filmov
tv
Mitosis | Stages of Mitosis | Cell cycle | Lecture 3

Показать описание
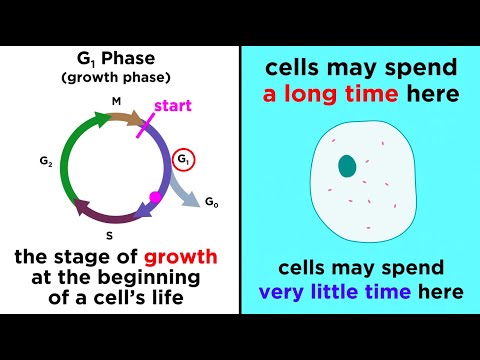
Mitosis Nuclear division follows interphase.
This may be referred to as the M phase (M for mitosis). Growth stops temporarily during mitosis. After the M phase, when the nucleus has divided into two, the whole cell divides to create two genetically identical cells.
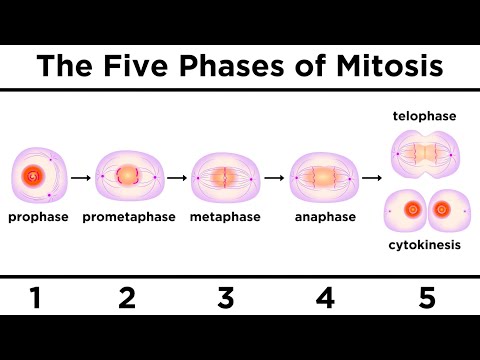
Mitosis is divided into the following four stages:
• Prophase
• Metaphase
• Anaphase
• Telophase
1. Prophase
Chromosomal material condenses to form compact mitotic chromosomes. Chromosomes are seen to be composed of two chromatids attached together at the centromere. Initiation of the assembly of mitotic spindle, the microtubules, the proteinaceous components of the cell cytoplasm help in the process. Cells at the end of prophase, when viewed under the microscope, do not show golgi complexes, endoplasmic reticulum, nucleolus and the nuclear envelope. ER is manufactured by the nuclear membrane. During cell division the nuclear membrane disappears (or stretches beyond visibility), and the ER membrane is generally not visible, but the ribosomes are still there in their free form. I imagine when 2 new cells are formed, ER membrane once again arises from the nuclear membrane and "collects" free ribosomes to re-form new ER. I seem to recall that another membranous organelle, the Golgi apparatus, also "disappears"; however, the double-membraned mitochondria will remain in the cell(s) throughout the various stages of mitosis, most likely to provide the energy required for cell division.
Metaphase
The key features of metaphase are: Spindle fibers attach to kinetochores of chromosomes. Chromosomes are moved to spindle equator and get aligned along metaphase plate through spindle fibers to both poles.
Anaphase
The following key events: Centromeres split and chromatids separate. Chromatids move to opposite poles.
Telophase
This is the stage which shows the following key events: Chromosomes cluster at opposite spindle poles and their identity is lost as discrete elements. Nuclear envelope assembles around the chromosome clusters. Nucleolus, golgi complex and ER reform. Cytokinesis Mitosis accomplishes not only the segregation of duplicated chromosomes into daughter nuclei (karyokinesis), but the cell itself is divided into two daughter cells by a separate process called cytokinesis at the end of which cell division is complete.
#PhasesOfMitosis #CellCycle&Mitosis #MitosisCellDivision
This may be referred to as the M phase (M for mitosis). Growth stops temporarily during mitosis. After the M phase, when the nucleus has divided into two, the whole cell divides to create two genetically identical cells.
Mitosis is divided into the following four stages:
• Prophase
• Metaphase
• Anaphase
• Telophase
1. Prophase
Chromosomal material condenses to form compact mitotic chromosomes. Chromosomes are seen to be composed of two chromatids attached together at the centromere. Initiation of the assembly of mitotic spindle, the microtubules, the proteinaceous components of the cell cytoplasm help in the process. Cells at the end of prophase, when viewed under the microscope, do not show golgi complexes, endoplasmic reticulum, nucleolus and the nuclear envelope. ER is manufactured by the nuclear membrane. During cell division the nuclear membrane disappears (or stretches beyond visibility), and the ER membrane is generally not visible, but the ribosomes are still there in their free form. I imagine when 2 new cells are formed, ER membrane once again arises from the nuclear membrane and "collects" free ribosomes to re-form new ER. I seem to recall that another membranous organelle, the Golgi apparatus, also "disappears"; however, the double-membraned mitochondria will remain in the cell(s) throughout the various stages of mitosis, most likely to provide the energy required for cell division.
Metaphase
The key features of metaphase are: Spindle fibers attach to kinetochores of chromosomes. Chromosomes are moved to spindle equator and get aligned along metaphase plate through spindle fibers to both poles.
Anaphase
The following key events: Centromeres split and chromatids separate. Chromatids move to opposite poles.
Telophase
This is the stage which shows the following key events: Chromosomes cluster at opposite spindle poles and their identity is lost as discrete elements. Nuclear envelope assembles around the chromosome clusters. Nucleolus, golgi complex and ER reform. Cytokinesis Mitosis accomplishes not only the segregation of duplicated chromosomes into daughter nuclei (karyokinesis), but the cell itself is divided into two daughter cells by a separate process called cytokinesis at the end of which cell division is complete.
#PhasesOfMitosis #CellCycle&Mitosis #MitosisCellDivision
Комментарии
 0:03:04
0:03:04
 0:08:27
0:08:27
 0:06:21
0:06:21
 0:47:16
0:47:16
 0:09:53
0:09:53
 0:06:29
0:06:29
 0:01:22
0:01:22
 0:00:22
0:00:22
 0:50:55
0:50:55
 0:09:20
0:09:20
 0:05:43
0:05:43
 0:12:12
0:12:12
 0:10:42
0:10:42
 0:05:19
0:05:19
 0:01:34
0:01:34
 0:12:40
0:12:40
 0:11:34
0:11:34
 0:15:19
0:15:19
 0:00:55
0:00:55
 0:00:56
0:00:56
 0:02:53
0:02:53
 0:55:31
0:55:31
 0:05:01
0:05:01
 0:05:57
0:05:57