filmov
tv
DHCP explained- DORA Process

Показать описание
Please join me on udemy for Full CCNA 200-301 v1.1 training
We all use mobile phones and laptops or pc at home or at office to access network resources such as internet or a printer etc.
To access the network and its resources every device on a TCP/IP-based network must have a unique unicast
IP address.
Along with IP address each device must be assigned a default gateway and IP Address of DNS servers
Two basic IP address assignment methods:
Static
Dynamic
■ Static:
An IP address is statically assigned to a device by the administrator.
The administrator configures the IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and name servers IP manually.
Static address assignment is an extra burden for the administrator—especially on large-scale networks— who must configure the address on every end system in the network.
■ Dynamic
IP addresses are assigned to the end systems by DHCP server.
DHCP stands for dynamic host configuration protocol
(DHCP) is a client/server protocol used for address assignment.
With DHCP, this entire process is automated and managed centrally.
This method relieves the administrator of manually assigning an address to every network device.
On the client machine you have to select the option as obtain ip add and dns automatically.
It automatically provides all the parameters to the end device
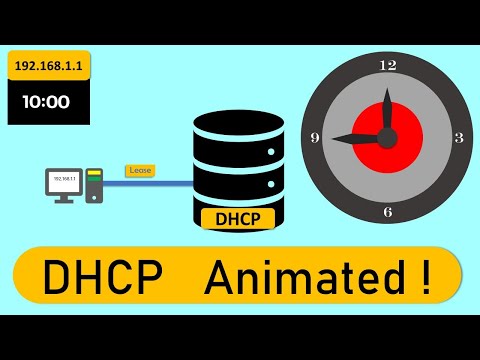
DHCP Scope is a pool of IP addresses or usually a range of consecutive numbers within a single IP subnet maintained by DHCP server. DHCP server assigns IP’s to the client from this pool/scope.
Any numbers that the administrator does not want to have handed out can be excluded from the pool
DHCP adopts the concept of a “lease” in IP allocation.
It sets a “lease duration” and allow the client to use the allocated IP address only during the set lease duration.
If the client want to renew or wishes to use the allocated IP address for longer than the lease duration, it should request the DHCP server for renewal of the lease.
If the device is disconnected or powered off , it releases the IP instead and returns to the pool for reallocation.
#DHCP #DORA #CCNA #IP
what happens when DHCP client requests an IP address from DHCP Server.
There are some messages which are exchanged between the DHCP Server and Client.
This process is divided in to four steps
1. DHCPDISCOVER :
* When a DHCP client first boots up, it broadcasts a DHCPDiscover message. This message is intiated from DHCP Client to DHCP Server, to find the DHCP server on the local network
2. DHCPOFFER :
If a DHCP server exists on the local segment, it will respond with a DHCPOffer.
This offer message is From DHCP Server to DHCP Client , to offer the IP Parameters, which contains IP address, subnet mask etc.
3. DHCPREQUEST:
* Once the client receives the offer, it will respond with a DHCPRequest, indicating that it will accept the offered protocol information.
* This message is from DHCP Client to DHCP Server, giving a request to get the offered IP Parameters
4. DHCPACK:
Finally, the server responds with DHCPAck, acknowledging the client acceptance of offered protocol information
This message is from DHCP server to DHCP Client, giving confirmation to use the the offered IP parameters.
This process is also known as DORA process.
DHCP is a UDP service.
Uses two UDP port numbers for its operations
DHCP Server uses the UDP port 67 and DHCP client uses UDP port 68.
Use of ports number prevents an application from getting a message from a completely different protocol.
If the client and server are on different subnets, well a DHCP Helper or DHCP Relay Agent must be used in this case.
Other than dynamically assigning IP addresses to client machines DHCP also has the ability to provide various other interesting parameters or DHCP options to client machines, like timezone information, boot arguments/paths, NTP servers, static routes, host name of the client, very useful for IoT and any device without user
For more information on DHCP options/ parameters please go through RFC1533
#CCNA #DHCP #Free
We all use mobile phones and laptops or pc at home or at office to access network resources such as internet or a printer etc.
To access the network and its resources every device on a TCP/IP-based network must have a unique unicast
IP address.
Along with IP address each device must be assigned a default gateway and IP Address of DNS servers
Two basic IP address assignment methods:
Static
Dynamic
■ Static:
An IP address is statically assigned to a device by the administrator.
The administrator configures the IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and name servers IP manually.
Static address assignment is an extra burden for the administrator—especially on large-scale networks— who must configure the address on every end system in the network.
■ Dynamic
IP addresses are assigned to the end systems by DHCP server.
DHCP stands for dynamic host configuration protocol
(DHCP) is a client/server protocol used for address assignment.
With DHCP, this entire process is automated and managed centrally.
This method relieves the administrator of manually assigning an address to every network device.
On the client machine you have to select the option as obtain ip add and dns automatically.
It automatically provides all the parameters to the end device
DHCP Scope is a pool of IP addresses or usually a range of consecutive numbers within a single IP subnet maintained by DHCP server. DHCP server assigns IP’s to the client from this pool/scope.
Any numbers that the administrator does not want to have handed out can be excluded from the pool
DHCP adopts the concept of a “lease” in IP allocation.
It sets a “lease duration” and allow the client to use the allocated IP address only during the set lease duration.
If the client want to renew or wishes to use the allocated IP address for longer than the lease duration, it should request the DHCP server for renewal of the lease.
If the device is disconnected or powered off , it releases the IP instead and returns to the pool for reallocation.
#DHCP #DORA #CCNA #IP
what happens when DHCP client requests an IP address from DHCP Server.
There are some messages which are exchanged between the DHCP Server and Client.
This process is divided in to four steps
1. DHCPDISCOVER :
* When a DHCP client first boots up, it broadcasts a DHCPDiscover message. This message is intiated from DHCP Client to DHCP Server, to find the DHCP server on the local network
2. DHCPOFFER :
If a DHCP server exists on the local segment, it will respond with a DHCPOffer.
This offer message is From DHCP Server to DHCP Client , to offer the IP Parameters, which contains IP address, subnet mask etc.
3. DHCPREQUEST:
* Once the client receives the offer, it will respond with a DHCPRequest, indicating that it will accept the offered protocol information.
* This message is from DHCP Client to DHCP Server, giving a request to get the offered IP Parameters
4. DHCPACK:
Finally, the server responds with DHCPAck, acknowledging the client acceptance of offered protocol information
This message is from DHCP server to DHCP Client, giving confirmation to use the the offered IP parameters.
This process is also known as DORA process.
DHCP is a UDP service.
Uses two UDP port numbers for its operations
DHCP Server uses the UDP port 67 and DHCP client uses UDP port 68.
Use of ports number prevents an application from getting a message from a completely different protocol.
If the client and server are on different subnets, well a DHCP Helper or DHCP Relay Agent must be used in this case.
Other than dynamically assigning IP addresses to client machines DHCP also has the ability to provide various other interesting parameters or DHCP options to client machines, like timezone information, boot arguments/paths, NTP servers, static routes, host name of the client, very useful for IoT and any device without user
For more information on DHCP options/ parameters please go through RFC1533
#CCNA #DHCP #Free
Комментарии
 0:05:51
0:05:51
 0:05:48
0:05:48
 0:25:26
0:25:26
 0:10:10
0:10:10
 0:08:16
0:08:16
 0:10:27
0:10:27
 0:13:43
0:13:43
 0:09:56
0:09:56
 0:25:39
0:25:39
 0:07:57
0:07:57
 0:02:40
0:02:40
 0:07:21
0:07:21
 0:18:33
0:18:33
 0:06:14
0:06:14
 0:09:18
0:09:18
 0:07:32
0:07:32
 0:05:25
0:05:25
 0:06:43
0:06:43
 0:08:30
0:08:30
 0:09:45
0:09:45
 0:37:02
0:37:02
 0:08:53
0:08:53
 0:10:41
0:10:41
 0:16:31
0:16:31