filmov
tv
CMOS Logic Gates Explained | Logic Gate Implementation using CMOS logic

Показать описание
In this video, the CMOS logic gates are explained. By watching this video, you will learn how to implement different logic gates using CMOS logic gate.
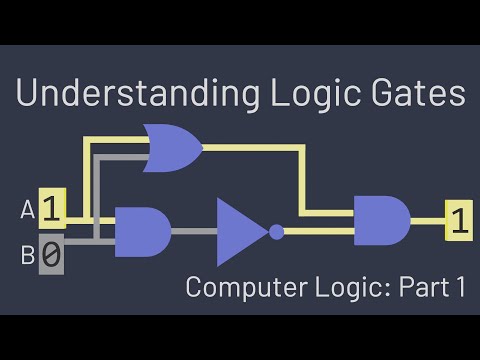
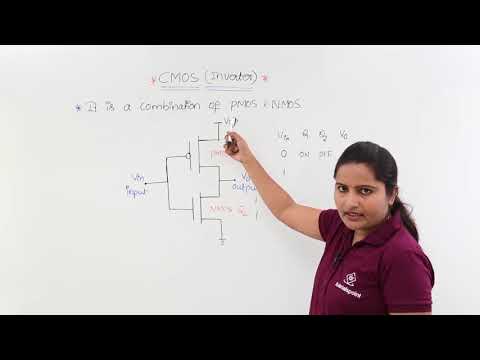
CMOS stands for Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor. The CMOS logic gate consist of complementary pair of NMOS and PMOS transistors. The NMOS transistors are used in the pull-down network and PMOS transistors are used in the pull-up network.
In the video, it is also explained that , why PMOS transistors are used in pull-up network and NMOS transistors are used in pull-down network. And at the later part of the video, the power consumption of the CMOS logic gates is also briefly discussed.
By watching this video, you will learn the following topics:
0:00 Introduction
0:48 What is CMOS ?
3:12 NMOS Inverter and Issue with NMOS transistors
7:05 Why NMOS passes weak logic '1' and strong logic '0'
9:17 Why PMOS passes weak logic '0' and strong logic '1'
11:48 CMOS Inverter (NOT gate using CMOS Logic)
16:04 NAND and NOR gates using CMOS logic
20:35 AND and OR gates using CMOS logic
21:40 XOR and XNOR gates using CMOS logic
25:29 Power Dissipation in CMOS logic gates
For notes on CMOS logic gates, check this article:
For more videos on Digital Electronics, check this playlist:
This video will be helpful to all the students of science and engineering in understanding the CMOS logic gates.
#allaboutelectronics
#digitalelectronics
#logicgates
#cmos
Support the channel through membership program:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Follow my second channel:
Follow me on Facebook:
Follow me on Instagram:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
CMOS stands for Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor. The CMOS logic gate consist of complementary pair of NMOS and PMOS transistors. The NMOS transistors are used in the pull-down network and PMOS transistors are used in the pull-up network.
In the video, it is also explained that , why PMOS transistors are used in pull-up network and NMOS transistors are used in pull-down network. And at the later part of the video, the power consumption of the CMOS logic gates is also briefly discussed.
By watching this video, you will learn the following topics:
0:00 Introduction
0:48 What is CMOS ?
3:12 NMOS Inverter and Issue with NMOS transistors
7:05 Why NMOS passes weak logic '1' and strong logic '0'
9:17 Why PMOS passes weak logic '0' and strong logic '1'
11:48 CMOS Inverter (NOT gate using CMOS Logic)
16:04 NAND and NOR gates using CMOS logic
20:35 AND and OR gates using CMOS logic
21:40 XOR and XNOR gates using CMOS logic
25:29 Power Dissipation in CMOS logic gates
For notes on CMOS logic gates, check this article:
For more videos on Digital Electronics, check this playlist:
This video will be helpful to all the students of science and engineering in understanding the CMOS logic gates.
#allaboutelectronics
#digitalelectronics
#logicgates
#cmos
Support the channel through membership program:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Follow my second channel:
Follow me on Facebook:
Follow me on Instagram:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Комментарии
 0:28:11
0:28:11
 0:07:54
0:07:54
 0:13:01
0:13:01
 0:07:28
0:07:28
 0:03:59
0:03:59
 0:12:07
0:12:07
 0:03:01
0:03:01
 0:07:05
0:07:05
 0:10:49
0:10:49
 0:05:50
0:05:50
 0:04:55
0:04:55
 0:08:02
0:08:02
 0:20:02
0:20:02
 0:19:17
0:19:17
 0:05:47
0:05:47
 0:10:18
0:10:18
 0:12:23
0:12:23
 0:01:56
0:01:56
 0:54:07
0:54:07
 0:13:02
0:13:02
 0:09:02
0:09:02
 0:00:23
0:00:23
 0:08:07
0:08:07
 0:02:56
0:02:56