filmov
tv
19.3 Galvanic Cells | General Chemistry

Показать описание
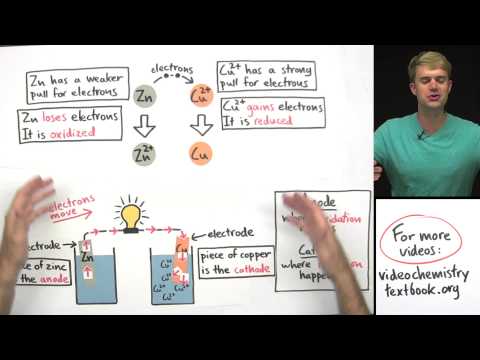
Chad provides a thorough lesson about galvanic cells (aka voltaic cells). The lesson begins with a comparison and contrast of galvanic cells vs electrolytic cells. Galvanic cells involve a spontaneous reaction that produces energy (electricity), while electrolytic cells involve a nonspontaneous reaction that consumes energy. In the galvanic cell electrons travel through the wire from anode (which is negative) to cathode (which is positive). In the electrolytic cell electrons still travel from anode to cathode but the signs are the opposite (anode is positive and cathode negative).
In the galvanic cell the two half reactions take place in separate half-cells the solutions of which are connected by a salt bridge. Anions travel through the salt bridge to the anode, and cations travel through the salt bridge to the cathode in order to maintain electrical neutrality in the solutions of both half-cells. Finally, it is common for the anode to lose mass and the cathode to gain mass in galvanic cells over time, though a common exception is when inert electrodes are used.
00:00 Lesson Introduction
00:25 Galvanic Cell vs Electrolytic Cell
04:29 Anode and Cathode in a Galvanic Cell
14:04 Salt Bridge in a Galvanic Cell
22:04 Inert Electrode
In the galvanic cell the two half reactions take place in separate half-cells the solutions of which are connected by a salt bridge. Anions travel through the salt bridge to the anode, and cations travel through the salt bridge to the cathode in order to maintain electrical neutrality in the solutions of both half-cells. Finally, it is common for the anode to lose mass and the cathode to gain mass in galvanic cells over time, though a common exception is when inert electrodes are used.
00:00 Lesson Introduction
00:25 Galvanic Cell vs Electrolytic Cell
04:29 Anode and Cathode in a Galvanic Cell
14:04 Salt Bridge in a Galvanic Cell
22:04 Inert Electrode
Комментарии
 0:27:42
0:27:42
 0:20:34
0:20:34
 0:09:31
0:09:31
 0:27:14
0:27:14
 0:10:01
0:10:01
 0:09:30
0:09:30
 1:59:00
1:59:00
 0:13:33
0:13:33
 0:16:28
0:16:28
 0:10:39
0:10:39
 0:06:12
0:06:12
 0:13:05
0:13:05
 0:08:44
0:08:44
 0:14:43
0:14:43
 0:03:09
0:03:09
 0:16:37
0:16:37
 0:11:20
0:11:20
 0:19:22
0:19:22
 0:15:01
0:15:01
 0:39:34
0:39:34
 0:10:22
0:10:22
 0:14:52
0:14:52
 0:12:13
0:12:13
 0:19:10
0:19:10