class 10
26. Voltmeter sabaq
27. Voltmeter ilm
28. Voltmeter foundation
29. Voltmeter khan
30. Voltmeter haythem
31. Ammeter in urdu
#voltmeter
#10thphysics
#measurementofpotentialdifferenceand
Комментарии
 0:14:44
0:14:44
 0:04:06
0:04:06
 0:03:18
0:03:18
 0:14:48
0:14:48
 0:08:55
0:08:55
 0:10:52
0:10:52
 0:03:22
0:03:22
 0:11:42
0:11:42
 1:44:34
1:44:34
 0:01:59
0:01:59
 0:08:00
0:08:00
 0:05:54
0:05:54
 0:06:26
0:06:26
 0:08:06
0:08:06
 0:15:33
0:15:33
 0:08:00
0:08:00
 0:06:59
0:06:59
 0:02:37
0:02:37
 0:00:55
0:00:55
 0:05:01
0:05:01
 0:11:30
0:11:30
 0:23:16
0:23:16
 0:17:56
0:17:56
 0:01:08
0:01:08