filmov
tv
springboot log4j logging | log4j | log4j with springboot | springboot log4j demo | okay java

Показать описание
springboot log4j logging | log4j with springboot | springboot log4j demo | okay java
Special thanks to a super subscriber Sasi K :)
Download the source code
#Log4J configuration
# Log file path
Log4j
Log4j is a fast, reliable and flexible logging framework which is written in java. It is an open-source logging API for java.
Log4j Architecture
Log4j follows a layered architecture where each layer is used to provide different objects to perform different tasks.
Logger object
is used to enable the log4j in java class
also responsible for taking logging information
These methods are:
debug()
info()
warn()
error()
fatal()
Appender object(Interface)
The Appender object is responsible for publishing logging information to various preferred destinations such as a file, database, console, Unix Syslog, etc.
1. FileAppender –
A. RollingFileAppender
B. DailyRollingFileAppender
2. ConsoleAppender
3. JDBCAppender
4. SMTPAppender
5. SocketAppender
6. SyslogAppender
7. TelnetAppender
8. WriterAppender
Layout object
is used to format logging information in different styles (human-readable and reusable.).
SimpleLayout : level – logging info
PatternLayout : format the output based on conversion pattern specified
HTMLLayout : It formats the output as an HTML table.
XMLLayout : xml format
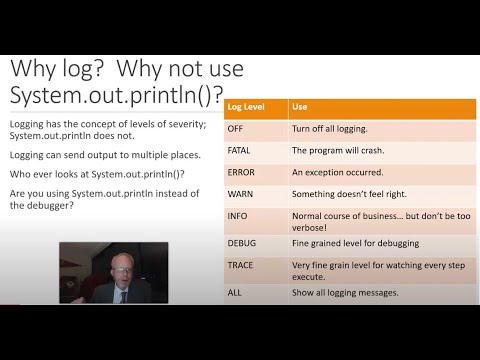
Log Level Description
ALL This level turns on all levels of logging. It includes the custom logging levels that you have defined. Once this one is configured and the levels are not considered at all, then all the appenders will start pouring the log events in log files.
DEBUG Debug is used a lot for debugging the application at development time. Every log message will appear to log files once this level is set. It basically belongs to developers.
INFO The INFO logging level is used to record messages about routine application operation. In real-time, system administrators watch the info logs to ensure what's happening on the system right now, and if there is any problem in normal flow.
WARN WARN log level is used to indicate that you might have a problem and that you've detected an unusual situation. Maybe you were demanding to invoke a service, and it failed a couple of times before connecting on an automatic retry. It is unexpected and unusual, but no real harm was done, and it's not known whether the issue will persist or recur. Someone should investigate warnings.
ERROR The ERROR log level is used to denote a serious problem that you must have to investigate immediately. Not as serious as FATAL, but still a problem. It simply means that your application has met really undesired state. For example, unexpected formatted input, database unavailability.
FATAL The FATAL log level, like ERROR, designates a problem. But unlike ERROR, it designates a very serious error event. You will not consider their presence very much on a normal day, but once they appear, it signals very bad news, even the application of death.
OFF This is the highest possible rank and is intended to turn off logging.
TRACE This has been recently introduced in version 1.2 and includes more information to debug level logs.
Special thanks to a super subscriber Sasi K :)
Download the source code
#Log4J configuration
# Log file path
Log4j
Log4j is a fast, reliable and flexible logging framework which is written in java. It is an open-source logging API for java.
Log4j Architecture
Log4j follows a layered architecture where each layer is used to provide different objects to perform different tasks.
Logger object
is used to enable the log4j in java class
also responsible for taking logging information
These methods are:
debug()
info()
warn()
error()
fatal()
Appender object(Interface)
The Appender object is responsible for publishing logging information to various preferred destinations such as a file, database, console, Unix Syslog, etc.
1. FileAppender –
A. RollingFileAppender
B. DailyRollingFileAppender
2. ConsoleAppender
3. JDBCAppender
4. SMTPAppender
5. SocketAppender
6. SyslogAppender
7. TelnetAppender
8. WriterAppender
Layout object
is used to format logging information in different styles (human-readable and reusable.).
SimpleLayout : level – logging info
PatternLayout : format the output based on conversion pattern specified
HTMLLayout : It formats the output as an HTML table.
XMLLayout : xml format
Log Level Description
ALL This level turns on all levels of logging. It includes the custom logging levels that you have defined. Once this one is configured and the levels are not considered at all, then all the appenders will start pouring the log events in log files.
DEBUG Debug is used a lot for debugging the application at development time. Every log message will appear to log files once this level is set. It basically belongs to developers.
INFO The INFO logging level is used to record messages about routine application operation. In real-time, system administrators watch the info logs to ensure what's happening on the system right now, and if there is any problem in normal flow.
WARN WARN log level is used to indicate that you might have a problem and that you've detected an unusual situation. Maybe you were demanding to invoke a service, and it failed a couple of times before connecting on an automatic retry. It is unexpected and unusual, but no real harm was done, and it's not known whether the issue will persist or recur. Someone should investigate warnings.
ERROR The ERROR log level is used to denote a serious problem that you must have to investigate immediately. Not as serious as FATAL, but still a problem. It simply means that your application has met really undesired state. For example, unexpected formatted input, database unavailability.
FATAL The FATAL log level, like ERROR, designates a problem. But unlike ERROR, it designates a very serious error event. You will not consider their presence very much on a normal day, but once they appear, it signals very bad news, even the application of death.
OFF This is the highest possible rank and is intended to turn off logging.
TRACE This has been recently introduced in version 1.2 and includes more information to debug level logs.
Комментарии
 0:13:41
0:13:41
 0:09:38
0:09:38
 0:15:21
0:15:21
 0:33:02
0:33:02
 0:04:01
0:04:01
 0:16:33
0:16:33
 0:13:46
0:13:46
 0:13:50
0:13:50
 0:04:08
0:04:08
 0:08:14
0:08:14
 1:04:11
1:04:11
 0:10:21
0:10:21
 0:06:26
0:06:26
 0:11:26
0:11:26
 0:14:41
0:14:41
 0:21:08
0:21:08
 0:01:30
0:01:30
 0:10:47
0:10:47
 0:41:20
0:41:20
 0:05:11
0:05:11
 0:36:44
0:36:44
 0:04:52
0:04:52
 0:08:52
0:08:52
 0:38:40
0:38:40