filmov
tv
Lecture 12 | Integration through a Branch Cut | Example 1 | Theta Classes

Показать описание
From this lecture we are going to learn about how to solve an improper integral involving multi valued function. So firstly we will discuss about branch point, branch cut in a brief manner and then we will solve given integral. While solving integrals involving multi valued function we will learn how to avoid branch point when it comes on the boundary of the contour and we are also going to see how to select a branch cut. After that we will find residue and using Cauchy's Residue Theorem we will solve the integral.
In case if anyone has any doubt regarding this lecture do mention it in the comment section.
Keep connected with Theta Classes to study various topics of higher mathematics.
In case if anyone has any doubt regarding this lecture do mention it in the comment section.
Keep connected with Theta Classes to study various topics of higher mathematics.
Lecture 12 | Integration through a Branch Cut | Example 1 | Theta Classes
Finding the Area Between Two Curves by Integration
Integration Using The Substitution Rule
Integration and the fundamental theorem of calculus | Chapter 8, Essence of calculus
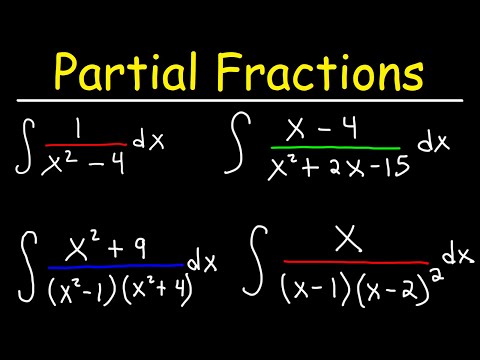
Integration By Partial Fractions
Lecture 12: Integration on manifolds (International Winter School on Gravity and Light 2015)
Math 2B. Calculus. Lecture 12. Trigonometric Substitution
Calculus 2 Lecture 7.4: Integration By Partial Fractions
#12thmaths Integration by parts 12th maths rbse & cbse board exercise -7.6 Lecture -10
Integration By Parts
Calculus 2 Lecture 7.1: Integration By Parts
12th Integration IMP Proof Lecture -12
Calculus 1 Lecture 5.1: Finding Area Between Two Curves
Lecture 12: Lebesgue Integrable Functions, the Lebesgue Integral and the Dominated Convergence...
Triple Integration | Lecture 12 | Evaluation of Triple Integral using Cylindrical Coordinates
Calculus 1 Lecture 4.1: An Introduction to the Indefinite Integral
Integration into Inverse trigonometric functions using Substitution
Integrals Class 12 Maths | Basics of Integration | Chapter 7 of NCERT | Lecture 1
Introductory Calculus: Oxford Mathematics 1st Year Student Lecture
Understand Calculus in 35 Minutes
Calculus 2 Lecture 7.3: Integrals By Trigonometric Substitution
12th Maths 2 | Chapter 3 | Indefinite Integral | Lecture 1 | Maharashtra Board |
Complex integration||Line integrals of complex functions||Complex analysis||Lecture 12
Math 2B. Calculus. Lecture 13. Integration by Partial Fractions
Комментарии
 0:51:30
0:51:30
 0:07:52
0:07:52
 0:10:40
0:10:40
 0:20:46
0:20:46
 0:41:07
0:41:07
 1:28:15
1:28:15
 0:49:04
0:49:04
 2:55:43
2:55:43
 0:40:44
0:40:44
 0:13:17
0:13:17
 1:54:37
1:54:37
 0:22:51
0:22:51
 1:33:46
1:33:46
 1:24:57
1:24:57
 0:09:30
0:09:30
 2:45:37
2:45:37
 0:38:08
0:38:08
 0:25:07
0:25:07
 0:58:03
0:58:03
 0:36:22
0:36:22
 2:09:24
2:09:24
 0:35:53
0:35:53
 0:35:31
0:35:31
 0:50:06
0:50:06