filmov
tv
Oscilloscope Probe Fundamentals

Показать описание
This video explains the basics of oscilloscope probes, including the most common probe types as well as explain how to choose an appropriate probe for a given measurement application.
Timeline:
00:00 Introduction
01:03 About probes
02:03 About probe bandwidth
02:56 About probe loading
03:53 Choosing the channel impedance / termination
05:28 Passive probes
06:20 Attenuation in passive probes
07:21 Configuring probe attenuation
08:08 Switchable probes
08:46 1X probes
09:37 10X probes
10:36 Importance of a short ground connection
11:39 Compensating passive probes
12:16 Why is probe compensation necessary?
13:19 How are probes compensated?
14:07 Probe compensation examples
14:55 Measuring current with an oscilloscope
16:11 About (clamping) current probes
16:48 Measuring AC and/or DC probes
17:28 Current probe parameters
18:41 Connecting to the oscilloscope
19:38 Connecting to the circuit under test
20:17 Multiple loops for increased current sensitivity
21:09 Zeroing current probes
22:11 Demagnetization / degauss
23:16 Deskew
24:37 About single-ended measurements
25:50 About differential measurements
26:38 Two ways of measuring differential voltages
27:01 Two single-ended probes (quasi-differential)
27:50 Differential probes
28:48 Aside: twisting differential probe leads
29:25 Advantages and disadvantages of differential probes
30:35 Differential probe specifications
31:00 Common mode rejection ratio (CMRR)
32:10 Differential mode range (DMR)
33:29 Common mode range (CMR)
34:36 What do we mean by an “active” probe?
35:22 About active probes
36:18 Using active probes
37:08 Characteristics of active probes
37:30 Active probes and loading
38:27 Active probes and bandwidth
39:18 About offset range
40:40 Active probes and offset range
41:30 Summary
Timeline:
00:00 Introduction
01:03 About probes
02:03 About probe bandwidth
02:56 About probe loading
03:53 Choosing the channel impedance / termination
05:28 Passive probes
06:20 Attenuation in passive probes
07:21 Configuring probe attenuation
08:08 Switchable probes
08:46 1X probes
09:37 10X probes
10:36 Importance of a short ground connection
11:39 Compensating passive probes
12:16 Why is probe compensation necessary?
13:19 How are probes compensated?
14:07 Probe compensation examples
14:55 Measuring current with an oscilloscope
16:11 About (clamping) current probes
16:48 Measuring AC and/or DC probes
17:28 Current probe parameters
18:41 Connecting to the oscilloscope
19:38 Connecting to the circuit under test
20:17 Multiple loops for increased current sensitivity
21:09 Zeroing current probes
22:11 Demagnetization / degauss
23:16 Deskew
24:37 About single-ended measurements
25:50 About differential measurements
26:38 Two ways of measuring differential voltages
27:01 Two single-ended probes (quasi-differential)
27:50 Differential probes
28:48 Aside: twisting differential probe leads
29:25 Advantages and disadvantages of differential probes
30:35 Differential probe specifications
31:00 Common mode rejection ratio (CMRR)
32:10 Differential mode range (DMR)
33:29 Common mode range (CMR)
34:36 What do we mean by an “active” probe?
35:22 About active probes
36:18 Using active probes
37:08 Characteristics of active probes
37:30 Active probes and loading
38:27 Active probes and bandwidth
39:18 About offset range
40:40 Active probes and offset range
41:30 Summary
Комментарии
 0:43:12
0:43:12
 0:02:58
0:02:58
 0:07:37
0:07:37
 0:32:57
0:32:57
 0:06:54
0:06:54
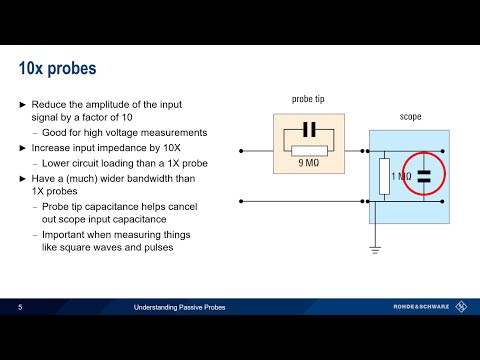 0:05:44
0:05:44
 0:05:20
0:05:20
 0:11:49
0:11:49
 0:12:40
0:12:40
 0:00:12
0:00:12
 0:11:30
0:11:30
 0:19:54
0:19:54
 0:09:17
0:09:17
 0:12:32
0:12:32
 0:04:33
0:04:33
 0:12:24
0:12:24
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:00:27
0:00:27
 0:08:02
0:08:02
 0:03:05
0:03:05
 0:04:30
0:04:30
 0:24:26
0:24:26
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:12:56
0:12:56