filmov
tv
Rigid & Flexible Pavements A Clear Understanding #civilengineering@Highwayengineering

Показать описание
4 Component Parts Of Flexible and Rigid Road Pavements Structure and Their Functions
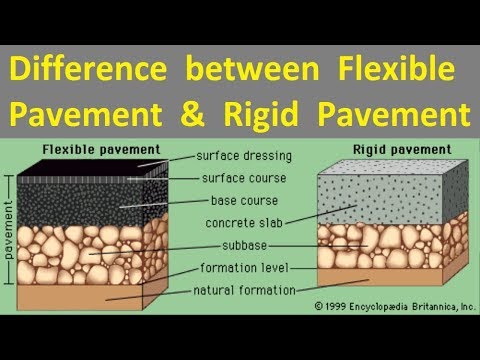
The following are the 4 component parts of road pavement:
Subgrade of formation.
Subbase course.
Base course.
4 Surface course or
wearing course
1) Subgrade or Formation
The finished and compacted surface of earthwork on which a road
pavement rests is called subgrade or formation.
Functions of Subgrade
The Functions of subgrade are as follows:
To provide adequate and uniform support to the road pavements.
To bear ultimately the entire load of pavement including the traffic load transmitted through
the pavement.
2) Sub-base course
The layer of granular material such as burnt clinker, gravel, or slag
provided in between the subgrade and base course in a road pavement is called a
sub-base course. In some places, boulder stones or bricks are also used as a
sub-base course.
Function of Sub-base Course
The functions of sub-base course are:
To improve the bearing capacity of the subgrade.
To provide additional help to the base and surface course in distributing the load.
To prevent the undesirable entry of fine-grained soils from subgrade to base course.
To minimize the damaging effect of frost action.
To improve the drainage.
3) Base Course
The layer of broken stones or brick provided over the subbase course or
immediately over the subgrade in the absence of subbase, in a road pavement is
called base course.
Function of Base Course
The Functions of the base course are as follows:
To act as the foundation of the road pavement and to transfer the traffic load safely to the subbase and subgrade.
To withstand high shearing stresses due to the impact of traffic.
To prevent the undesirable entry of subgrade soil in the pavement when the base course is
constructed directly over the subgrade.
4) Surface Course or Wearing Course
The topmost layer of the road pavement directly exposed to the traffic is called the surface course or wearing course. In flexible pavement, normally a bituminous surface is used as a wearing course. In Rigid Pavement, the
cement concrete layer acts as a base course as well as a wearing course.
Functions of Surface or Wearing Course
The Functions of the surface or wearing course are as follows:
To provide a smooth and uniform rigid surface.
To resist the abrasive forces of traffic.
To prevent dust nuisance.
To act as a structure
The following are the 4 component parts of road pavement:
Subgrade of formation.
Subbase course.
Base course.
4 Surface course or
wearing course
1) Subgrade or Formation
The finished and compacted surface of earthwork on which a road
pavement rests is called subgrade or formation.
Functions of Subgrade
The Functions of subgrade are as follows:
To provide adequate and uniform support to the road pavements.
To bear ultimately the entire load of pavement including the traffic load transmitted through
the pavement.
2) Sub-base course
The layer of granular material such as burnt clinker, gravel, or slag
provided in between the subgrade and base course in a road pavement is called a
sub-base course. In some places, boulder stones or bricks are also used as a
sub-base course.
Function of Sub-base Course
The functions of sub-base course are:
To improve the bearing capacity of the subgrade.
To provide additional help to the base and surface course in distributing the load.
To prevent the undesirable entry of fine-grained soils from subgrade to base course.
To minimize the damaging effect of frost action.
To improve the drainage.
3) Base Course
The layer of broken stones or brick provided over the subbase course or
immediately over the subgrade in the absence of subbase, in a road pavement is
called base course.
Function of Base Course
The Functions of the base course are as follows:
To act as the foundation of the road pavement and to transfer the traffic load safely to the subbase and subgrade.
To withstand high shearing stresses due to the impact of traffic.
To prevent the undesirable entry of subgrade soil in the pavement when the base course is
constructed directly over the subgrade.
4) Surface Course or Wearing Course
The topmost layer of the road pavement directly exposed to the traffic is called the surface course or wearing course. In flexible pavement, normally a bituminous surface is used as a wearing course. In Rigid Pavement, the
cement concrete layer acts as a base course as well as a wearing course.
Functions of Surface or Wearing Course
The Functions of the surface or wearing course are as follows:
To provide a smooth and uniform rigid surface.
To resist the abrasive forces of traffic.
To prevent dust nuisance.
To act as a structure
 0:03:01
0:03:01
 0:05:41
0:05:41
 0:03:07
0:03:07
 0:00:13
0:00:13
 0:06:50
0:06:50
 0:06:04
0:06:04
 0:05:32
0:05:32
 0:09:39
0:09:39
 0:05:11
0:05:11
 0:15:42
0:15:42
 0:15:18
0:15:18
 0:00:21
0:00:21
 0:00:22
0:00:22
 0:02:30
0:02:30
 0:04:44
0:04:44
 0:00:12
0:00:12
 0:17:56
0:17:56
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:09:30
0:09:30
 0:04:58
0:04:58
 0:01:23
0:01:23
 0:00:14
0:00:14
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:17:34
0:17:34