filmov
tv
Bivariate normal Distribution #Statistics #overview #Multivariate Distribution Explained 9836793076
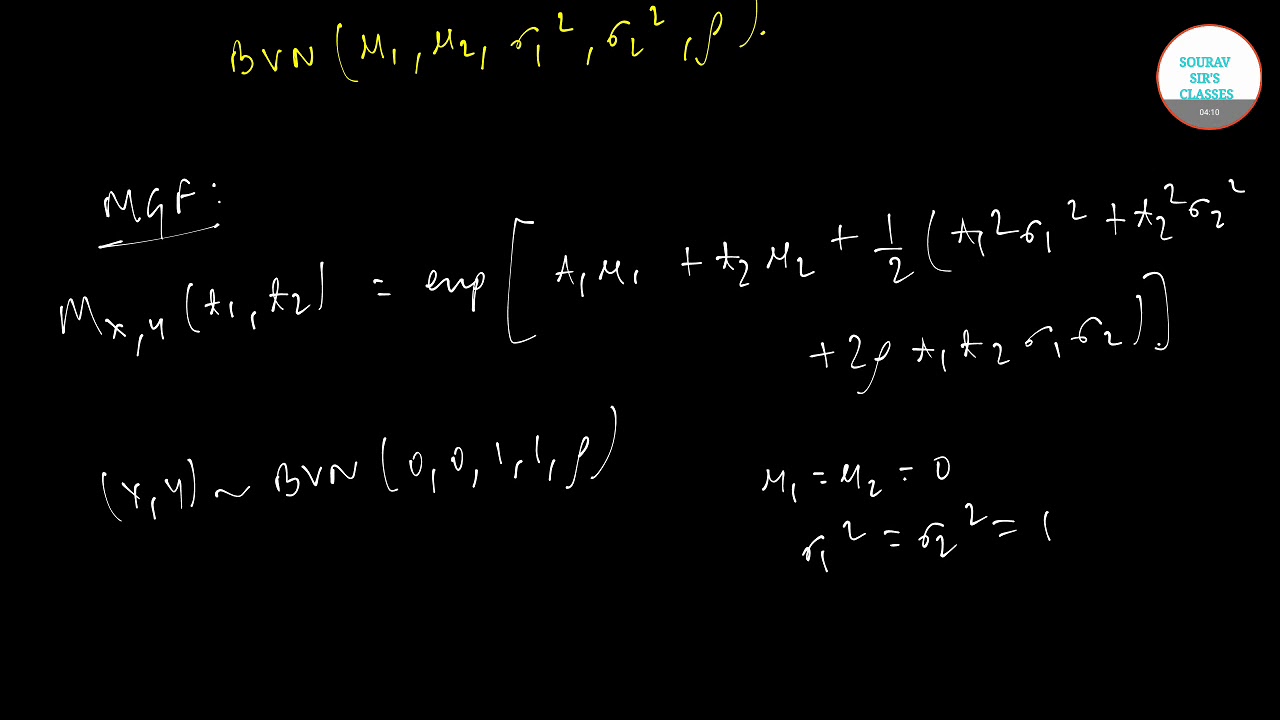
Показать описание
Bivariate normal Distribution #Statistics #overview #Multivariate Distribution Explained 9836793076
GIVE US A CALL / WHATSAPP AT +919836793076
FOR COMPLETE LECTURES / STUDY MATERIALS /NOTES /GUIDENCE / PAST YEAR SOLVED +SAMPLE PAPAERS /TRICKS /MCQ / SHORT CUT/ VIDEO LECTURES /LIVE + ONLINE CLASSES
Also find us at….
The “regular” normal distribution has one random variable; A bivariate normal distribution is made up of two independent random variables. The two variables in a bivariate normal are both are normally distributed, and they have a normal distribution when both are added together. Visually, the bivariate normal distribution is a three-dimensional bell curve.
Francis Galton (1822-1911) was one of the first mathematicians to study the bivariate normal distribution in depth, during his study on the heights of parents and their adult children. Bravais, Gauss, Laplace, Plana also studied the distribution in the early nineteenth century (Balakrishnan & Lai, 2009).
The bivariare distribution can be described in many different ways and as such, there isn’t a unified agreement for a succinct definition. Some of the more common ways to characterize it include:
Random variables X & Y are bivariate normal if aX + bY has a normal distribution for all a,b∈R.
X and Y are jointly normal if they can be expressed as X = aU + bV, and Y = cU + dV (Bertsekas & Tsitsiklis, 2002)
If a and b are non-zero constants, aX + bY has a normal distribution (Johnson & Kotz, 1972).
If X – aY and Y are independent and if Y – bx and X are independent for all a,b (such that ab ≠ 0 or 1), then (X,Y) has a normal distribution (Rao, 1975).
bivariate normal distribution in r
bivariate normal distribution matlab
bivariate normal distribution ellipse
bivariate normal distribution cdf
bivariate normal distribution excel
derivation of mgf of bivariate normal distribution
bivariate distribution pdf
construct bivariate normal distribution
Page navigation
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Next
Complementary results
Knowledge result
Image result for bivariate normal distribution
Image result for bivariate normal distribution
Image result for bivariate normal distribution
Image result for bivariate normal distribution
Image result for bivariate normal distribution
Image result for bivariate normal distribution
Image result for bivariate normal distribution
More images
Multivariate normal distribution
DescriptionIn probability theory and statistics, the multivariate normal distribution, multivariate Gaussian distribution, or joint normal distribution is a generalization of the one-dimensional normal distribution to higher dimensions. Wikipedia
GIVE US A CALL / WHATSAPP AT +919836793076
FOR COMPLETE LECTURES / STUDY MATERIALS /NOTES /GUIDENCE / PAST YEAR SOLVED +SAMPLE PAPAERS /TRICKS /MCQ / SHORT CUT/ VIDEO LECTURES /LIVE + ONLINE CLASSES
Also find us at….
The “regular” normal distribution has one random variable; A bivariate normal distribution is made up of two independent random variables. The two variables in a bivariate normal are both are normally distributed, and they have a normal distribution when both are added together. Visually, the bivariate normal distribution is a three-dimensional bell curve.
Francis Galton (1822-1911) was one of the first mathematicians to study the bivariate normal distribution in depth, during his study on the heights of parents and their adult children. Bravais, Gauss, Laplace, Plana also studied the distribution in the early nineteenth century (Balakrishnan & Lai, 2009).
The bivariare distribution can be described in many different ways and as such, there isn’t a unified agreement for a succinct definition. Some of the more common ways to characterize it include:
Random variables X & Y are bivariate normal if aX + bY has a normal distribution for all a,b∈R.
X and Y are jointly normal if they can be expressed as X = aU + bV, and Y = cU + dV (Bertsekas & Tsitsiklis, 2002)
If a and b are non-zero constants, aX + bY has a normal distribution (Johnson & Kotz, 1972).
If X – aY and Y are independent and if Y – bx and X are independent for all a,b (such that ab ≠ 0 or 1), then (X,Y) has a normal distribution (Rao, 1975).
bivariate normal distribution in r
bivariate normal distribution matlab
bivariate normal distribution ellipse
bivariate normal distribution cdf
bivariate normal distribution excel
derivation of mgf of bivariate normal distribution
bivariate distribution pdf
construct bivariate normal distribution
Page navigation
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Next
Complementary results
Knowledge result
Image result for bivariate normal distribution
Image result for bivariate normal distribution
Image result for bivariate normal distribution
Image result for bivariate normal distribution
Image result for bivariate normal distribution
Image result for bivariate normal distribution
Image result for bivariate normal distribution
More images
Multivariate normal distribution
DescriptionIn probability theory and statistics, the multivariate normal distribution, multivariate Gaussian distribution, or joint normal distribution is a generalization of the one-dimensional normal distribution to higher dimensions. Wikipedia
 0:03:59
0:03:59
 0:07:55
0:07:55
 0:05:13
0:05:13
 0:08:49
0:08:49
 0:22:56
0:22:56
 0:01:24
0:01:24
 0:24:18
0:24:18
 0:07:08
0:07:08
 1:14:06
1:14:06
 0:08:51
0:08:51
 0:26:23
0:26:23
 0:08:20
0:08:20
 0:19:49
0:19:49
 0:14:50
0:14:50
 0:08:42
0:08:42
 0:09:00
0:09:00
 0:05:30
0:05:30
 0:03:19
0:03:19
 0:05:27
0:05:27
 0:29:16
0:29:16
 0:17:34
0:17:34
 0:03:37
0:03:37
 0:30:11
0:30:11
 0:22:40
0:22:40