filmov
tv
Stages of mitosis visualised😍
Показать описание
Stages of mitosis visualised😍
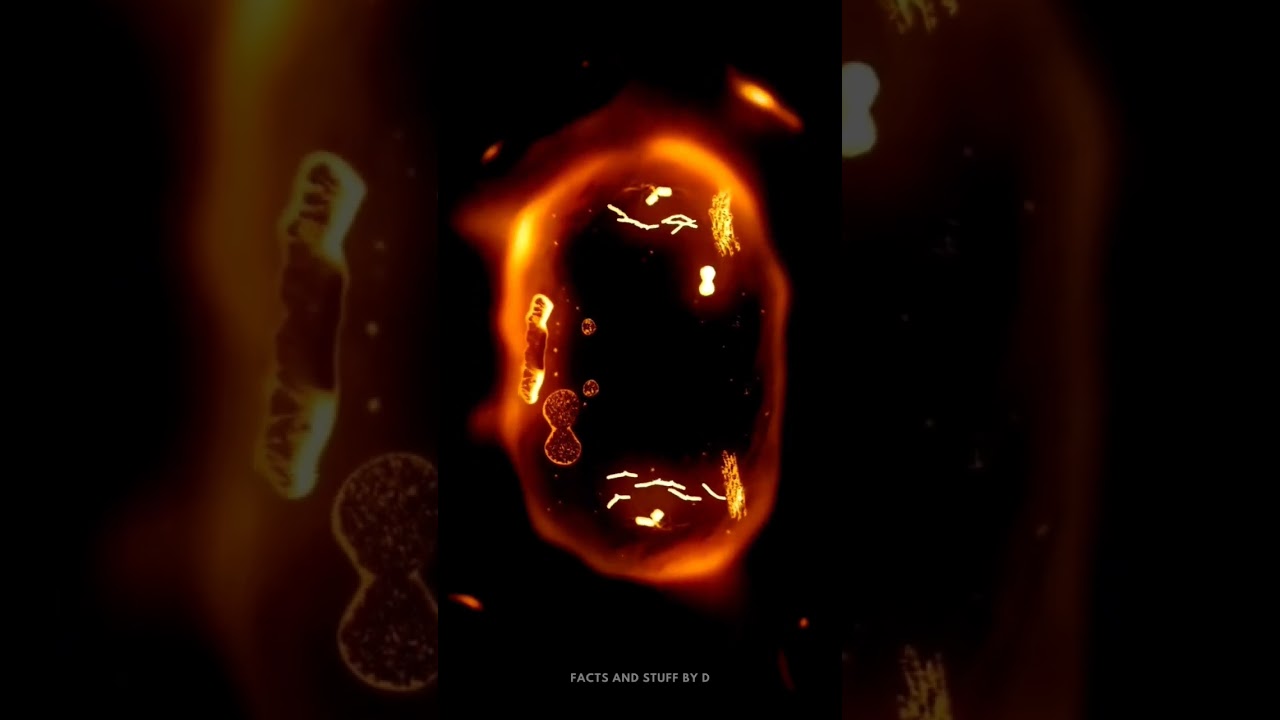
Mitosis is a complex process of cell division that occurs in all eukaryotic organisms, including plants, animals, and fungi. The stages of mitosis are typically divided into four distinct phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
During prophase, the chromatin in the nucleus of the cell begins to condense into distinct chromosomes, which can be seen under a microscope. The nuclear envelope also breaks down, and the centrosomes move to opposite poles of the cell, creating the spindle fibers that will eventually pull the chromosomes apart.
In metaphase, the spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes and align them along the equator of the cell, called the metaphase plate.
In anaphase, the spindle fibers begin to shorten and pull the sister chromatids of each chromosome apart. The chromatids move towards opposite poles of the cell.
Finally, in telophase, the spindle fibers disappear, and the nuclear envelope reforms around each set of separated chromosomes, forming two identical nuclei. The cytoplasm of the cell also begins to divide, in a process called cytokinesis, resulting in two new daughter cells, each with a complete set of chromosomes.
These stages of mitosis are critical for the proper replication and distribution of genetic material in cells, and understanding the process is essential to the study of cell biology and genetics
Credits : @facts_and_stuff_by_d
Mitosis is a complex process of cell division that occurs in all eukaryotic organisms, including plants, animals, and fungi. The stages of mitosis are typically divided into four distinct phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
During prophase, the chromatin in the nucleus of the cell begins to condense into distinct chromosomes, which can be seen under a microscope. The nuclear envelope also breaks down, and the centrosomes move to opposite poles of the cell, creating the spindle fibers that will eventually pull the chromosomes apart.
In metaphase, the spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes and align them along the equator of the cell, called the metaphase plate.
In anaphase, the spindle fibers begin to shorten and pull the sister chromatids of each chromosome apart. The chromatids move towards opposite poles of the cell.
Finally, in telophase, the spindle fibers disappear, and the nuclear envelope reforms around each set of separated chromosomes, forming two identical nuclei. The cytoplasm of the cell also begins to divide, in a process called cytokinesis, resulting in two new daughter cells, each with a complete set of chromosomes.
These stages of mitosis are critical for the proper replication and distribution of genetic material in cells, and understanding the process is essential to the study of cell biology and genetics
Credits : @facts_and_stuff_by_d
 0:00:18
0:00:18
 0:00:22
0:00:22
 0:03:04
0:03:04
 0:00:31
0:00:31
 0:08:27
0:08:27
 0:00:23
0:00:23
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:01:34
0:01:34
 0:00:32
0:00:32
 0:01:29
0:01:29
 0:06:29
0:06:29
 0:05:01
0:05:01
 0:01:50
0:01:50
 0:06:22
0:06:22
 0:02:02
0:02:02
 0:00:26
0:00:26
 0:05:19
0:05:19
 0:00:23
0:00:23
 0:22:00
0:22:00
 0:15:19
0:15:19
 0:01:08
0:01:08
 0:09:20
0:09:20
 0:08:54
0:08:54
 0:01:04
0:01:04