filmov
tv
GED Math - Polygons

Показать описание
Our mobile app, which has been used by over 50,000 people to help them study, offers thousands of practice GED questions with detailed feedback for every question. Free to install.
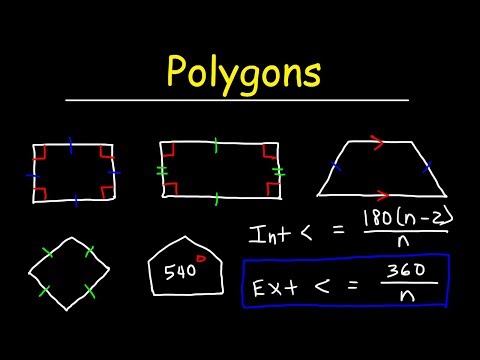
This GED math video goes over polygons. Things we need to know include that triangles add up to 180 degrees, we find the perimeter of a triangle by adding up the three sides, and the area of a triangle is found by the formula A = 1/2(base)(height). You also need to be familiar with pythagorean theorem. We go over examples in the video.
Interior Angles
The three interior angles in a triangle add up to 180 degrees. For example, if we know that the first two angles are 40 and 60, which total 100, then we know that the third angle must be 80 degrees. 180 − 100= 80.
Perimeter
The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the three sides. If the sides of a triangle are 4, 6, and 10 feet, then the perimeter is 20 feet.
Pythagorean Theorem
Pythagorean Theorem states that in a right triangle, a^2 + b^2 = c^2. The hypotenuse is c^2 while a^2 and b^2 are generally just referred to as the legs of the triangle. Here’s a practice question:
The legs of a triangle measure are 5 and 8. What is the hypotenuse?
5^2 + 8^2 = c^2
25 + 64 = c^2
89 = c^2
c = square root of 89, or approximately 9.4
Right, Isosceles, and Equilateral Triangles
An equilateral has three equal sides, an isosceles has two equal sides, and a right triangle has two acute angles.
Area of a Triangle
If the base is 10 and the height is 5, what is the area of this triangle?
A = 1/2bh
A= ½(10)(5)
A= 25
#ged #GedMath #polygons
This GED math video goes over polygons. Things we need to know include that triangles add up to 180 degrees, we find the perimeter of a triangle by adding up the three sides, and the area of a triangle is found by the formula A = 1/2(base)(height). You also need to be familiar with pythagorean theorem. We go over examples in the video.
Interior Angles
The three interior angles in a triangle add up to 180 degrees. For example, if we know that the first two angles are 40 and 60, which total 100, then we know that the third angle must be 80 degrees. 180 − 100= 80.
Perimeter
The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the three sides. If the sides of a triangle are 4, 6, and 10 feet, then the perimeter is 20 feet.
Pythagorean Theorem
Pythagorean Theorem states that in a right triangle, a^2 + b^2 = c^2. The hypotenuse is c^2 while a^2 and b^2 are generally just referred to as the legs of the triangle. Here’s a practice question:
The legs of a triangle measure are 5 and 8. What is the hypotenuse?
5^2 + 8^2 = c^2
25 + 64 = c^2
89 = c^2
c = square root of 89, or approximately 9.4
Right, Isosceles, and Equilateral Triangles
An equilateral has three equal sides, an isosceles has two equal sides, and a right triangle has two acute angles.
Area of a Triangle
If the base is 10 and the height is 5, what is the area of this triangle?
A = 1/2bh
A= ½(10)(5)
A= 25
#ged #GedMath #polygons
 0:07:51
0:07:51
 0:22:39
0:22:39
 0:06:56
0:06:56
 0:09:55
0:09:55
 0:11:20
0:11:20
 0:09:52
0:09:52
 0:00:33
0:00:33
 0:08:35
0:08:35
 0:09:58
0:09:58
 0:10:53
0:10:53
 0:08:20
0:08:20
 0:06:59
0:06:59
 0:36:47
0:36:47
 0:03:12
0:03:12
 0:06:05
0:06:05
 0:00:28
0:00:28
 0:24:02
0:24:02
 0:00:44
0:00:44
 0:04:06
0:04:06
 0:00:40
0:00:40
 0:08:18
0:08:18
 0:08:21
0:08:21
 0:04:13
0:04:13
 0:00:20
0:00:20