filmov
tv
Learn Biology: Classification- The Taxonomic Hierarchy

Показать описание
Mahalo biology expert Mary Poffenroth explains the classification system of species and the taxonomic hierarchy.
The Taxonomic Hierarchy
---------------------------------------------------------------------
This taxonomic system was initially pioneered by
Carl Linnaeus in the 18th century. Linnaeus used Latin terms to arrange species according to observable similarities and differences in their physical morphology. With recent innovations in molecular biology, the traditional classification system has been made more precise by the possibility of going beyond superficial similarities and mapping similarities and differences between species at the genetic level.
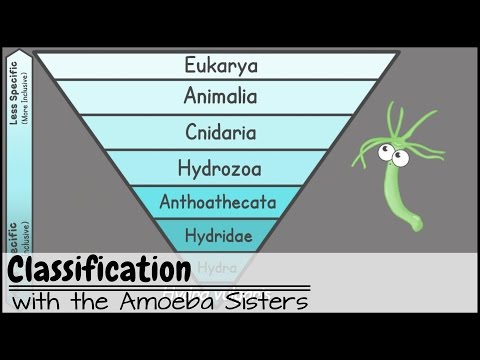
Following this hierarchy, the highest level, domain, distinguishes between bacteria and organisms with a true cell nucleus. The next level down, kingdom, distinguishes plants from animals. Below the kingdom level, at the level of phylum, we can differentiate between vertebrates and creatures with no backbone. Among the vertebrates, you can differentiate mammals from birds, fish and reptiles at the class level. Among mammals, you can differentiate between ones that eat meat and ones that don't. Some mammals belong to the order
Classification of a Sample Species
---------------------------------------------------------------------
In order to form a clearer idea of these categories, it is helpful to think of a specific example, like a mountain lion.
At the domain level, a mountain lion belongs to the category of
Eukarya, which are organisms with a cellular nucleus, unlike bacteria. At the kingdom level, it is Animalia, as opposed to a plant or a fungus. Mountain lions belong to the phylum Chordata, which are animals that have a backbone, in contrast to Arthropoda (spiders) or Porifera (sponges).
The c
Read more by visiting our page at:
The Taxonomic Hierarchy
---------------------------------------------------------------------
This taxonomic system was initially pioneered by
Carl Linnaeus in the 18th century. Linnaeus used Latin terms to arrange species according to observable similarities and differences in their physical morphology. With recent innovations in molecular biology, the traditional classification system has been made more precise by the possibility of going beyond superficial similarities and mapping similarities and differences between species at the genetic level.
Following this hierarchy, the highest level, domain, distinguishes between bacteria and organisms with a true cell nucleus. The next level down, kingdom, distinguishes plants from animals. Below the kingdom level, at the level of phylum, we can differentiate between vertebrates and creatures with no backbone. Among the vertebrates, you can differentiate mammals from birds, fish and reptiles at the class level. Among mammals, you can differentiate between ones that eat meat and ones that don't. Some mammals belong to the order
Classification of a Sample Species
---------------------------------------------------------------------
In order to form a clearer idea of these categories, it is helpful to think of a specific example, like a mountain lion.
At the domain level, a mountain lion belongs to the category of
Eukarya, which are organisms with a cellular nucleus, unlike bacteria. At the kingdom level, it is Animalia, as opposed to a plant or a fungus. Mountain lions belong to the phylum Chordata, which are animals that have a backbone, in contrast to Arthropoda (spiders) or Porifera (sponges).
The c
Read more by visiting our page at:
Комментарии
 0:02:30
0:02:30
 0:12:16
0:12:16
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:07:42
0:07:42
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:11:27
0:11:27
 0:00:11
0:00:11
 0:03:10
0:03:10
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:09:16
0:09:16
 0:04:11
0:04:11
 0:02:53
0:02:53
 0:03:20
0:03:20
 0:13:01
0:13:01
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:11:33
0:11:33
 0:04:01
0:04:01
 0:12:56
0:12:56
 0:01:44
0:01:44
 0:08:18
0:08:18
 0:00:25
0:00:25
 0:01:58
0:01:58
 0:03:59
0:03:59
![Biological Classification [Monera]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/qnxEXTgqYCY/hqdefault.jpg) 0:00:14
0:00:14