filmov
tv
PHYS 146 Fluid Dynamics, part 1: Fluid Flow

Показать описание
Video lecture for PHYS 146 at the University of Alberta. For the iBook on the course go to:
or for a hard copy:
Flow is a defining characteristic of a fluid. This lecture introduces the concept of surface tension and then covers the types of fluid flow using examples both in nature and the lab. To conclude the continuity equation is introduced and used to characterize the flow of incompressible liquid in a pipe.
or for a hard copy:
Flow is a defining characteristic of a fluid. This lecture introduces the concept of surface tension and then covers the types of fluid flow using examples both in nature and the lab. To conclude the continuity equation is introduced and used to characterize the flow of incompressible liquid in a pipe.
PHYS 146 Fluid Dynamics, part 1: Fluid Flow
PHYS 146 Fluid Dynamics, part 2: Bernoulli's Equation
PHYS 146 Fluid Dynamics, part 3: Viscosity
PHYS 146 Fluid Statics, part 1: Pressure and Density
PHYS 146 Fluid Statics, part 4: Buoyancy
PHYS 146 Fluid Statics, part 3: Pressure Gauges
PHYS 146 Fluid Statics part 2: Static Pressure
Physics Fluid Dynamics 1 of 25 Viscosity & Fluid Flow Introduction
Fluid Mechanics Hyrdraulics: Open Channel Flow Equations for Various Shapes
Fluid mechanics 146
Fluid Dynamics (1/5)
Physics 34 Fluid Dynamics (10 of 24) Viscosity & Fluid Flow: Different Types of Flow
PHYS 146 Elasticity part 1: Stress and Strain
PHYS 146 Elasticity part 3: Moduli of Elasticity
PHYS 146 Elasticity part 4: Elastic Limits
PHYS 146 Elasticity part 2: Young's Modulus
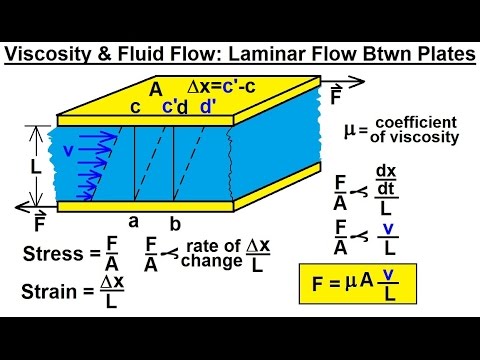
Physics 34 Fluid Dynamics (13 of 24) Viscosity & Fluid Flow: Laminar Flow Between Plates
1. Fluid Dynamics - Intro
PHYS 146 Waves part 1: Wave Types and Properties
PHYS 146 Oscillations Part 1: Derivation of Simple Harmonic Motion
Fluid Statics: Part 1
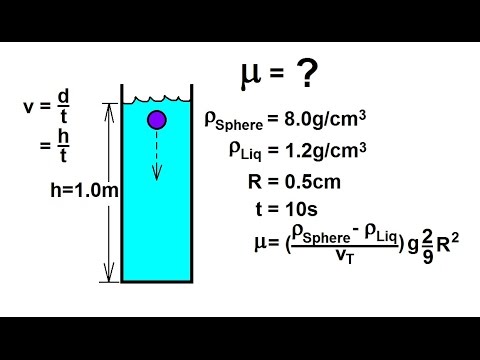
Physics 34 Fluid Dynamics (9 of 24) Viscosity & Fluid Flow: Calculate the Viscosity: Ex 1
Fluid mechanics
Fluid Flow - Part 1
Комментарии
 0:14:57
0:14:57
 0:25:54
0:25:54
 0:16:10
0:16:10
 0:12:33
0:12:33
 0:19:32
0:19:32
 0:18:41
0:18:41
 0:26:15
0:26:15
 0:06:24
0:06:24
 0:00:11
0:00:11
 0:22:01
0:22:01
 0:15:21
0:15:21
 0:03:46
0:03:46
 0:32:22
0:32:22
 0:22:40
0:22:40
 0:20:19
0:20:19
 0:36:45
0:36:45
 0:07:33
0:07:33
 0:02:07
0:02:07
 0:25:28
0:25:28
 0:26:01
0:26:01
 0:23:05
0:23:05
 0:05:38
0:05:38
 0:00:54
0:00:54
 0:14:09
0:14:09