filmov
tv
Big Bang or Steady State? Wrong Question! (Variable Speed of Light Cosmology)
Показать описание
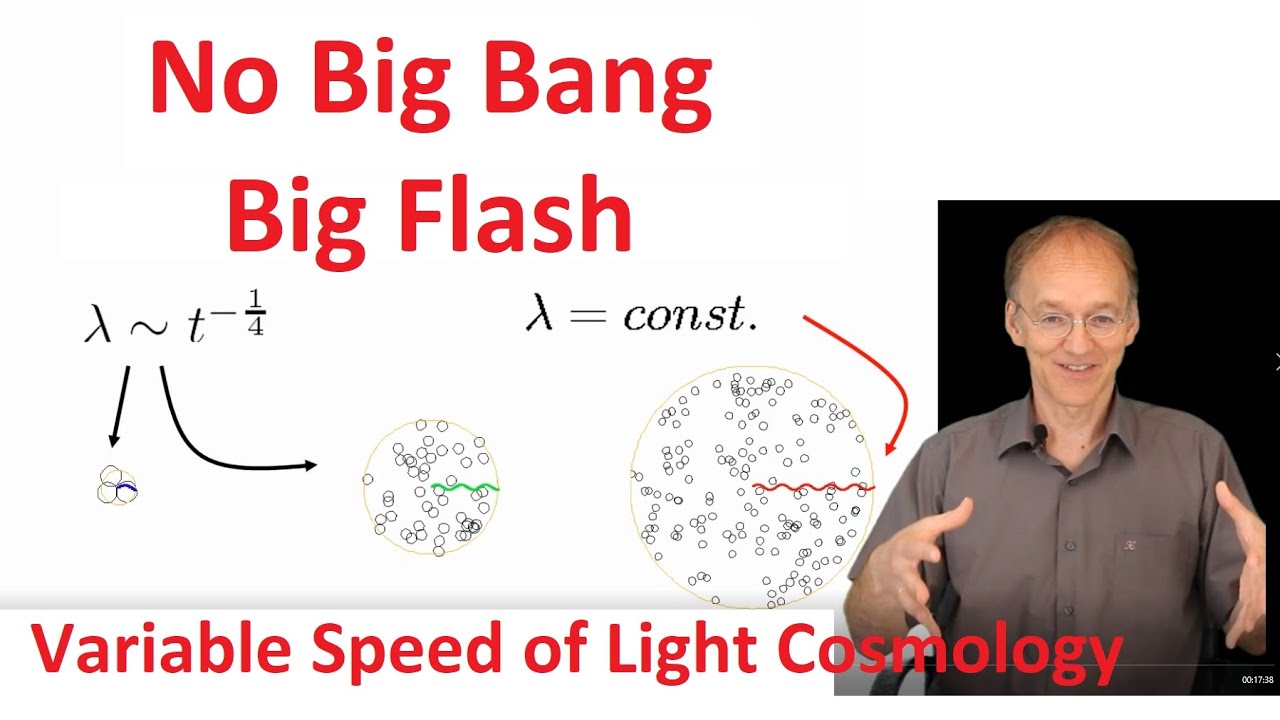
Variable speed of light offers an intriguing explanation of the cosmological redshift: no material expansion, just light spreads. As a consequence, the beginning of the universe is better understood as an horizon of one elementary particle (Big Flash). Contrarily to conventional cosmology, the value of the nuclear density becomes meaningful.
Cosmic Clash: Big Bang Theory vs Steady State Theory – Which Prevails?
Steady State Theory
Classroom Aid - Big Bang vs Steady State
Origin of the Universe Theories - The Big Bang Theory - Steady State Theory and Pulsating Theory
Evidence for Big Bang Cosmology
What Is the Steady-State Theory in Cosmology?
Big Bang or Steady State? Wrong Question! (Variable Speed of Light Cosmology)
Origins of the Universe 101 | National Geographic
Origins: Theories of the Universe | Episode 4: Steady State Theory explained
Steady State vs Big Bang
THE STEADY-STATE THEORY || It challenged the Big Bang Theory!
The Big Bang | Astrophysics | Physics| FuseSchool
Eternal Universe: The New Theory that Might Change the Way we Think About the Universe
The Big Bang
The Controversial Debate Big Bang vs Steady State Theory
Einstein The Steady State Theory
ORIGIN OF THE UNIVERSE | THE BIG BANG THEORY | THE STEADY STATE THEORY | IN BRIEF AND SIMPLE.
Steady-State Model of the Universe
The Steady State Theory of The Universe
What Is The Big Bang Theory? | The Dr. Binocs Show - Best Learning Videos For Kids | Peekaboo Kidz
Is universe eternal or evolving? Big Bang vs. Steady State Theory.
An alternative to big bang theory | The Steady State theory | #cosmology #astronomy #astrophysics
The Big Bang Theory - Explained (expanding universe theory)
GCSE Big bang vs steady state theory question ?
Комментарии
 0:03:13
0:03:13
 0:12:53
0:12:53
 0:01:07
0:01:07
 0:04:17
0:04:17
 0:12:19
0:12:19
 0:03:00
0:03:00
 0:25:34
0:25:34
 0:05:50
0:05:50
 0:05:01
0:05:01
 0:04:43
0:04:43
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:04:20
0:04:20
 0:16:12
0:16:12
 0:01:56
0:01:56
 0:00:52
0:00:52
 0:00:51
0:00:51
 0:05:09
0:05:09
 0:45:12
0:45:12
 0:05:04
0:05:04
 0:05:30
0:05:30
 0:06:42
0:06:42
 0:00:34
0:00:34
 0:04:12
0:04:12
 0:04:53
0:04:53