filmov
tv
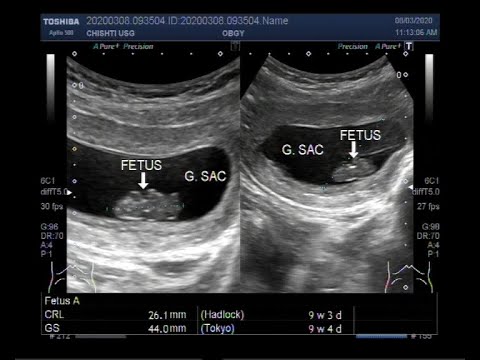
A Missed abortion also called a Missed miscarriage, of about 11.5 weeks.

Показать описание
This video shows a Missed abortion also called a Missed miscarriage, of about 11.5 weeks.
Although a variety of terms are used to describe early pregnancy failure, in the presence of clear-cut sonographic evidence that a nonliving embryo is present, the term embryonic demise should apply.
Ultrasound diagnosis of miscarriage should only be considered when either a mean gestation sac diameter is equal to or more than 25 mm with no obvious yolk sac or a fetal pole with a crown rump length of equal to or more than 7 mm without evidence of fetal cardiac activity. Transvaginal ultrasound is the mainstay in the diagnosis of miscarriage.
A missed abortion is a nonviable intrauterine pregnancy that has been retained within the uterus without spontaneous abortion. Typically, no symptoms exist besides amenorrhea, and the patient finds out that the pregnancy stopped developing earlier when a fetal heartbeat is not observed or heard at the appropriate time. An ultrasound usually confirms the diagnosis.
In addition to signs of fetal life on sonography, sub-chorionic bleeding is an important factor affecting the outcome of gestations in patients with clinical threatened abortion. The most common cause for first trimester spontaneous abortion is fetal chromosomal abnormalities.
While most practitioners wait until at least 6 weeks to perform the first ultrasound, a gestational sac can be seen as early as 4 1/2 weeks after your last period; a heartbeat can be detected as early as 5 to 6 weeks (though it might not be detected that early in all cases).
A Missed abortion is a Missed miscarriage in which the fetus didn't form or fetal demise had occurred, but the placenta and embryonic tissues are still in the uterus. It's known more commonly as a missed miscarriage. It's also sometimes called a Silent miscarriage. A missed abortion is not an elective abortion.
Missed miscarriage means that the baby has stopped growing or there is fetal demise but there are no miscarriage symptoms such as bleeding or pain. It can also be called a delayed miscarriage.
Some women do not experience any symptoms of miscarriage at all; however, possible miscarriage Signs besides bleeding include:
Mild to severe cramps.
Pain in back or abdomen.
Loss of pregnancy symptoms, such as nausea or vomiting.
White-pink mucus.
Passing tissue or clot-like material.
To make the diagnosis with ultrasound the findings may include, but not be limited to: absence of fetal pole, lack of growth of fetal pole, fetal pole with no evident cardiac activity, lack of yolk sac at the appropriate gestational age, de-shaped yolk sac or placental separation.
The umbilical cord forms by the fifth week of development, replacing the yolk sac as the source of nutrients for the embryo. Umbilical cord is a cord that connects the developing baby to the mother in utero. The umbilical cord attaches to the baby at the abdomen and to the mother at the placenta. The cord forms during the fifth week of gestation (seventh week of pregnancy).
Treatment of missed abortion?
Misoprostol is a non-invasive, effective medical method for the completion of abortion in missed abortion. Sublingual misoprostol of 600 ug or vaginal misoprostol of 800 ugs may be a good choice for the first dose.
In the case of fetal demise, a dead fetus that has been in the uterus for 4 weeks can cause changes in the body's clotting system. These changes can put a woman at a much higher chance of significant bleeding if she waits for a long time after the fetal demise to deliver the pregnancy.
The term 'early fetal death' refers to conditions in which the fetus is no longer alive, but the uterus has not yet started to expel its contents. A variety of terms were previously used to describe this condition, including 'blighted ovum', 'missed abortion', and 'silent miscarriage'
Miscarriage is a word used to describe the early loss of a pregnancy before 20 weeks of pregnancy. It usually happens in the first trimester. Unfortunately, between 10 and 15 percent of known pregnancies end in miscarriage.
There are three hypothetical causes of Fetal demise in the first trimester.
1). Parvovirus fetal infection, the primary viral infection of the myocardial cells initially causes myocarditis, leading to hydropic cardiac failure and demise.
2). Bone marrow transient aplastic crisis occurs as the primum movens for anemia, leading to the sequence of congestive heart failure/hydrops/death.
3) Placentitis without fetal infection causes placental dysfunction and ultimately fetal demise.
IUGR has various causes. The most common cause is a problem in the placenta (the tissue that carries food and blood to the baby). Birth defects and genetic disorders can cause IUGR. If the mother has an infection, high blood pressure is smoking, drinking too much alcohol, or abusing drugs, her baby might have IUGR.
Although a variety of terms are used to describe early pregnancy failure, in the presence of clear-cut sonographic evidence that a nonliving embryo is present, the term embryonic demise should apply.
Ultrasound diagnosis of miscarriage should only be considered when either a mean gestation sac diameter is equal to or more than 25 mm with no obvious yolk sac or a fetal pole with a crown rump length of equal to or more than 7 mm without evidence of fetal cardiac activity. Transvaginal ultrasound is the mainstay in the diagnosis of miscarriage.
A missed abortion is a nonviable intrauterine pregnancy that has been retained within the uterus without spontaneous abortion. Typically, no symptoms exist besides amenorrhea, and the patient finds out that the pregnancy stopped developing earlier when a fetal heartbeat is not observed or heard at the appropriate time. An ultrasound usually confirms the diagnosis.
In addition to signs of fetal life on sonography, sub-chorionic bleeding is an important factor affecting the outcome of gestations in patients with clinical threatened abortion. The most common cause for first trimester spontaneous abortion is fetal chromosomal abnormalities.
While most practitioners wait until at least 6 weeks to perform the first ultrasound, a gestational sac can be seen as early as 4 1/2 weeks after your last period; a heartbeat can be detected as early as 5 to 6 weeks (though it might not be detected that early in all cases).
A Missed abortion is a Missed miscarriage in which the fetus didn't form or fetal demise had occurred, but the placenta and embryonic tissues are still in the uterus. It's known more commonly as a missed miscarriage. It's also sometimes called a Silent miscarriage. A missed abortion is not an elective abortion.
Missed miscarriage means that the baby has stopped growing or there is fetal demise but there are no miscarriage symptoms such as bleeding or pain. It can also be called a delayed miscarriage.
Some women do not experience any symptoms of miscarriage at all; however, possible miscarriage Signs besides bleeding include:
Mild to severe cramps.
Pain in back or abdomen.
Loss of pregnancy symptoms, such as nausea or vomiting.
White-pink mucus.
Passing tissue or clot-like material.
To make the diagnosis with ultrasound the findings may include, but not be limited to: absence of fetal pole, lack of growth of fetal pole, fetal pole with no evident cardiac activity, lack of yolk sac at the appropriate gestational age, de-shaped yolk sac or placental separation.
The umbilical cord forms by the fifth week of development, replacing the yolk sac as the source of nutrients for the embryo. Umbilical cord is a cord that connects the developing baby to the mother in utero. The umbilical cord attaches to the baby at the abdomen and to the mother at the placenta. The cord forms during the fifth week of gestation (seventh week of pregnancy).
Treatment of missed abortion?
Misoprostol is a non-invasive, effective medical method for the completion of abortion in missed abortion. Sublingual misoprostol of 600 ug or vaginal misoprostol of 800 ugs may be a good choice for the first dose.
In the case of fetal demise, a dead fetus that has been in the uterus for 4 weeks can cause changes in the body's clotting system. These changes can put a woman at a much higher chance of significant bleeding if she waits for a long time after the fetal demise to deliver the pregnancy.
The term 'early fetal death' refers to conditions in which the fetus is no longer alive, but the uterus has not yet started to expel its contents. A variety of terms were previously used to describe this condition, including 'blighted ovum', 'missed abortion', and 'silent miscarriage'
Miscarriage is a word used to describe the early loss of a pregnancy before 20 weeks of pregnancy. It usually happens in the first trimester. Unfortunately, between 10 and 15 percent of known pregnancies end in miscarriage.
There are three hypothetical causes of Fetal demise in the first trimester.
1). Parvovirus fetal infection, the primary viral infection of the myocardial cells initially causes myocarditis, leading to hydropic cardiac failure and demise.
2). Bone marrow transient aplastic crisis occurs as the primum movens for anemia, leading to the sequence of congestive heart failure/hydrops/death.
3) Placentitis without fetal infection causes placental dysfunction and ultimately fetal demise.
IUGR has various causes. The most common cause is a problem in the placenta (the tissue that carries food and blood to the baby). Birth defects and genetic disorders can cause IUGR. If the mother has an infection, high blood pressure is smoking, drinking too much alcohol, or abusing drugs, her baby might have IUGR.
Комментарии
 0:04:30
0:04:30
 0:06:05
0:06:05
 0:09:07
0:09:07
 0:04:42
0:04:42
 0:06:51
0:06:51
 0:05:40
0:05:40
 0:23:46
0:23:46
 0:05:51
0:05:51
 8:00:01
8:00:01
 0:03:44
0:03:44
 0:06:23
0:06:23
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:06:49
0:06:49
 0:02:35
0:02:35
 0:07:53
0:07:53
 0:00:39
0:00:39
 0:16:22
0:16:22
 0:02:28
0:02:28
 0:01:54
0:01:54
 0:00:55
0:00:55
 0:04:39
0:04:39
 0:03:10
0:03:10
 0:01:58
0:01:58
 0:03:45
0:03:45