filmov
tv
BGP AS Override Lab - EVE-NG Lab for CCNP and CCIE

Показать описание
GET THIS LAB RIGHT NOW!
Welcome to Network Engineer Pro. I'm Rafael, CCIE 64356.
I'm working on ton of content (videos, labs and more) to help you learn networking. If you want to stay up to date on what I'm working on and be the first to know then head to my website where you can sign up and get notified:
You can also follow me on Facebook:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Loop prevention in BGP is done by verifying the AS number in the AS Path. If the receiving router sees its own AS number in the AS Path of the received BGP packet, the packet is dropped. The receiving Router assumes that the packet was originated from its own AS and has reached the same place from where it originated initially.
The feature could be a disaster if customers are using same AS number along the various sites and disallows customer sites having identical AS numbers to be linked by another AS number. In such a scenario, routing updates from one site will be dropped when the other site receives them.
To override this feature, AS-Override function causes to replace the AS number of originating router with the AS number of the sending BGP router. The command is neighbor ip-address as-override and can only be executed under the VPNv4 address-family.
BGP AS Override needs to be understood well in order to understand the BGP loop prevention behavior, But why BGP AS Override might create a dangerous situation, and what are the alternatives of BGP AS Override will be explained in this post.
What is BGP AS Override
BGP AS Override feature is used to change the AS number or numbers in the AS Path attribute. Without BGP AS-Override, let's see what would happen.
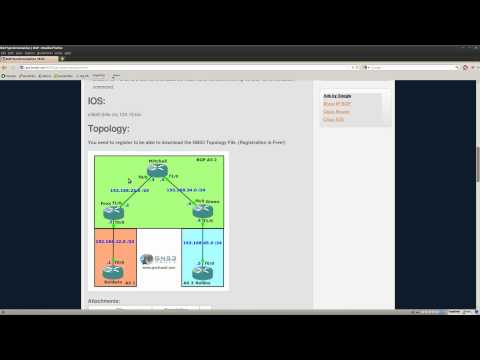
In this topology, Customer BGP AS is AS 100. The customer has two locations. Service Provider, in the middle, let's say providing MPLS VPN service for the customer. As you can understand from the topology, Service Provider is running EBGP with the Customer, because they have different BGP Autonomous Systems.
The service provider in the above topology has BGP AS 200. Left customer router, when it advertises BGP update message to the R2, R2 sends to R3 and when R3 sends to R4, R4 wouldn't accept the BGP update, When R4 receives that update, it will check the AS-Path attribute and would see its own BGP AS number in the AS Path. Thus is by default rejected, due to EBGP loop prevention. If the router sees its own BGP AS number, anywhere (Origin AS, any mid-AS, or last AS) in the AS Path, it doesn't accept the BGP update. But what if, like in the above picture, the customer wants to, or needs to use the same BGP AS number in every location that they have.
In this case, they need to accept the BGP update, otherwise, end-to-end reachability cannot be achieved. There are two solutions to the above requirement. By the way, not accepting prefixes/BGP updates is not a problem. It is just how BGP works. One of the solutions is, that R2 receives a BGP update from R1 with AS 100, then R3 receives from R2, and in the BGP AS Path, it is still AS 100 at R3. With BGP AS Override feature, R3 can change customers' BGP AS numbers with its own BGP AS number. So, R3 during advertisement to R4 replaces BGP AS 100 with BGP AS 200.
Change the AS number with its own AS number. And finally, when R4 receives it since it won't see its own AS number in the BGP update, R4 accepted the announcements, and end-to-end connectivity is achieved. In the next post, we will look at what can be the problem if the BGP AS Override feature is used.
BGP’s one of the key loop prevention mechanism is to match the AS number in the AS path of the received BGP update.
If the BGP AS-path attribute has the AS number of the receiving router in then that BGP route is not installed in the BGP routing table.
This BGP feature though useful for loop prevention can sometimes cause issues in the network (especially for a big enterprise spanning across multiple locations) where a customer has multiple sites spread geographically, connected by some ISP and using the same AS number.
AS Override :
Its feature allows a provider edge (PE) router to change private autonomous system used by customer edge (CE) device on an external BGP session running on a VPN routing and forwarding access link. The private AS number is changed to PEAS number.
Welcome to Network Engineer Pro. I'm Rafael, CCIE 64356.
I'm working on ton of content (videos, labs and more) to help you learn networking. If you want to stay up to date on what I'm working on and be the first to know then head to my website where you can sign up and get notified:
You can also follow me on Facebook:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Loop prevention in BGP is done by verifying the AS number in the AS Path. If the receiving router sees its own AS number in the AS Path of the received BGP packet, the packet is dropped. The receiving Router assumes that the packet was originated from its own AS and has reached the same place from where it originated initially.
The feature could be a disaster if customers are using same AS number along the various sites and disallows customer sites having identical AS numbers to be linked by another AS number. In such a scenario, routing updates from one site will be dropped when the other site receives them.
To override this feature, AS-Override function causes to replace the AS number of originating router with the AS number of the sending BGP router. The command is neighbor ip-address as-override and can only be executed under the VPNv4 address-family.
BGP AS Override needs to be understood well in order to understand the BGP loop prevention behavior, But why BGP AS Override might create a dangerous situation, and what are the alternatives of BGP AS Override will be explained in this post.
What is BGP AS Override
BGP AS Override feature is used to change the AS number or numbers in the AS Path attribute. Without BGP AS-Override, let's see what would happen.
In this topology, Customer BGP AS is AS 100. The customer has two locations. Service Provider, in the middle, let's say providing MPLS VPN service for the customer. As you can understand from the topology, Service Provider is running EBGP with the Customer, because they have different BGP Autonomous Systems.
The service provider in the above topology has BGP AS 200. Left customer router, when it advertises BGP update message to the R2, R2 sends to R3 and when R3 sends to R4, R4 wouldn't accept the BGP update, When R4 receives that update, it will check the AS-Path attribute and would see its own BGP AS number in the AS Path. Thus is by default rejected, due to EBGP loop prevention. If the router sees its own BGP AS number, anywhere (Origin AS, any mid-AS, or last AS) in the AS Path, it doesn't accept the BGP update. But what if, like in the above picture, the customer wants to, or needs to use the same BGP AS number in every location that they have.
In this case, they need to accept the BGP update, otherwise, end-to-end reachability cannot be achieved. There are two solutions to the above requirement. By the way, not accepting prefixes/BGP updates is not a problem. It is just how BGP works. One of the solutions is, that R2 receives a BGP update from R1 with AS 100, then R3 receives from R2, and in the BGP AS Path, it is still AS 100 at R3. With BGP AS Override feature, R3 can change customers' BGP AS numbers with its own BGP AS number. So, R3 during advertisement to R4 replaces BGP AS 100 with BGP AS 200.
Change the AS number with its own AS number. And finally, when R4 receives it since it won't see its own AS number in the BGP update, R4 accepted the announcements, and end-to-end connectivity is achieved. In the next post, we will look at what can be the problem if the BGP AS Override feature is used.
BGP’s one of the key loop prevention mechanism is to match the AS number in the AS path of the received BGP update.
If the BGP AS-path attribute has the AS number of the receiving router in then that BGP route is not installed in the BGP routing table.
This BGP feature though useful for loop prevention can sometimes cause issues in the network (especially for a big enterprise spanning across multiple locations) where a customer has multiple sites spread geographically, connected by some ISP and using the same AS number.
AS Override :
Its feature allows a provider edge (PE) router to change private autonomous system used by customer edge (CE) device on an external BGP session running on a VPN routing and forwarding access link. The private AS number is changed to PEAS number.
 0:10:40
0:10:40
 0:03:39
0:03:39
 0:17:07
0:17:07
 0:03:31
0:03:31
 0:04:09
0:04:09
 0:03:15
0:03:15
 0:28:47
0:28:47
 0:14:39
0:14:39
 0:05:45
0:05:45
 0:07:12
0:07:12
 0:12:15
0:12:15
 0:12:15
0:12:15
 0:11:20
0:11:20
 0:05:53
0:05:53
 0:10:53
0:10:53
 0:15:06
0:15:06
 0:15:22
0:15:22
 0:13:12
0:13:12
 0:04:45
0:04:45
 0:05:37
0:05:37
 0:25:57
0:25:57
 0:14:42
0:14:42
 0:19:45
0:19:45
 0:21:11
0:21:11