filmov
tv
How to find the Oxidation Number for C in CO3 2- (Carbonate ion).

Показать описание
To find the correct oxidations state of C in CO3 2- (the Carbonate ion), and each element in the ion, we use a few rules and some simple math.
First, since the Carbonate ion has an overall charge of -2 we could say that the oxidation numbers in CO3 2- need to add up to charge on the ion.
We write the oxidation number (O.N.) for elements that we know and use these to figure out oxidation number for C.
----------
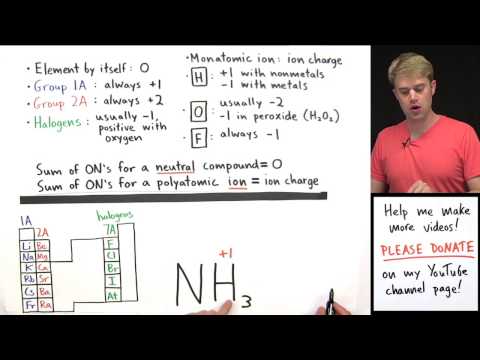
GENERAL RULES
Free elements have an oxidation state of zero (e.g. Na, Fe, H2, O2, S8).
In an ion the all Oxidation numbers must add up to the charge on the ion.
In a neutral compound all Oxidation Numbers must add up to zero.
Group 1 = +1
Group 2 = +2
Hydrogen with Non-Metals = +1
Hydrogen with Metals (or Boron) = -1
Fluorine = -1
Oxygen = -2 (except in H2O2 or with Fluorine)
Group 17(7A) = -1 except with Oxygen and other halogens lower in the group
----------
We know that Oxygen usually is -2 with a few exceptions. When Oxygen is in a peroxide, like H2O2 (Hydrogen peroxide), it has a charge of -1. When it is bonded to Fluorine (F) it has an oxidation number of +2.
Here it is bonded to C so the oxidation number on Oxygen is -2. Using this information we can figure out the oxidation number for the element C in CO3 2-.
First, since the Carbonate ion has an overall charge of -2 we could say that the oxidation numbers in CO3 2- need to add up to charge on the ion.
We write the oxidation number (O.N.) for elements that we know and use these to figure out oxidation number for C.
----------
GENERAL RULES
Free elements have an oxidation state of zero (e.g. Na, Fe, H2, O2, S8).
In an ion the all Oxidation numbers must add up to the charge on the ion.
In a neutral compound all Oxidation Numbers must add up to zero.
Group 1 = +1
Group 2 = +2
Hydrogen with Non-Metals = +1
Hydrogen with Metals (or Boron) = -1
Fluorine = -1
Oxygen = -2 (except in H2O2 or with Fluorine)
Group 17(7A) = -1 except with Oxygen and other halogens lower in the group
----------
We know that Oxygen usually is -2 with a few exceptions. When Oxygen is in a peroxide, like H2O2 (Hydrogen peroxide), it has a charge of -1. When it is bonded to Fluorine (F) it has an oxidation number of +2.
Here it is bonded to C so the oxidation number on Oxygen is -2. Using this information we can figure out the oxidation number for the element C in CO3 2-.
Комментарии
 0:31:15
0:31:15
 0:07:00
0:07:00
 0:13:26
0:13:26
 0:16:05
0:16:05
 0:13:13
0:13:13
 0:00:56
0:00:56
 0:04:27
0:04:27
 0:15:25
0:15:25
 0:38:43
0:38:43
 0:06:00
0:06:00
 0:00:25
0:00:25
 0:04:11
0:04:11
 0:01:28
0:01:28
 1:06:37
1:06:37
 0:03:56
0:03:56
 0:04:58
0:04:58
 0:09:47
0:09:47
 0:01:35
0:01:35
 0:05:56
0:05:56
 0:03:19
0:03:19
 0:03:52
0:03:52
 0:01:34
0:01:34
 0:01:07
0:01:07
 0:01:46
0:01:46