filmov
tv
How to Configure Static NAT on Cisco Router in Cisco Packet Tracer | SYSNETTECH Solutions

Показать описание
This video shows you how to configure Static NAT on Cisco Router using the Packet Tracer software.
To configure #Static #NAT:
Step 1: If you have not installed #PacketTracer before, please refer to the following videos to install Packet Tracer on Windows, Linux, and macOS.
Step 2: After installing it, add two Cisco Routers, one Cisco Switch, and two computers to the Packet Tracer workspace.
Step 3: Specify local and WAN IP addresses.
Step 4: Configure the 192.168.1.0/24 network for the local network and the 10.0.0.1/30 network for the WAN.
Step 5: Assign IP addresses to the computers on the local network.
Step 6: Assign IP addresses to the GigabitEthernet interfaces of Router0 and Router1 and turn the ports on.
Step 7: Test the connection by pinging Router1 over PC0 and PC1.
Step 8: Next, configure the interface as follows because the Gig0/1 interface of Router0 is in the IP NAT INSIDE field.
R1# conf t
R1(config)# interface gig0/1
R1(config-if)# ip nat inside
R1(config-if)# exit
R1(config)# interface gig0/0
R1(config-if)# ip nat outside
Step 9: After you have defined the Router's IP NAT regions, execute the following command to configure Static NAT in Router0 global configuration mode.
R1# conf t
R1(config)# ip nat inside source static 192.168.10.10 10.0.0.1
Step 10: If you ping Router1 over PC0, you can see that the network connection is established.
Step 11: Now, ping to Router1 from PC1 and check that PC1 cannot reach Router1.
Step 12: Since we have not configured Static NAT for PC1, PC1 will not be able to reach Router1.
Step 13: Execute the following commands in user mode to verify and control Static NAT.
➦ show ip nat translation
➦ show ip nat statistics
➦ clear ip nat statistics
➦ debug ip nat
Step 14: Don't forget to subscribe to our YouTube channel for more videos on Cisco Networking training with Packet Tracer!
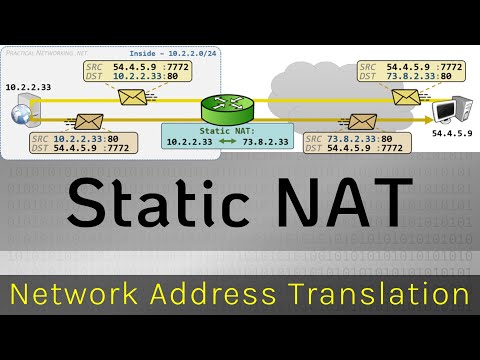
What is Static NAT?
Static NAT creates a fixed translation of real address(es) to mapped address(es). With dynamic NAT and PAT, each host uses a different address or port for each subsequent translation. Because the mapped address is the same for each consecutive connection with static NAT, and a persistent translation rule exists, static NAT allows hosts on the destination network to initiate traffic to a translated host (if an access list exists that allows it).
The main difference between dynamic NAT and a range of addresses for static NAT is that static NAT allows a remote host to initiate a connection to a translated host (if an access list exists that allows it), while dynamic NAT does not. You also need an equal number of mapped addresses as real addresses with static NAT.
──────BEST PRODUCT FOR CISCO TRAINING───────
───────────────RELATED VIDEOS───────────────
➊ How to Configure RIP Routing
➋ How to Configure Static Routing
➌ How to Connect Two Networks in Packet Tracer
➍ How to Configure RIP Version 2
➎ How to Configure EIGRP
───────────────FOLLOW US───────────────────
✔ Facebook
✔ Twitter
✔ Pinterest
✔ Instagram
✔ LinkedIn
███████████████████████████████████████████
To configure #Static #NAT:
Step 1: If you have not installed #PacketTracer before, please refer to the following videos to install Packet Tracer on Windows, Linux, and macOS.
Step 2: After installing it, add two Cisco Routers, one Cisco Switch, and two computers to the Packet Tracer workspace.
Step 3: Specify local and WAN IP addresses.
Step 4: Configure the 192.168.1.0/24 network for the local network and the 10.0.0.1/30 network for the WAN.
Step 5: Assign IP addresses to the computers on the local network.
Step 6: Assign IP addresses to the GigabitEthernet interfaces of Router0 and Router1 and turn the ports on.
Step 7: Test the connection by pinging Router1 over PC0 and PC1.
Step 8: Next, configure the interface as follows because the Gig0/1 interface of Router0 is in the IP NAT INSIDE field.
R1# conf t
R1(config)# interface gig0/1
R1(config-if)# ip nat inside
R1(config-if)# exit
R1(config)# interface gig0/0
R1(config-if)# ip nat outside
Step 9: After you have defined the Router's IP NAT regions, execute the following command to configure Static NAT in Router0 global configuration mode.
R1# conf t
R1(config)# ip nat inside source static 192.168.10.10 10.0.0.1
Step 10: If you ping Router1 over PC0, you can see that the network connection is established.
Step 11: Now, ping to Router1 from PC1 and check that PC1 cannot reach Router1.
Step 12: Since we have not configured Static NAT for PC1, PC1 will not be able to reach Router1.
Step 13: Execute the following commands in user mode to verify and control Static NAT.
➦ show ip nat translation
➦ show ip nat statistics
➦ clear ip nat statistics
➦ debug ip nat
Step 14: Don't forget to subscribe to our YouTube channel for more videos on Cisco Networking training with Packet Tracer!
What is Static NAT?
Static NAT creates a fixed translation of real address(es) to mapped address(es). With dynamic NAT and PAT, each host uses a different address or port for each subsequent translation. Because the mapped address is the same for each consecutive connection with static NAT, and a persistent translation rule exists, static NAT allows hosts on the destination network to initiate traffic to a translated host (if an access list exists that allows it).
The main difference between dynamic NAT and a range of addresses for static NAT is that static NAT allows a remote host to initiate a connection to a translated host (if an access list exists that allows it), while dynamic NAT does not. You also need an equal number of mapped addresses as real addresses with static NAT.
──────BEST PRODUCT FOR CISCO TRAINING───────
───────────────RELATED VIDEOS───────────────
➊ How to Configure RIP Routing
➋ How to Configure Static Routing
➌ How to Connect Two Networks in Packet Tracer
➍ How to Configure RIP Version 2
➎ How to Configure EIGRP
───────────────FOLLOW US───────────────────
███████████████████████████████████████████
Комментарии
 0:10:26
0:10:26
 0:11:17
0:11:17
 0:03:57
0:03:57
 0:12:21
0:12:21
 0:07:24
0:07:24
 0:15:48
0:15:48
 0:11:17
0:11:17
 0:13:52
0:13:52
 0:03:52
0:03:52
 0:08:04
0:08:04
 0:06:21
0:06:21
 0:07:50
0:07:50
 0:13:47
0:13:47
 0:06:40
0:06:40
 0:06:48
0:06:48
 0:10:36
0:10:36
 0:02:35
0:02:35
 0:03:39
0:03:39
 0:11:27
0:11:27
 0:10:49
0:10:49
 0:32:10
0:32:10
 0:17:04
0:17:04
 0:03:17
0:03:17
 0:11:12
0:11:12