filmov
tv
reciprocal translocation

Показать описание
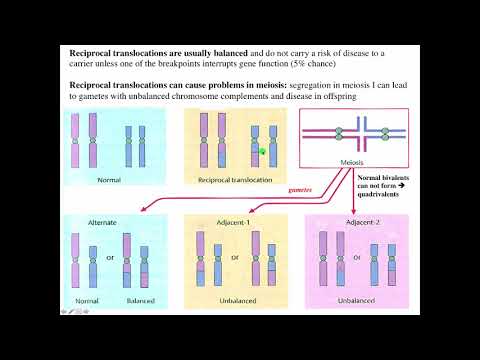
A translocation in which 2 different chromosomes have exchanged segments with each other. Translocation is a genetic abnormality in which part of a chromosome moves to another chromosome.
(Types of translocations: number of breaks involved)
• simple translocation: 1 break
• reciprocal translocation: 2 breaks (main type)
• shift type translocation: 3 breaks
• complex translocation: 4 or more breaks
• reciprocal translocation: Exchange of segments from two nonhomologous chromosomes.
• nonreciprocal translocation: One-way translocations in which a chromosomal segment is transferred to a nonhomologous chromosome.
• Robertsonian translocation: An entire chromosome attaches to another at the centromere. E.g. translocation Down syndrome.
• balanced translocation: With no genetic information extra or missing, and ideally full functionality. There is no phenotypic effect.
• unbalanced translocation: With extra (duplicated) and/or missing (deleted) genes. Likely to cause significant health and/or developmental problems.
(Types of translocations: number of breaks involved)
• simple translocation: 1 break
• reciprocal translocation: 2 breaks (main type)
• shift type translocation: 3 breaks
• complex translocation: 4 or more breaks
• reciprocal translocation: Exchange of segments from two nonhomologous chromosomes.
• nonreciprocal translocation: One-way translocations in which a chromosomal segment is transferred to a nonhomologous chromosome.
• Robertsonian translocation: An entire chromosome attaches to another at the centromere. E.g. translocation Down syndrome.
• balanced translocation: With no genetic information extra or missing, and ideally full functionality. There is no phenotypic effect.
• unbalanced translocation: With extra (duplicated) and/or missing (deleted) genes. Likely to cause significant health and/or developmental problems.
 0:06:13
0:06:13
 0:01:50
0:01:50
 0:07:00
0:07:00
 0:17:33
0:17:33
 0:00:51
0:00:51
 0:08:42
0:08:42
 0:59:07
0:59:07
 0:08:26
0:08:26
 0:00:46
0:00:46
 0:17:20
0:17:20
 0:22:28
0:22:28
 0:03:27
0:03:27
 0:00:41
0:00:41
 0:02:20
0:02:20
 0:00:57
0:00:57
 0:08:30
0:08:30
 0:58:53
0:58:53
 0:00:20
0:00:20
 0:12:49
0:12:49
 0:07:26
0:07:26
 0:02:35
0:02:35
 0:13:12
0:13:12
 0:08:49
0:08:49
 0:13:34
0:13:34