filmov
tv
Relay Explained: The Most Important Electronics Component

Показать описание
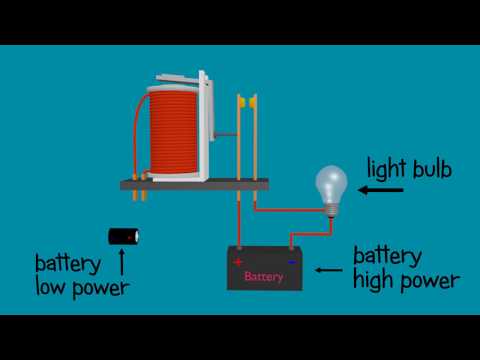
A relay is an electrically operated switch that allows a low-power electrical signal to control a higher-power circuit. It's commonly used in various electrical systems to manage large electrical loads with minimal control power.
How a Relay Works:
1. Electromagnetism: Inside the relay, there’s an electromagnet, which is a coil of wire that produces a magnetic field when a current passes through it.
2. Control Circuit: The small control circuit powers the electromagnet, and when the control signal is sent (usually low voltage or current), it activates the electromagnet.
3. Switching Mechanism: The magnetic field pulls a metal contact (or armature) to open or close a larger circuit, allowing or stopping the flow of current through it.
4. Output Circuit: The contacts in the output circuit are connected to the higher-power load. Depending on the relay type, the output circuit can be normally open (NO) or normally closed (NC):
Normally Open (NO): The circuit is off when no control signal is present, and it closes when the relay is activated.
Normally Closed (NC): The circuit is on when no control signal is present, and it opens when the relay is activated.
Types of Relays:
Electromechanical Relays (EMRs): These relays use physical moving parts (the electromagnet and armature) to switch the circuit.
Solid-State Relays (SSRs): These use electronic components, like transistors or thyristors, to switch the circuit without moving parts, making them faster and more durable.
Common Applications:
Automotive: Relays are used in car ignition systems, lights, and air conditioning.
Home Appliances: Relays help manage high-power devices like ovens, HVAC systems, and washing machines.
Industrial Systems: Relays control motors, pumps, and safety equipment, especially where automation is involved.
Relays are important because they allow a small electrical signal to safely control much larger currents, protecting circuits and preventing damage to sensitive electronics.
How a Relay Works:
1. Electromagnetism: Inside the relay, there’s an electromagnet, which is a coil of wire that produces a magnetic field when a current passes through it.
2. Control Circuit: The small control circuit powers the electromagnet, and when the control signal is sent (usually low voltage or current), it activates the electromagnet.
3. Switching Mechanism: The magnetic field pulls a metal contact (or armature) to open or close a larger circuit, allowing or stopping the flow of current through it.
4. Output Circuit: The contacts in the output circuit are connected to the higher-power load. Depending on the relay type, the output circuit can be normally open (NO) or normally closed (NC):
Normally Open (NO): The circuit is off when no control signal is present, and it closes when the relay is activated.
Normally Closed (NC): The circuit is on when no control signal is present, and it opens when the relay is activated.
Types of Relays:
Electromechanical Relays (EMRs): These relays use physical moving parts (the electromagnet and armature) to switch the circuit.
Solid-State Relays (SSRs): These use electronic components, like transistors or thyristors, to switch the circuit without moving parts, making them faster and more durable.
Common Applications:
Automotive: Relays are used in car ignition systems, lights, and air conditioning.
Home Appliances: Relays help manage high-power devices like ovens, HVAC systems, and washing machines.
Industrial Systems: Relays control motors, pumps, and safety equipment, especially where automation is involved.
Relays are important because they allow a small electrical signal to safely control much larger currents, protecting circuits and preventing damage to sensitive electronics.
 0:03:15
0:03:15
 0:02:07
0:02:07
 0:04:20
0:04:20
 0:01:59
0:01:59
 0:03:32
0:03:32
 0:13:00
0:13:00
 0:03:56
0:03:56
 0:03:43
0:03:43
 0:07:54
0:07:54
 0:07:22
0:07:22
 0:04:03
0:04:03
 0:10:46
0:10:46
 0:08:01
0:08:01
 0:05:59
0:05:59
 0:05:17
0:05:17
 0:09:50
0:09:50
 0:05:02
0:05:02
 0:00:45
0:00:45
 0:05:11
0:05:11
 0:03:40
0:03:40
 0:09:43
0:09:43
 0:07:36
0:07:36
 0:00:45
0:00:45
 0:02:28
0:02:28