filmov
tv
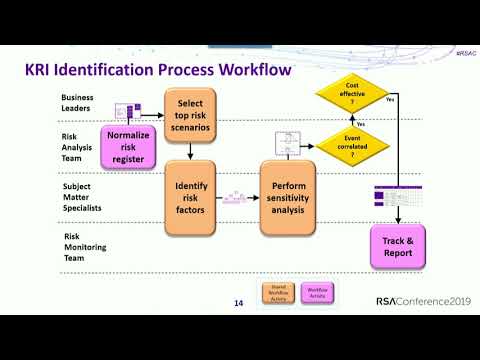
Developing KRIs for Risk Monitoring

Показать описание
🎓 MCSI Certified GRC Expert 🎓
📖 ✔️ MCSI Governance, Risk and Compliance Library ✔️📖
KRIs (Key Risk Indicators) are measurable metrics or indicators that provide insights into the potential occurrence or impact of risks within an organization. They help in monitoring and assessing the status of risks and can serve as early warning signals for potential issues or vulnerabilities. Here's a discussion on KRI selection criteria, the benefits of using KRIs, and how to optimize KRIs for effective risk monitoring:
KRI Selection Criteria:
Relevance: KRIs should be directly related to the risks that are most critical to the organization's objectives and operations. They should provide meaningful information about the likelihood or impact of those risks.
Measurability: KRIs need to be quantifiable or have specific qualitative measures to enable consistent monitoring and comparison over time. They should have reliable and accurate data sources.
Sensitivity: KRIs should be sensitive enough to detect changes or deviations that could indicate an increase in risk exposure. They should be capable of capturing significant shifts in risk levels.
Timeliness: KRIs should provide timely information to enable proactive risk management. They should be available and reported with a frequency that allows for effective monitoring and response.
Actionability: KRIs should provide actionable insights. They should be tied to specific risk mitigation strategies or triggers that prompt timely action.
Scalability: Consider the organization's size and complexity when selecting KRIs. They should be scalable and applicable to different business units, departments, or projects within the organization.
Benefits of Using KRIs:
Early Warning: KRIs act as leading indicators, enabling organizations to identify and respond to risks before they materialize into significant issues or threats.
Risk Monitoring: KRIs provide a systematic approach to monitoring risks by providing quantifiable data and indicators. They help in tracking risk trends and changes over time.
Proactive Risk Management: By focusing on KRIs, organizations can prioritize their risk management efforts and allocate resources effectively to address high-priority risks.
Decision Making: KRIs provide valuable data and insights that support informed decision making. They assist in assessing the potential impact of risks on business objectives and aid in making risk-informed choices.
Communication and Reporting: KRIs provide a concise and standardized way of communicating risk information across the organization. They facilitate effective reporting to stakeholders, including senior management and the board of directors.
Optimization of KRIs for Effective Risk Monitoring:
Alignment with Objectives: Ensure that selected KRIs align with the organization's strategic objectives, risk appetite, and specific risk management goals.
Data Quality and Reliability: Pay attention to the quality, accuracy, and reliability of data sources used for calculating KRIs. Establish robust data collection and validation processes.
Regular Review and Evaluation: Periodically review and evaluate the relevance and effectiveness of KRIs. Assess whether they are still aligned with the organization's risk landscape and modify or replace them as needed.
Contextualization: Consider the context and specific characteristics of the organization, industry, or project when selecting and interpreting KRIs. Avoid relying solely on generic or industry-standard indicators.
Integration with Risk Governance: Ensure that KRIs are integrated into the organization's risk governance framework. Align them with risk appetite statements, risk tolerance levels, and risk reporting processes.
By following these principles, organizations can optimize their use of KRIs, enhance risk monitoring capabilities, and foster a proactive risk management culture.
📖 ✔️ MCSI Governance, Risk and Compliance Library ✔️📖
KRIs (Key Risk Indicators) are measurable metrics or indicators that provide insights into the potential occurrence or impact of risks within an organization. They help in monitoring and assessing the status of risks and can serve as early warning signals for potential issues or vulnerabilities. Here's a discussion on KRI selection criteria, the benefits of using KRIs, and how to optimize KRIs for effective risk monitoring:
KRI Selection Criteria:
Relevance: KRIs should be directly related to the risks that are most critical to the organization's objectives and operations. They should provide meaningful information about the likelihood or impact of those risks.
Measurability: KRIs need to be quantifiable or have specific qualitative measures to enable consistent monitoring and comparison over time. They should have reliable and accurate data sources.
Sensitivity: KRIs should be sensitive enough to detect changes or deviations that could indicate an increase in risk exposure. They should be capable of capturing significant shifts in risk levels.
Timeliness: KRIs should provide timely information to enable proactive risk management. They should be available and reported with a frequency that allows for effective monitoring and response.
Actionability: KRIs should provide actionable insights. They should be tied to specific risk mitigation strategies or triggers that prompt timely action.
Scalability: Consider the organization's size and complexity when selecting KRIs. They should be scalable and applicable to different business units, departments, or projects within the organization.
Benefits of Using KRIs:
Early Warning: KRIs act as leading indicators, enabling organizations to identify and respond to risks before they materialize into significant issues or threats.
Risk Monitoring: KRIs provide a systematic approach to monitoring risks by providing quantifiable data and indicators. They help in tracking risk trends and changes over time.
Proactive Risk Management: By focusing on KRIs, organizations can prioritize their risk management efforts and allocate resources effectively to address high-priority risks.
Decision Making: KRIs provide valuable data and insights that support informed decision making. They assist in assessing the potential impact of risks on business objectives and aid in making risk-informed choices.
Communication and Reporting: KRIs provide a concise and standardized way of communicating risk information across the organization. They facilitate effective reporting to stakeholders, including senior management and the board of directors.
Optimization of KRIs for Effective Risk Monitoring:
Alignment with Objectives: Ensure that selected KRIs align with the organization's strategic objectives, risk appetite, and specific risk management goals.
Data Quality and Reliability: Pay attention to the quality, accuracy, and reliability of data sources used for calculating KRIs. Establish robust data collection and validation processes.
Regular Review and Evaluation: Periodically review and evaluate the relevance and effectiveness of KRIs. Assess whether they are still aligned with the organization's risk landscape and modify or replace them as needed.
Contextualization: Consider the context and specific characteristics of the organization, industry, or project when selecting and interpreting KRIs. Avoid relying solely on generic or industry-standard indicators.
Integration with Risk Governance: Ensure that KRIs are integrated into the organization's risk governance framework. Align them with risk appetite statements, risk tolerance levels, and risk reporting processes.
By following these principles, organizations can optimize their use of KRIs, enhance risk monitoring capabilities, and foster a proactive risk management culture.
 0:05:41
0:05:41
 0:01:37
0:01:37
 0:35:42
0:35:42
 0:07:11
0:07:11
 0:32:18
0:32:18
 0:05:00
0:05:00
 0:34:27
0:34:27
 0:05:30
0:05:30
 0:01:42
0:01:42
 0:24:07
0:24:07
 0:00:23
0:00:23
 0:43:03
0:43:03
 0:05:11
0:05:11
 1:00:44
1:00:44
 0:06:14
0:06:14
 0:02:01
0:02:01
 0:05:45
0:05:45
 0:58:15
0:58:15
 0:33:30
0:33:30
 1:01:08
1:01:08
 0:01:08
0:01:08
 0:06:28
0:06:28
 0:01:16
0:01:16
 0:04:16
0:04:16